Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy II: Trials Therapy
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: In patients (pts) with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) despite DMARD treatment, sirukumab, a human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the IL-6 cytokine with high affinity, significantly reduced signs and symptoms and inhibited radiographic progression vs placebo at 52 wks in SIRROUND-D. Long-term efficacy (Wk 104) and safety (Wk 120) results are presented.
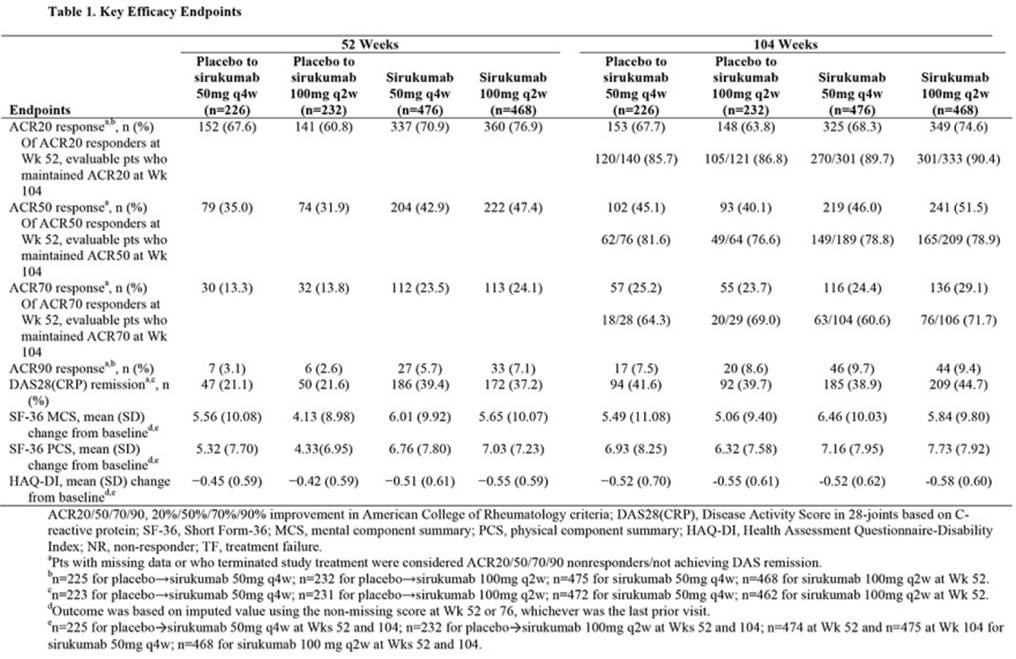
Methods: In this Phase 3 study, 1670 pts with moderate to severe active RA refractory to DMARDs (≥6/66 swollen and ≥6/68 tender joints and minimum CRP ≥8.0 mg/L) were randomized (1:1:1) to SC sirukumab 50mg q4w, sirukumab 100mg q2w, or placebo q2w. Pts in the placebo group with <20% improvement in swollen/tender joints at Wks 18 or 40 or still taking placebo at Wk 52 were re-randomized to sirukumab. Pts received blinded sirukumab in an active-controlled period from Wk 52 to 104, followed by a 16-wk safety phase to Wk 120. Efficacy endpoints, ACR20/50/70/90 responses, DAS28(CRP) remission, Short Form-36 (SF-36) Health Survey mental and physical component summary (MCS, PCS) scores, and HAQ-DI, were analyzed for pts on study treatment at Wk 52. Pts with data missing or who terminated study treatment were considered ACR20/50/70/90 non-responders and not achieving DAS28(CRP) remission. Missing MCS, PCS, and HAQ-DI scores were imputed using the non-missing score at Wk 52 or 76, whichever was the last prior visit. Treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs were assessed for all pts who received ≥1 dose of study drug.
Results: Of 1114 pts originally randomized to sirukumab and 556 to placebo, 944 and 458 were receiving sirukumab at Wk 52 for a total of 1402 pts in efficacy analyses from Wk 52 to 104. Of pts originally randomized to sirukumab, the proportions of pts achieving ACR20/50/70/90 responses and DAS28(CRP) remission were consistent at Wks 52 and 104 (Table); among those who achieved ACR20 and ACR50 responses at Wk 52, 90% and 79%, respectively, in each sirukumab dose group maintained them at Wk 104. Improvements from baseline in MCS and PCS scores and HAQ-DI were comparable for each outcome at Wks 52 and 104. Among pts originally randomized to placebo who crossed over to sirukumab, Wk 104 responses were similar to those for pts originally randomized to sirukumab. Through Wk 120 for all pts in the study, incidences of AEs and serious AEs, respectively, were similar with sirukumab 50mg q4w (84.0% and 17.7%) and 100mg q2w (86.7% and 16.5%). The most common AEs with sirukumab (≥10% in either group) were elevated liver enzymes, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, and injection site erythema. Serious AEs with the highest incidence were infections and infestations.
Conclusion: In this 2-year Phase 3 study of sirukumab in pts with active RA despite DMARDs, improvements in signs and symptoms of RA and health-related physical and emotional well-being were maintained. No new safety signals were reported through Wk 120.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Thorne C, Takeuchi T, Karpouzas G, Sheng S, Kurrasch R, Fei K, Hsu B. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety Results of a Global Phase 3 Trial of Sirukumab, an Anti–IL-6 Cytokine Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-and-safety-results-of-a-global-phase-3-trial-of-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-despite-disease-modifying/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-and-safety-results-of-a-global-phase-3-trial-of-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-despite-disease-modifying/