Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Ocular involvement in Behçet’s disease (BD) is a potential severe and disabling complication. Anti-TNF-α agents have shown an improvement of visual outcome in BD-related uveitis refractory to conventional immunosuppressive (IS) drugs. However, these drugs do not achieve control of intraocular inflammation in all patients or are not well tolerated. Tocilizumab (TCZ) has shown efficacy in different refractory ocular inflammatory diseases. To assess the efficacy of long-term therapy with TCZ in refractory uveitis associated to extraocular manifestations due to BD.
Methods:
Multicenter study of patients with BD refractory to standard systemic treatment.
Results: We followed up 14 patients (9 men/5 women) (26 affected eyes); mean age 40.8±19.5 years. Pattern of ocular involvement: panuveitis (10; 4 with retinal vasculitis), anterior (3) and posterior (1) uveitis; 8 recurrent and 6 chronic; 9 with cystoid macular edema. At TCZ onset the following extraocular manifestations were present: oral and/or genital ulcers (10), arthritis (6), folliculitis/pseudofolliculitis (6), erythema nodosum (3), livedo reticularis (1), intestinal affection (1) and neurological involvement (3).
Before TCZ, they had received corticosteroids (13 intraocular, 12 oral and 12 iv), conventional IS drugs and biologic agents: methotrexate (11), cyclosporine (8), azathioprine (10), colchicine (1), cyclophosphamide (2), mycophenolate mofetil (1), adalimumab (10), infliximab (6), golimumab (3), canakinumab (1), or etanercept (1). TCZ was used in monotherapy (7) or combined with conventional IS drugs (7) at 8 mg/kg/iv/4 w (11) or 162 mg/sc/w (3).
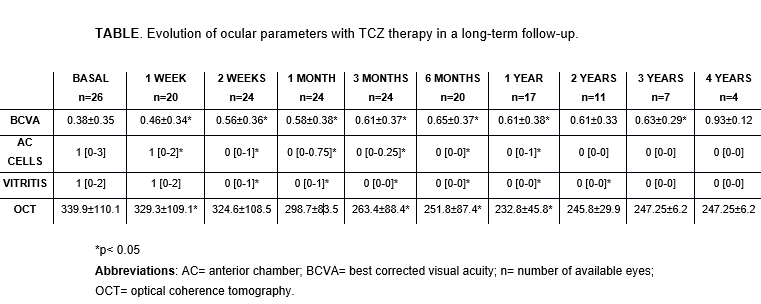
After a mean follow-up of 21.7±14.5 months using TCZ, all patients experienced ocular improvement, with complete remission in 10. However, TCZ was only effective in 5 of the patients with extraocular manifestations. TABLE shows the evolution of ocular parameters.
TCZ had to be withdrawn temporally in 1 case, due to an episode of cellulitis with sepsis, and definitely in 4 cases, due to a severe infusion reaction, arthritis impairment, persistence of oral ulcers or a new episode of uveitis (1 each). Prednisone dose was significantly reduced until suspension in all patients.
Conclusion:
TCZ seams a useful and secure therapy in highly refractory BD-related uveitis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gonzalez-Mazon I, Sanchez-Bilbao L, Atienza-Mateo B, Martín-Varillas J, PRIETO- PENA D, Calvo-Río V, Demetrio R, Palmou-Fontana N, Loricera J, Beltrán Catalán E, Hernández Garfella M, Valls-Pascual E, Atanés A, Cordero Coma M, Nolla J, carrasco-Cubero C, Sánchez J, Gonzalez-Gay M, Blanco R. Long-Term Follow-Up of Anti-IL6-Receptor Tocilizumab in Refractory Uveitis in Patients with Behçet Disease: Multicenter Study of 14 Patients in Clinical Practice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-follow-up-of-anti-il6-receptor-tocilizumab-in-refractory-uveitis-in-patients-with-behcet-disease-multicenter-study-of-14-patients-in-clinical-practice/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-follow-up-of-anti-il6-receptor-tocilizumab-in-refractory-uveitis-in-patients-with-behcet-disease-multicenter-study-of-14-patients-in-clinical-practice/