Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
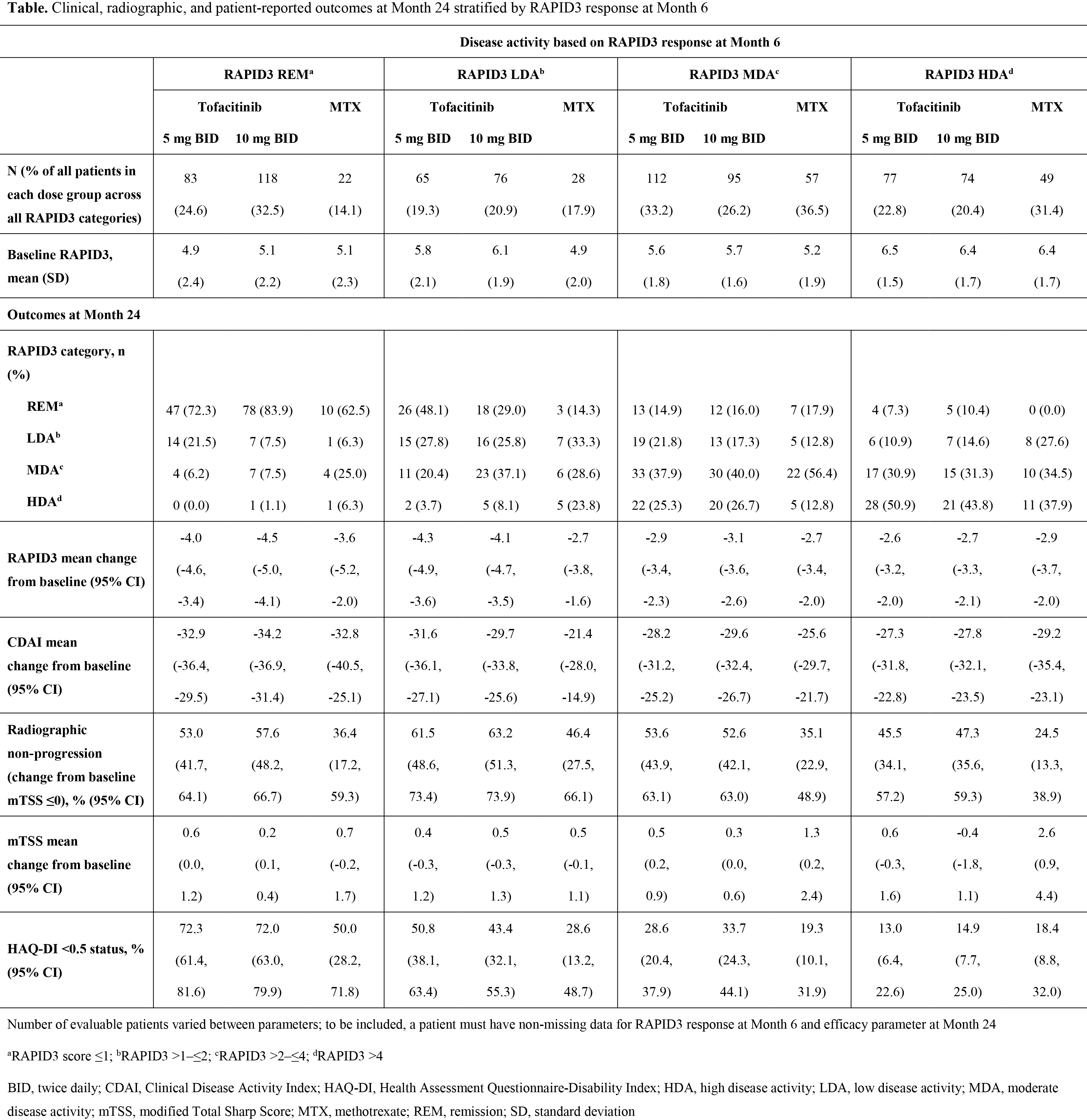
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. RAPID3 (Routine Assessment of Patient [Pt] Index Data 3) is a pooled index of the three RA core data set pt-reported outcomes (PROs): function, pain, and pt global assessment of disease activity. We compared clinical outcomes, radiographic progression, and PROs at Month 24 in pts achieving remission, low, moderate, and high disease activity (REM, LDA, MDA, and HDA) based on RAPID3 at Month 6.
Methods: ORAL Start (NCT01039688) was a 2-year, Phase 3 randomized controlled trial in which MTX-naïve pts with RA received tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID), tofacitinib 10 mg BID, or MTX titrated to 20 mg/week over 8 weeks. RAPID3 scores were calculated at Months 6 and 24 for pts with radiographs at both time points. To calculate RAPID3 scores, each of the 3 individual measures (PtGA visual analog scale [VAS], pain [VAS] and HAQ‑DI were scored from 0–10 for a total of 30, and divided by 3 to give an adjusted 0–10 score. Outcomes assessed at Month 24 included REM (defined as ≤1), LDA (>1–≤2), MDA (>2–≤4), and HDA (>4) rates based on RAPID3; change from baseline (CFB) in RAPID3, CDAI, and modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS); and proportion of pts with no radiographic progression based on CFB in mTSS ≤0 and HAQ-DI <0.5 (defined as normative).
Results: Pts with RAPID3 HDA at Month 6 had higher baseline RAPID3 scores than those achieving REM/LDA (Table). At Month 6, 24.6%, 32.5%, and 14.1% of pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID, tofacitinib 10 mg BID, and MTX achieved REM, respectively; 19.3%, 20.9%, and 17.9% LDA; 33.2%, 26.2%, and 36.5% MDA; and 22.8%, 20.4%, and 31.4% HDA. A higher proportion of patients were in RAPID3 REM and LDA with tofacitinib vs MTX. Regardless of treatment group, the majority of pts who achieved a specific response at Month 6 maintained or improved their responses at Month 24. CFB in RAPID3 and CDAI at Month 24 was greatest for pts who were in RAPID3 REM/LDA at Month 6. In each treatment group, patients in REM/LDA at Month 6 were more likely to achieve mTSS ≤0 at Month 24 than those with RAPID3 HDA at Month 6. Overall, regardless of RAPID3 category, a higher proportion of pts receiving tofacitinib than MTX had mTSS ≤0. Furthermore, CFB in mTSS at Month 24 with tofacitinib was generally similar across RAPID3 categories; with MTX, it was higher for patients with RAPID3 MDA and HDA. The proportion of pts with normative HAQ-DI scores at Month 24 was highest for pts achieving RAPID3 REM at Month 6, and lowest for those in RAPID3 HDA at Month 6, for each treatment group.
Conclusion: The majority of pts who attained a RAPID3 response at 6 months maintained that response at 24 months. More pts achieving RAPID3 REM or LDA at Month 6 were radiographic non-progressors or had normative HAQ-DI scores at Month 24, compared with those in RAPID3 MDA or HDA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Bergman MJ, Lee EB, Yazici Y, Wilkinson B, Takiya L, Wallenstein G, Zang C, Bananis E. Long-Term Clinical, Radiographic and Patient-Reported Outcomes Based on RAPID3 Responses with Tofacitinib at 6 Months [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-clinical-radiographic-and-patient-reported-outcomes-based-on-rapid3-responses-with-tofacitinib-at-6-months/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-clinical-radiographic-and-patient-reported-outcomes-based-on-rapid3-responses-with-tofacitinib-at-6-months/