Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Inflammation of the spine is believed to trigger a repair mechanism that results in syndesmophyte formation in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) patients (pts).1 Bone marrow fatty lesions (FLs) and axial skeleton erosions, visible on MRI T1 sequences, are post‑inflammatory changes that contribute significantly to models predicting new bone formation.2 It has previously been assumed that resolution of inflammatory lesions (INFLs) in anti‑TNF treated axSpA pts may be associated with an increase in FLs.3,4 RAPID‑axSpA was a long‑term study in pts with radiographic (r)‑axSpA / ankylosing spondylitis or non‑radiographic (nr)‑axSpA treated with certolizumab pegol (CZP), which rapidly suppressed active inflammation of the spine, with pts showing limited spinal radiographic progression over 4 years.5 Here, the incidence and association of active inflammation and chronic lesions (FLs, sclerosis, and erosions) in the spine of CZP treated axSpA pts over 4 years is reported.
Methods: RAPID‑axSpA (NCT01087762) was double‑blind and placebo (PBO)‑controlled to Week (Wk) 24, dose‑blind to Wk 48, and open‑label to Wk 204. Baseline (BL) CZP‑randomized pts (200 mg every 2 weeks [Q2W] or 400 mg Q4W) continued their assigned dose throughout; BL PBO‑randomized pts received CZP from Wk 16 (non-responders) or Wk 24. Blinded spinal MRI scans at BL, Wk 12, 48, 96, and 204 were assessed by 2 central readers to evaluate the presence/absence of active INFLs (Short Tau Inversion Recovery [STIR] sequence), FLs, sclerosis and erosions (T1 sequence) in vertebral edges (VEs) (present if recorded so by both readers). AxSpA pts with a valid BL and ≥1 post-BL assessment were included. Mean pt level lesion counts were estimated from mixed models with repeated measures (MMRM) fitted on observed data from CZP or PBO pts. Associations between INFLs and FLs at the VE level for all pts were described using cross‑tabulations.
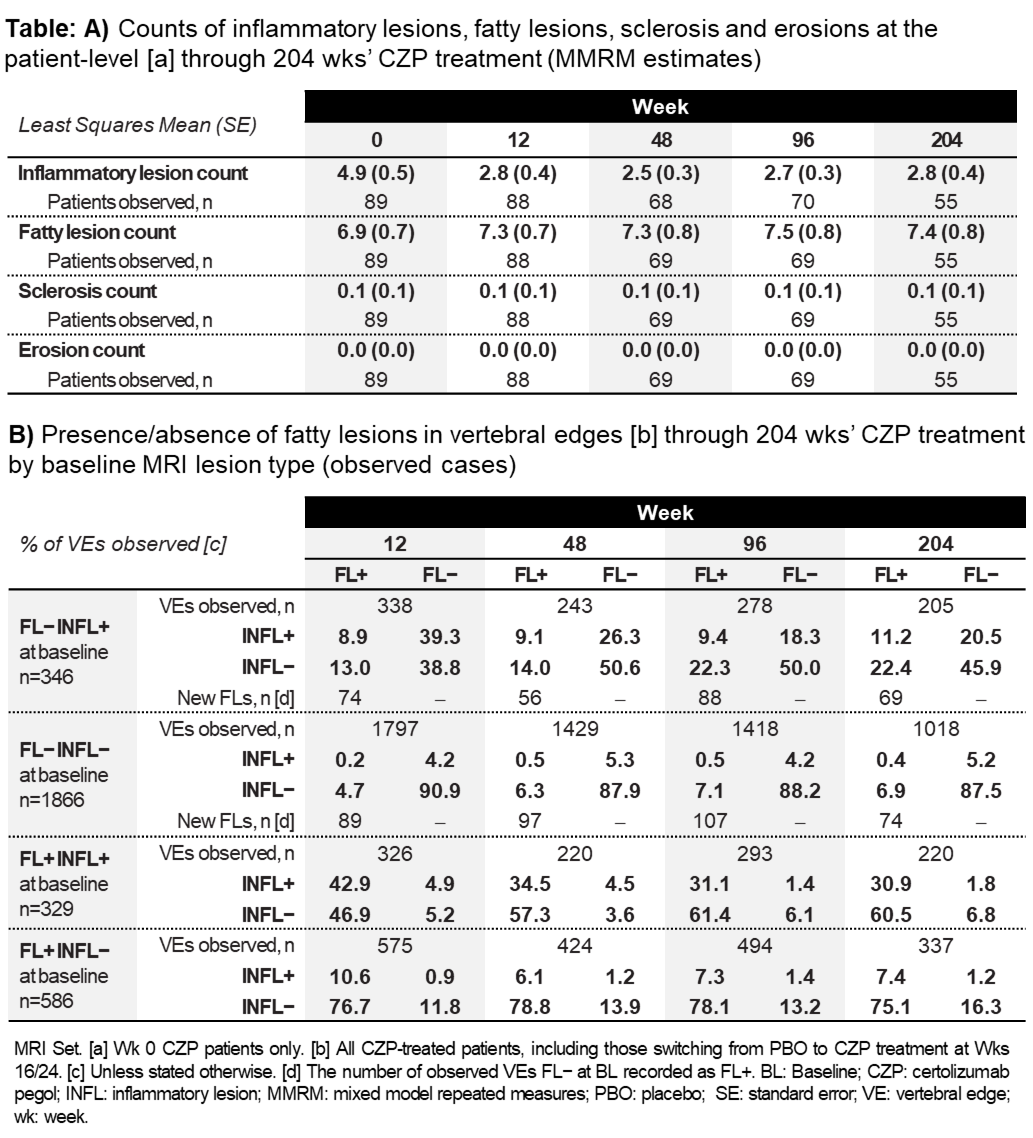
