Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The IL-23p19-subunit inhibitor guselkumab (GUS) demonstrated clinically meaningful improvements in fatigue through one year of treatment1 independent of its effects on ACR20 and MDA achievement2. In this post hoc analysis, the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy – Fatigue (FACIT-F) scale was used to: (a) evaluate the long-term effect of GUS in maintaining improvements in or further improving fatigue between week (W) 52 and W100, and to; (b) identify potential early (W8) predictors, in terms of fatigue, for improved long-term fatigue outcomes.
Methods: DISCOVER-2 enrolled adult patients (pts) with active PsA (≥5 swollen and ≥5 tender joints and CRP ≥0.6 mg/dl) who were naïve to biologics/JAK inhibitors. Pts were randomized (1:1:1) and treated with GUS 100 mg every 4W (Q4W); GUS 100mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo (PBO→GUS Q4W; crossing over to GUS Q4W at W24). Pts with baseline (BL) fatigue levels lower than the normative value (FACIT-F score ≤43)3 were included in these post hoc analyses (N=681). The proportions of pts with clinically meaningful improvement (≥4 points) from BL in FACIT-F and with normative FACIT-F levels between W52 and W100 were calculated using non-responder imputation (NRI) for missing data and compared over time within each treatment group with the McNemar test. Changes in FACIT-F over time were assessed with mixed models adjusting for time, treatment group, their interaction, and BL FACIT-F score. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analyses were conducted using Youden’s index to determine optimal cutoffs at W8 for predicting achievement of normative scores and clinically meaningful FACIT-F responses at W100.
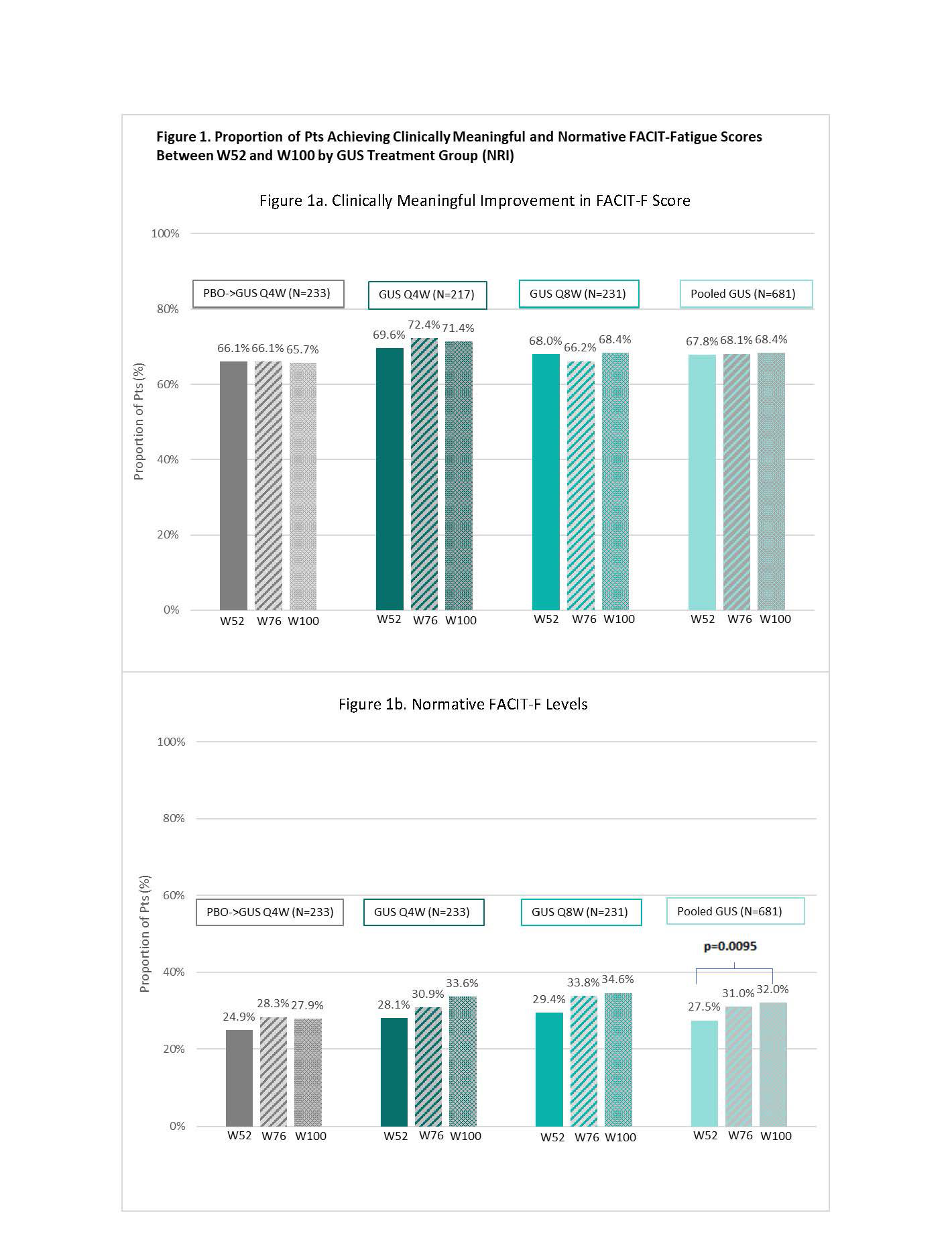
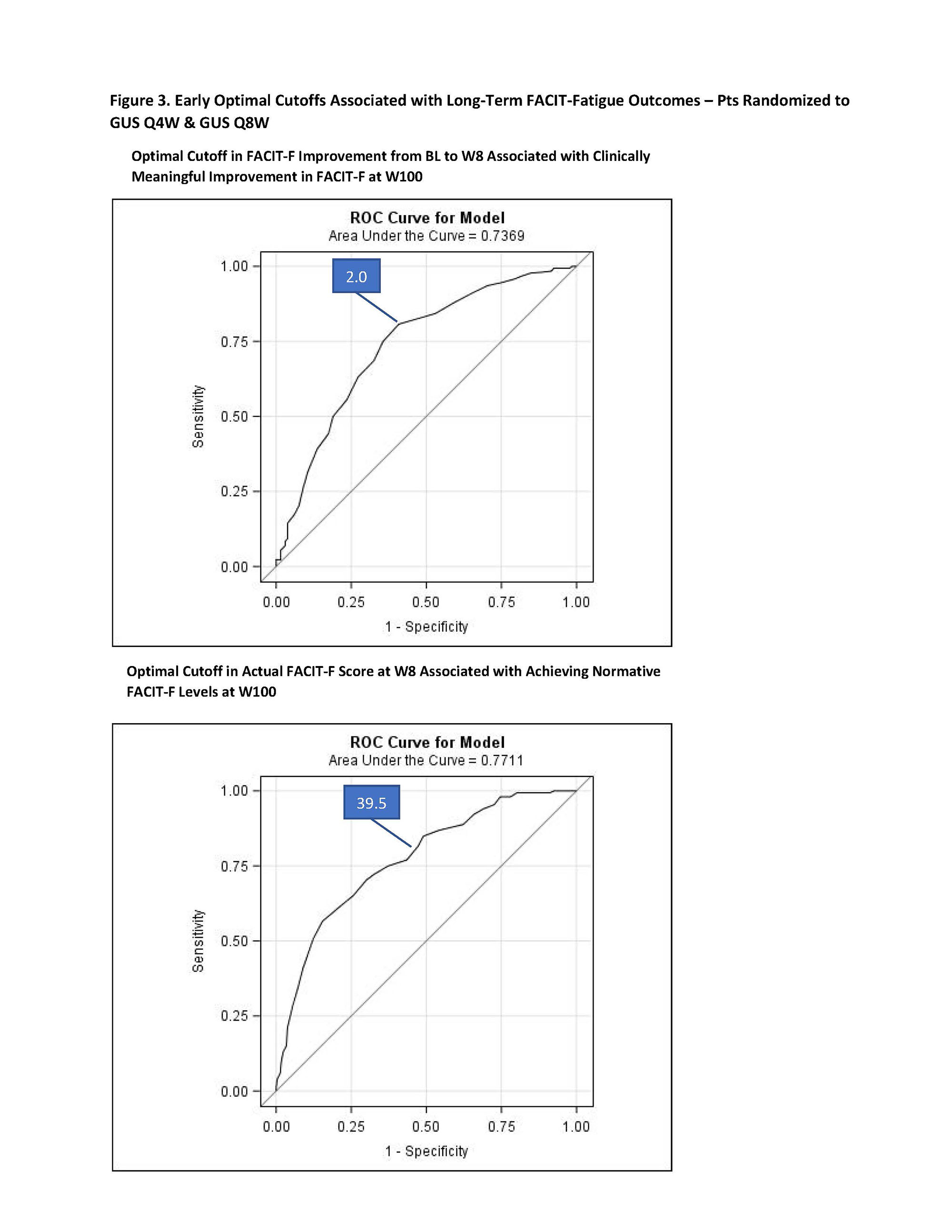
