Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:50AM
Background/Purpose: In the treatment of monogenic autoinflammatory diseases (AID), a heterogeneous group of diseases with excessive interleukin (IL)-1β release and severe systemic and organ inflammation, the anti-IL-1 inhibitor canakinumab (CAN) has been associated with rapid remission of symptoms in clinical trials as well as in real-life.1,2
The aim of the RELIANCE registry is to explore long-term effectiveness and safety of CAN under routine clinical practice conditions in patients with CAPS (cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes, including Muckle-Wells syndrome [MWS], familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome [FCAS], neonatal onset multisystem inflammatory disease [NOMID]/chronic infantile neurological cutaneous and articular syndrome [CINCA]), FMF (familial Mediterranean fever), TRAPS (tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome) and HIDS/MKD (hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome/mevalonate kinase deficiency).
1Kuemmerle-Deschner et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55(4):689-96
2De Benedetti et al. N Engl. J Med. 2018;378(20):1908-1919
Methods: This prospective, non-interventional, observational study based in Germany has a 3-year follow-up and enrolls pediatric ≥2 years and adult patients with clinically confirmed diagnoses of CAPS, FMF, TRAPS and HIDS/MKD routinely receiving CAN. In 6-monthly visits, clinical data and patient-reported outcomes are assessed. Study endpoints are long-term effectiveness and safety of CAN. Here, the CAPS cohort was analyzed.
Results: This 18-month interim-analysis includes 78 CAPS patients (49% females) enrolled by September 2019. Mean age at baseline was 25 years and mean duration of prior CAN treatment was 5.7 years. 64 patients (82%) had MWS, 2 FCAS, 7 NOMID/CINCA, 3 atypical CAPS and 2 lacked subtype diagnosis. Preferred CAN doses and intervals (% of all injections) were 300 mg q4w (every 4 weeks; 10.4), 150 mg q4w (16.9), 150 mg q8w (13.7) and 150 mg more than q9w (9). Disease activity, fatigue and social impairment by patients’ assessment, days absent from school/work, inflammatory markers, and remission by physician assessment were evaluated at 6-monthly intervals starting at baseline with last update at 18 months of follow-up (Table 1). The patient–reported AIDAI score of disease activity revealed inactive disease in 9 out of 12 months (Table 2). The results demonstrate sustained remission and disease control to remain stable over time. The incidence rate per 100 patient years was 25.67 for any serious adverse event (SAE) including 15.21 for serious drug-related adverse events (drSAE; Table 3). DrSAE were reported for 10/78 patients including cardiovascular disorder, pyrexia (3), chest pain, appendicitis, tonsillitis (2), haemophilus test positive, circulatory collapse, febrile convulsion, skin disorders (3), tonsillectomy, and preterm delivery. No deaths were reported. 3/78 patients discontinued CAN, 2 due to inefficacy, 1 due to loss of efficacy.
Conclusion: The 18-month interim analysis of the RELIANCE study, the longest running real-life CAN registry, demonstrates that long-term CAN treatment is well tolerated and effective in CAPS patients.
