Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: EQUATOR (NCT03101670) was a randomized, 16-week, Phase 2, multicenter, double-blind, placebo (PBO)‑controlled trial of filgotinib (FIL) in patients with active PsA ( Mease P, et al. Lancet 2018;392:2367–77) . In EQUATOR, FIL was well tolerated and was efficacious vs PBO for the primary endpoint of Week 16 ACR20 response. Patients completing EQUATOR could join an ongoing 304‑week OLE (EQUATOR2; NCT03320876). We report the findings of an interim analysis of EQUATOR2 at Week 100. Primary and secondary objectives were to assess safety/tolerability and efficacy, respectively.
Methods: In EQUATOR, patients with active moderate-to-severe PsA (≥5 swollen joints and ≥5 tender joints, fulfilling Classification for PsA [CASPAR] criteria) were randomized 1:1 to receive oral FIL 200 mg or PBO once daily (QD) for 16 weeks. At Week 16, patients could continue into the OLE, receiving FIL 200 mg QD. For this interim analysis, patients were followed for efficacy until the last patient completed their Week 100 visit; safety data were collected up to April 8, 2020. Efficacy measures included minimal disease activity (MDA; meeting 5/7 MDA criteria), MDA/very low disease activity (VLDA; meeting 7/7 MDA criteria), Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score (PASDAS) low disease activity (score ≤3.2) and VLDA (score ≤1.9), ACR20/50/70, and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75/90/100. The number and proportion of patients achieving each endpoint were calculated using observed case (OC) and non-responder imputation (NRI) approaches. Adverse events (AEs) per 100 patient-years of exposure (from first exposure to FIL) are summarized.
Results: Of 131 randomized patients, 124 (95%) completed EQUATOR and 122 (93%) were enrolled in the OLE, of whom 104 patients (85%) remained in the study at Week 100. Safety and tolerability were similar at Week 100 to a previous analysis conducted at Week 52 (Table 1). No unexpected safety issues were identified. By Week 100, 1 death (bilateral pneumonia, leading to toxic shock with multi-organ failure ) and 1 adjudicated major adverse cardiac event had occurred (both prior to Week 52). Five additional serious treatment-emergent AEs occurred from Week 52 to 100, including 1 serious infection (COVID-19). No deep vein thromboses or pulmonary embolisms occurred up to Week 100. Efficacy was sustained at Week 100 (Table 2). The response rate at Week 100 for all patients (regardless of original randomization to PBO or FIL) was 31.3% for MDA (NRI; 42.3% for OC; Figure), and 60.3%/43.5%/29.0% for ACR20/50/70 (NRI; 81.4%/58.8%/39.2% for OC). Of 15 patients originally randomized to FIL who were MDA responders at Week 16, 73.3% also had an MDA response at Week 100 (NRI). Sustained responses were observed at ≥3 consecutive visits (each of which was 12 weeks apart) for MDA in 34.4% of patients (NRI).
Conclusion: This interim analysis of long-term extension data from the PsA EQUATOR2 study found FIL 200 mg QD to be generally well tolerated up to Week 100 with a safety profile comparable to that seen up to Week 52. Response rates at Week 100 to FIL 200 mg QD were stable and comparable to those reported at Week 52. In most patients who were MDA responders at Week 16, responses were also seen at Week 100.
