Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Apremilast (APR), an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, works intracellularly to modulate inflammatory mediators. PALACE 3 compared the efficacy/safety of APR with placebo (PBO) in pts with active PsA and at least 1 psoriatic lesion ≥2 cm at baseline (BL) despite prior DMARDs and/or biologics.
Methods: Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to PBO, APR 20 mg BID (APR20), or APR 30 mg BID (APR30) stratified by BL DMARD use and BSA ≥3%. At wk 16, pts with <20% reduction from BL in swollen/tender joint counts qualified for protocol-defined early escape; those on PBO were re-randomized to APR20 or APR30 and those on APR remained on the initial APR dose. At wk 24, all remaining PBO pts were re-randomized to APR20 or APR30 through wk 52. Pts taking concurrent DMARDs were allowed to continue stable doses (MTX, sulfasalazine, leflunomide, or combination).
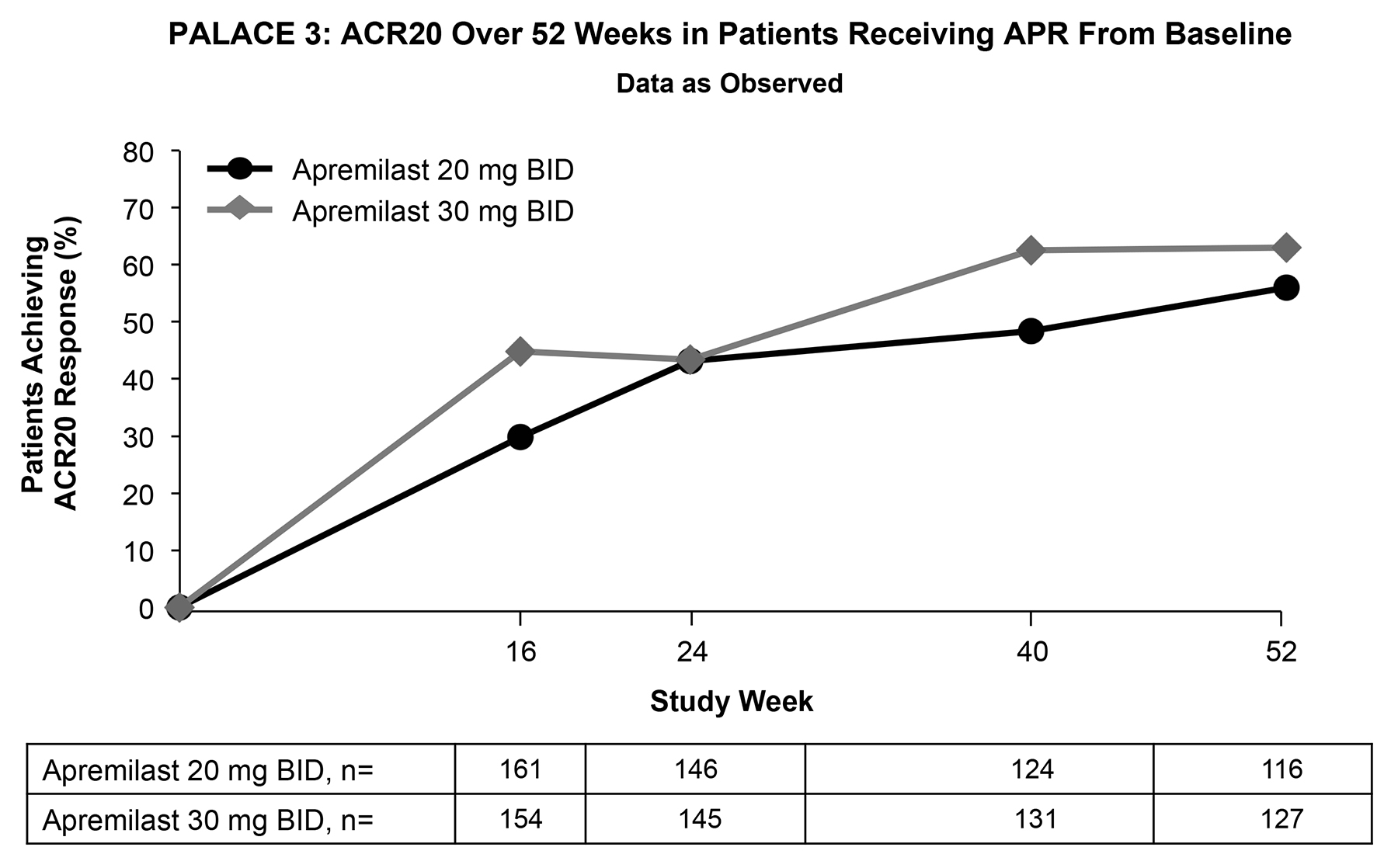
Results: 505 pts were randomized and received ≥1 dose of study drug (PBO, 169; APR20 169; APR30, 167). At wk 16 (primary endpoint), significantly more APR20 (29.4%; P=0.0235) and APR30 pts (42.8%; P<0.0001) achieved ACR20 vs PBO (18.9%). For those pts originally randomized to APR and completing 52 wks of study, improvements were maintained or increased over 52 wks for multiple endpoints, including: (1) ACR20 of 56.0% (APR20) and 63.0% (APR30) (Figure); (2) HAQ-DI mean change from BL (SD) of -0.332 (0.505) for APR20 and -0.350 (0.505) for APR30 pts, meeting the MCIDs of 0.13 and 0.30; and (3) in pts with BL BSA ≥3%, PASI-75 was achieved by 28.6% (APR20) and 39.1% (APR30) of pts; PASI-50 was achieved by 49.2% (APR20) and 54.7% (APR30). The magnitude of responses was higher for APR30 than APR20. Pts randomized to APR at wks 16 or 24 demonstrated results consistent with those originally randomized to APR. APR was generally well tolerated. AEs occurring in ≥5% of all pts exposed to APR through wk 52 were diarrhea, nausea, headache, URTI, nasopharyngitis, and vomiting. The majority of AEs were mild/moderate and predominantly did not lead to discontinuation. Gastrointestinal AEs occurred at a reduced incidence rate after the first wk of dosing. SAEs occurred in 5.4% (APR20) and 4.1% (APR30) of pts. No new safety signals were identified and the incidence of pts experiencing any AE was comparable over the 0-24 and 0-52 wk periods. No imbalance in the exposure-adjusted incidence rates of severe AEs, SAEs, major adverse cardiac events, serious infections including systemic opportunistic infection, or malignancies between APR and PBO was observed. No cases of TB (novel or reactivation) were reported in the APR treatment groups; TB screening was not required per protocol.
Conclusion: Over 52 wks, APR continued to demonstrate efficacy in the treatment of PsA and associated psoriasis, including clinically meaningful improvements in signs and symptoms and physical function. APR demonstrated an acceptable safety profile with up to 52 wks of treatment and was generally well tolerated.
Disclosure:
C. J. Edwards,
Pfizer,
2,
Pfizer, Samsung, Roche, Celgene,
5,
Roche, Pfizer, Abbott, Glaxo-SmithKline,
8;
F. J. Blanco,
Pfizer, Bioiberica, Gebro Pharma,
5;
J. Crowley,
AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer,
2,
AbbVie, Amgen,
5,
AbbVie,
8;
C. Hu,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
R. M. Stevens,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
C. A. Birbara,
Amgen, Lilly, Pfizer, Incyte, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb,
2.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-52-week-results-of-a-phase-3-randomized-controlled-trial-of-apremilast-an-oral-phosphodiesterase-4-inhibitor-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-current-skin-involvement-palace-3/