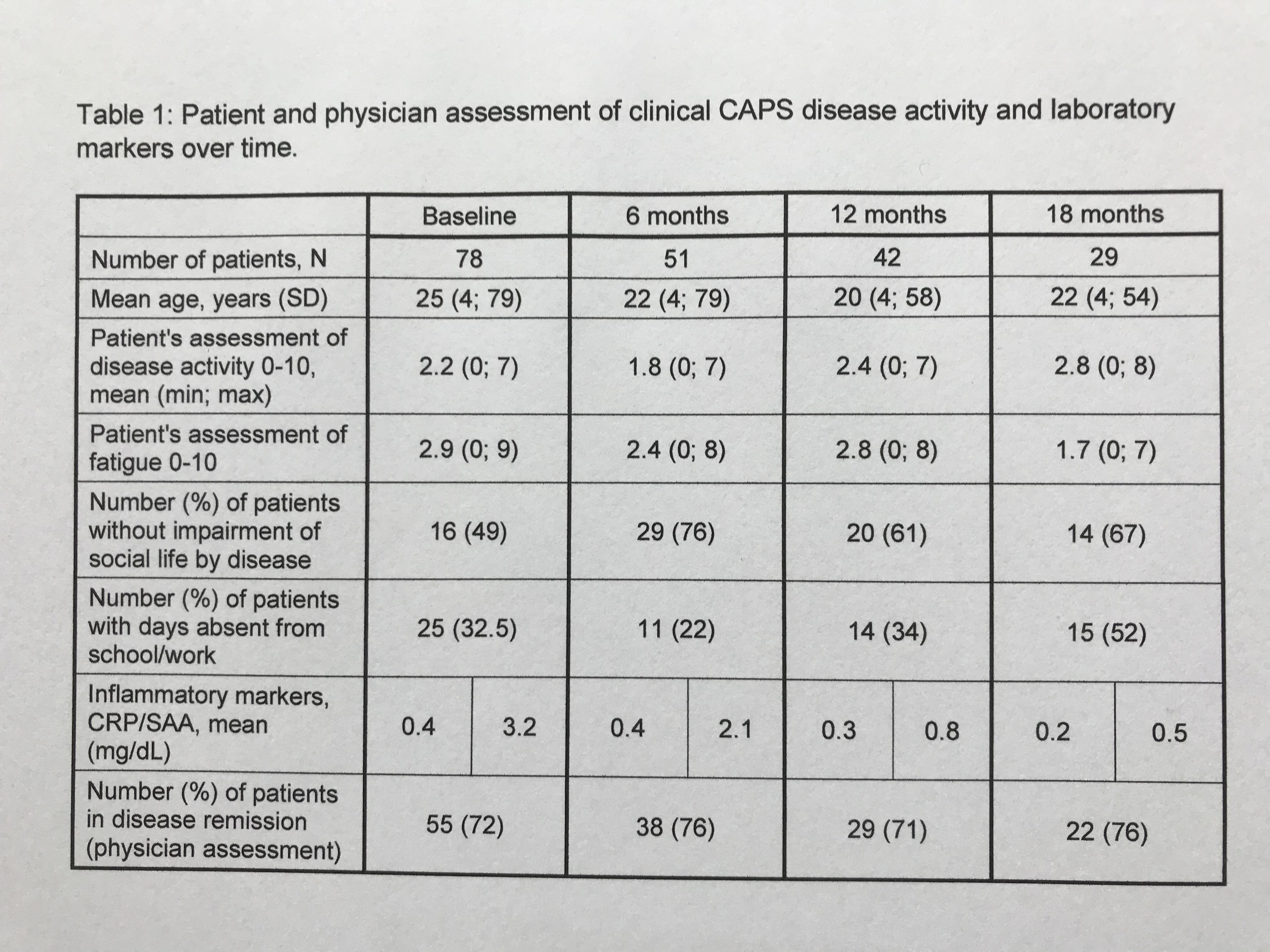 Table 1: Patient and physician assessment of clinical CAPS disease activity and laboratory markers over time
Table 1: Patient and physician assessment of clinical CAPS disease activity and laboratory markers over time
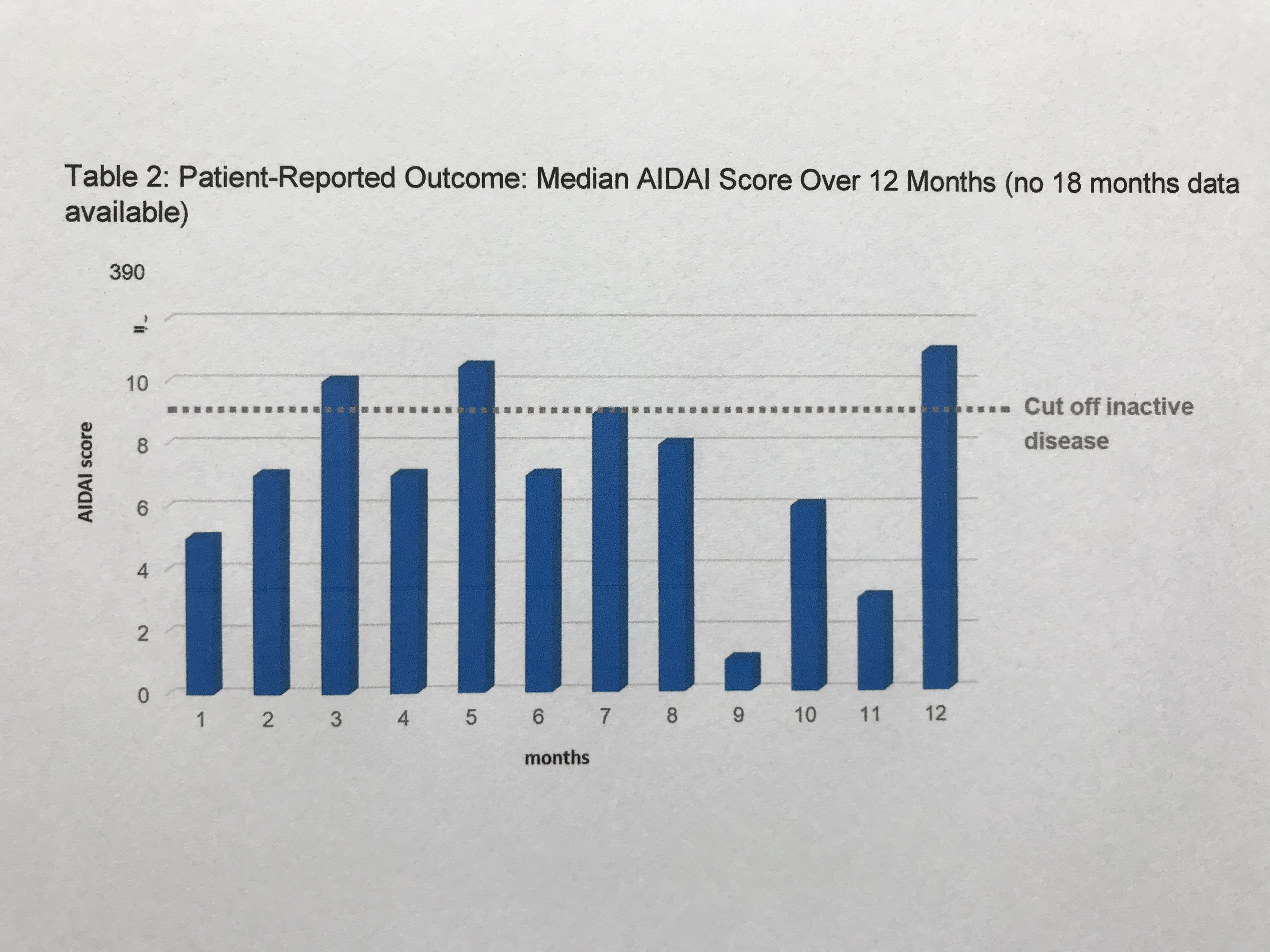 Table 2: Patient-Reported Outcome: Median AIDAI Score Over 12 Months (no 18 months data available)
Table 2: Patient-Reported Outcome: Median AIDAI Score Over 12 Months (no 18 months data available)