 Table 1. Overview of safety with FIL 200 mg QD at Week 52 and Week 100 of the EQUATOR2 OLE. *Defined as Grade ≥3. †Excludes deaths. AE, adverse event; FIL, filgotinib; OLE, open-label extension; PYE, patient-years of exposure; QD, once daily; RTI, respiratory tract infection; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event
Table 1. Overview of safety with FIL 200 mg QD at Week 52 and Week 100 of the EQUATOR2 OLE. *Defined as Grade ≥3. †Excludes deaths. AE, adverse event; FIL, filgotinib; OLE, open-label extension; PYE, patient-years of exposure; QD, once daily; RTI, respiratory tract infection; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event
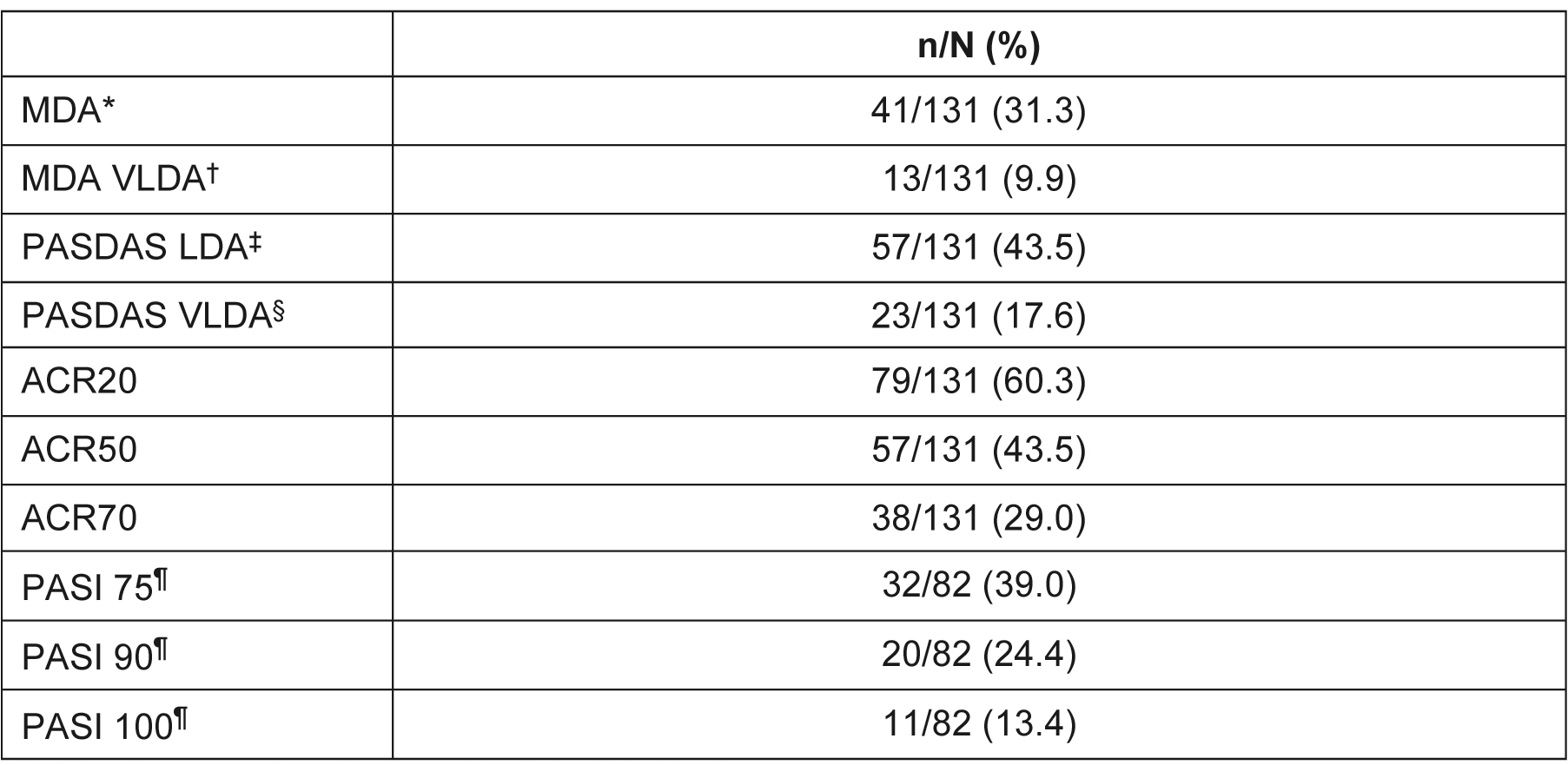 Table 2. Responders at Week 100 of the OLE (NRI). *Defined as meeting 5 out of 7 of the MDA criteria. †Defined as meeting 7 out of 7 of the MDA criteria. ‡Defined as a PASDAS score of ≤3.2. §Defined as a PASDAS score of ≤1.9. ¶PASI was only measured in patients with ≥3% of their body surface area affected by psoriasis. ACR, American College Rheumatology; LDA, low disease activity; MDA, minimal disease activity; NRI, non-responder imputation; OLE, open-label extension; PASDAS, Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score; PASI, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; VLDA, very low disease activity