Results: Of 325 randomized pts, 136 were eligible for these analyses. In BL CZP pts (n=89), active INFLs were reduced, and FL counts only slightly increased by Wk 12; both were sustained at a low level to Wk 204 (Table A). Very few VEs with erosions and sclerosis were observed at BL, and no changes in their frequency were observed to Wk 204 (Table A). Over 204 wks, the risk of developing new FLs was greater in VEs with vs without INFLs at BL, regardless of changes to INFLs in these VEs post‑BL (Table B). At BL the prevalence of FLs was greater in pts with >3 vs ≤3 years’ disease duration and more new FLs developed in pts with >3 years disease duration (data not shown).
Conclusion: Long‑term CZP treatment in axSpA pts was associated with rapid and sustained reduction in active inflammation, no increase in sclerosis and erosions, and a negligible increase in FLs in VEs over 4 years. More FLs developed in VEs in pts with >3 years disease duration and with INFLs at BL than without, which was not affected by resolution of INFLs, providing evidence of the importance of early treatment in pts with active axSpA.
References:
1. Appel H. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2008;10:356–63; 2. Baraliakos X. Ann Rheum Dis 2014 Oct;73:1819-25; 3. Maksymowych W. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:23–8; 4. Song I. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70:1257–63; 5. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:699–705.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Kruse S, Auteri S, de Peyrecave N, Nurminen T, Kumke T, Hoepken B, Braun J. Long‑Term Certolizumab Pegol Treatment of Axial Spondyloarthritis Is Associated with Rapid and Sustained Reduction of Active Inflammation and Minimal Structural Changes in the Spine: 4‑Year MRI Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long%e2%80%91term-certolizumab-pegol-treatment-of-axial-spondyloarthritis-is-associated-with-rapid-and-sustained-reduction-of-active-inflammation-and-minimal-structural-changes-in-the-spine-4/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long%e2%80%91term-certolizumab-pegol-treatment-of-axial-spondyloarthritis-is-associated-with-rapid-and-sustained-reduction-of-active-inflammation-and-minimal-structural-changes-in-the-spine-4/