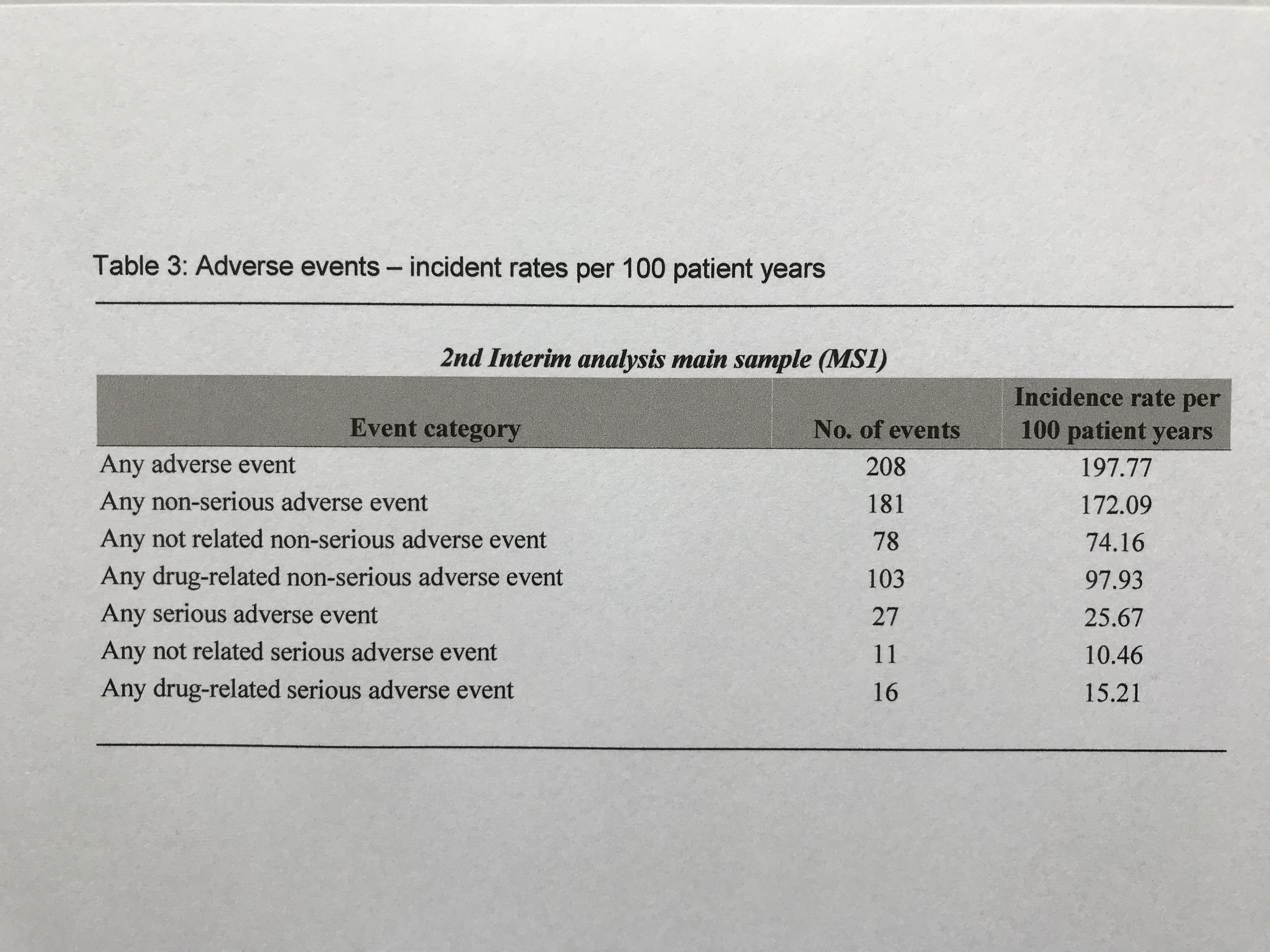 Table 3: Adverse events – incident rates per 100 patient years
Table 3: Adverse events – incident rates per 100 patient years
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kuemmerle-Deschner J, Kortus-Goetze B, Borte M, Foeldvari I, Horneff G, Janda A, Kallinich T, Oommen P, Schuetz C, Weller-Heinemann F, Weber-Arden J, Blank N. Long-Term Effectiveness of Canakinumab in Autoinflammatory Diseases – Interim Analysis of the CAPS Subgroup from the RELIANCE Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-effectiveness-of-canakinumab-in-autoinflammatory-diseases-interim-analysis-of-the-caps-subgroup-from-the-reliance-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-effectiveness-of-canakinumab-in-autoinflammatory-diseases-interim-analysis-of-the-caps-subgroup-from-the-reliance-registry/