Table 2. Responders at Week 100 of the OLE (NRI). *Defined as meeting 5 out of 7 of the MDA criteria. †Defined as meeting 7 out of 7 of the MDA criteria. ‡Defined as a PASDAS score of ≤3.2. §Defined as a PASDAS score of ≤1.9. ¶PASI was only measured in patients with ≥3% of their body surface area affected by psoriasis. ACR, American College Rheumatology; LDA, low disease activity; MDA, minimal disease activity; NRI, non-responder imputation; OLE, open-label extension; PASDAS, Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score; PASI, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; VLDA, very low disease activity
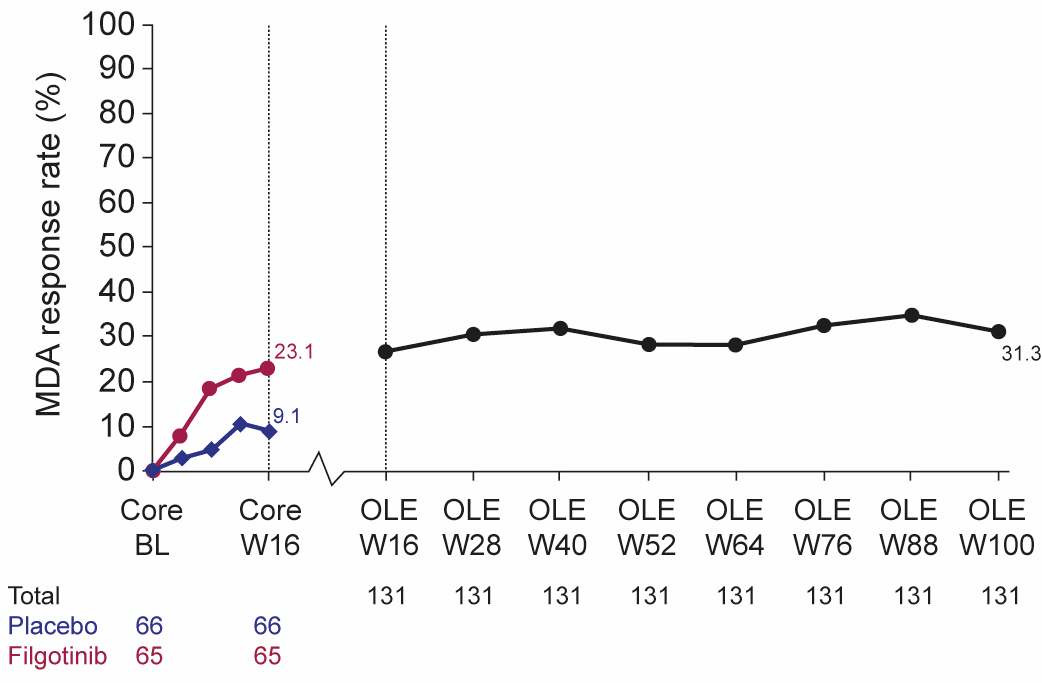 Figure 1. MDA response rate over time (NRI). BL, baseline; MDA, minimal disease activity; NRI, non-responder imputation; OLE, open-label extension; W, Week
Figure 1. MDA response rate over time (NRI). BL, baseline; MDA, minimal disease activity; NRI, non-responder imputation; OLE, open-label extension; W, Week
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates L, Gladman D, Van den Bosch F, Helliwell P, Rychlewska-Hańczewska A, Stanislavchuk M, Gilles L, Gheyle L, Liu K, Trivedi M, Alani M, Besuyen R, Mease P. Long-term Outcomes with Filgotinib, an Oral Selective Janus Kinase 1 Inhibitor: 100-week Data from an Open-label Extension (OLE) Study in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-outcomes-with-filgotinib-an-oral-selective-janus-kinase-1-inhibitor-100-week-data-from-an-open-label-extension-ole-study-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-psa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-outcomes-with-filgotinib-an-oral-selective-janus-kinase-1-inhibitor-100-week-data-from-an-open-label-extension-ole-study-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-psa/