Results: At BL, the mean (SD) FACIT-F score was 28.3 (8.7) with similar levels across treatment groups. At W52, 66.1%, 69.6%, 68.0%, and 67.8% of pts in the PBO→GUS Q4W, GUS Q4W, GUS Q8W, and pooled GUS groups, respectively, achieved clinically meaningful improvements from BL in FACIT-F score; response rates were maintained through W100 (Figure 1a). Normative FACIT-F levels were achieved by 24.9%, 28.1% 29.4% and 27.5% of pts in each treatment group, respectively, at W52, and by increasingly greater proportions of pts through W100 (Figure 2b). Significant improvements from BL in FACIT-F scores were observed at W52 (all nominal p< 0.05), with further improvements seen from W52 to W100 across all GUS groups (Figure 2). ROC optimal cutoff in FACIT-F improvement from BL to W8 associated with a clinically meaningful improvement in FACIT-F at W100 was ≥2.0 (nominal p< 0.0001); while for achieving normative FACIT-F levels at W100, the optimal cutoff in actual FACIT-F score at W8 was ≥39.5 (nominal p< 0.0001) (Figure 3).
Conclusion: The clinically meaningful improvements in fatigue seen after 1 year of GUS treatment were further enhanced through 2 years, at which time nearly a third of GUS-treated pts reported normative FACIT-F levels. Early targets in FACIT-F levels achieved with GUS were identified to aid in guiding treatment decisions in routine clinical practice.
References:
1. Ritchlin CT et al. RMD Open. 2022 Mar;8(1);e002195.
2. Rahman P et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Jul 14;23(1):190.
3. Montan I et al. Value Health. 2018 Nov;21(11):1313-1321.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gladman D, Starr M, Ranza R, Bravo Perdomo A, Strauss M, Shawi M, Han C, Rampakakis E, Ostor A, Mease P. Long-term Efficacy of Guselkumab in Fatigue and Identification of Early Treatment Targets: Post Hoc Analysis Through 2 Years of a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study Conducted in Biologic-naïve Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-of-guselkumab-in-fatigue-and-identification-of-early-treatment-targets-post-hoc-analysis-through-2-years-of-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-conducted/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-of-guselkumab-in-fatigue-and-identification-of-early-treatment-targets-post-hoc-analysis-through-2-years-of-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-conducted/