Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of adalimumab in patients with non-infectious intermediate, posterior, or panuveitis, by immunosuppressant (IMM) use.
Methods: Adult patients who completed or had a treatment failure in the VISUAL I/II trials were eligible to enter the Phase III open-label extension study, VISUAL III. Patients received adalimumab 40 mg every other week in VISUAL III, and interim follow-up data were collected through Weeks 0 to 78. Efficacy measures assessed included proportion of patients with: no active inflammatory lesions in both eyes; anterior chamber (AC) cell grade ≤0.5+ in both eyes; vitreous haze (VH) grade ≤0.5+ in both eyes; quiescence (defined as no active inflammatory lesions AND AC cell grade ≤0.5+ AND VH grade ≤0.5+); and steroid-free quiescence. Mean steroid dose and mean best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) were also assessed. Missing data were imputed using non-responder imputation for categorical endpoints, last observation carried forward for continuous variables, and as-observed for steroid dose. Efficacy was analyzed by IMM (methotrexate, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, or azathioprine) use. Adverse events (AEs) were reported from first adalimumab dose in VISUAL III through interim cut-off date of Oct 31, 2016, with analysis by IMM use.
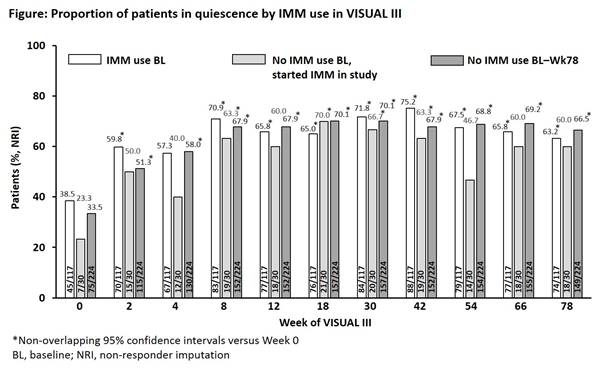
Results: Of 371 patients included in the intent-to-treat analysis, 117 (31.5%) were using IMM at VISUAL III baseline (BL) and 30 (8.1%) started IMM during VISUAL III. The proportion of patients with quiescence improved over time irrespective of IMM use; compared with Week 0, 95% confidence intervals were non-overlapping at most time points (Figure). Numeric improvements were achieved in steroid-free quiescence, steroid dose reduction, and BCVA, with no difference by IMM use. No new safety signals were detected through 130 weeks of treatment and AE rates were generally consistent with previous VISUAL trials; some AEs, notably serious infections and malignancies, were slightly higher with concomitant IMM use.
Conclusion: Exploratory analyses from the VISUAL III trial demonstrated that efficacy in adalimumab-treated patients was sustained or improved through 78 weeks of treatment, irrespective of IMM use. AE rates were consistent with previous VISUAL trials, although numerically higher rates for a subset of AEs were observed in patients taking IMM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guex-Crosier Y, Foster CS, Nakai K, Goto H, Douglas K, Pathai S, Kron M, Song AP, Van Calster J, Adan A. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Adalimumab By Immunosuppressant Use in Patients with Non-Infectious Uveitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-and-safety-of-adalimumab-by-immunosuppressant-use-in-patients-with-non-infectious-uveitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-efficacy-and-safety-of-adalimumab-by-immunosuppressant-use-in-patients-with-non-infectious-uveitis/