Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Targeting B-cells remains an attractive option in Lupus Nephritis (LN) despite the negative results of RCTs.
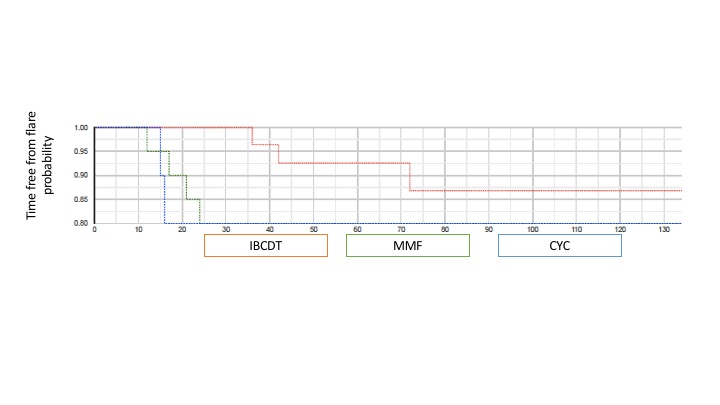
Methods: Sixty patients with active LN were included in the present study. Thirty patients were administered an intensified B-cell depletion therapy (IBCDT; 4 weekly Rituximab 375mg/sm and 2more doses after 1and2 months;2 infusions of 10 mg/kg cyclophosphamide (CYC),3 methylprednisolone pulses), followed by oral prednisone (rapidly tapered to 5mg/day by the end of the 3rd month). No further immunosuppressive maintenance therapy was given. Thirty patients matched for LN class and age were selected as controls: 20 received 3 methylprednisolone pulses days followed by oral prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)2-3 g/day, while 10 were given the Euro Lupus CYC.
Results: At 12 months, complete renal remission was observed in 93% of patients on IBCDT, in 62.7% on MMF, and in 75% on CYC. When assessed at 12 months, the dose of oral prednisone was lower in the IBCDT group (mean±SD 2.9±5.0mg/dl) than in those on MMF (10.5±8.0 mg/day,p< 0.01) or in the CYC group (7.5±9.0mg/day,p< 0.01). Mean follow-up after treatment was 44.5 months (ICQ36–120months), 48.6 months (ICQ36–120months), and 45.3 (ICQ36–120months) for IBCDT, MMF and CYC, respectively. At their last follow-up visit, we observed no significant differences in terms of proteinuria, serum creatinine, nor in the frequency of new flares among the three groups.
Conclusion: When compared to conventional regimens with MMF and CYC, sustained clinical remission even without maintenance immunosuppressive therapy was obtained by the IBCDT. Moreover, IBCDT had a significant steroid-sparing effect and a lower rate of flares compared to either MMF- or CYC- based conventional protocols.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Roccatello D, Sciascia S, Fenoglio R, Daniela R. Long-Term Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Lupus Nephritis Treated with an Intensified B-Cell Depletion Protocol: A Matched Case-Control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-clinical-outcomes-of-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-treated-with-an-intensified-b-cell-depletion-protocol-a-matched-case-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-clinical-outcomes-of-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-treated-with-an-intensified-b-cell-depletion-protocol-a-matched-case-control-study/