Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate and leflunomide are anchor conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment. Although methotrexate is the usual recommended concomitant csDMARD along with biological DMARDs (bDMARDs), leflunomide is an alternative treatment option. Objective of this study was to describe leflunomide survival with concomitant bDMARDs use.
Methods: TReasure is a multicenter, web-based registry of RA and spondyloarthritis patients receiving targeted treatments. As of May 2018, 1401 RA patients were recorded. Age, sex, disease duration, BMI, initial bDMARDs, acute phase reactants, swollen and tender joint counts (28 joints), patient global assessment of disease activity, pain VAS, DAS-28, CDAI, and SDAI were recorded before starting bDMARDs. Patients starting a bDMARD were divided into two groups. Group 1 included patients receiving concomitant leflunomide with or without other csDMARDs combined with leflunomide. Group 2 consisted of patients using other concomitant csDMARDs or combinations that did not include leflunomide. DAS-28 disease state at the last recorded visit was compared. Retention rate of leflunomide was calculated by Kaplan-Meier analysis.
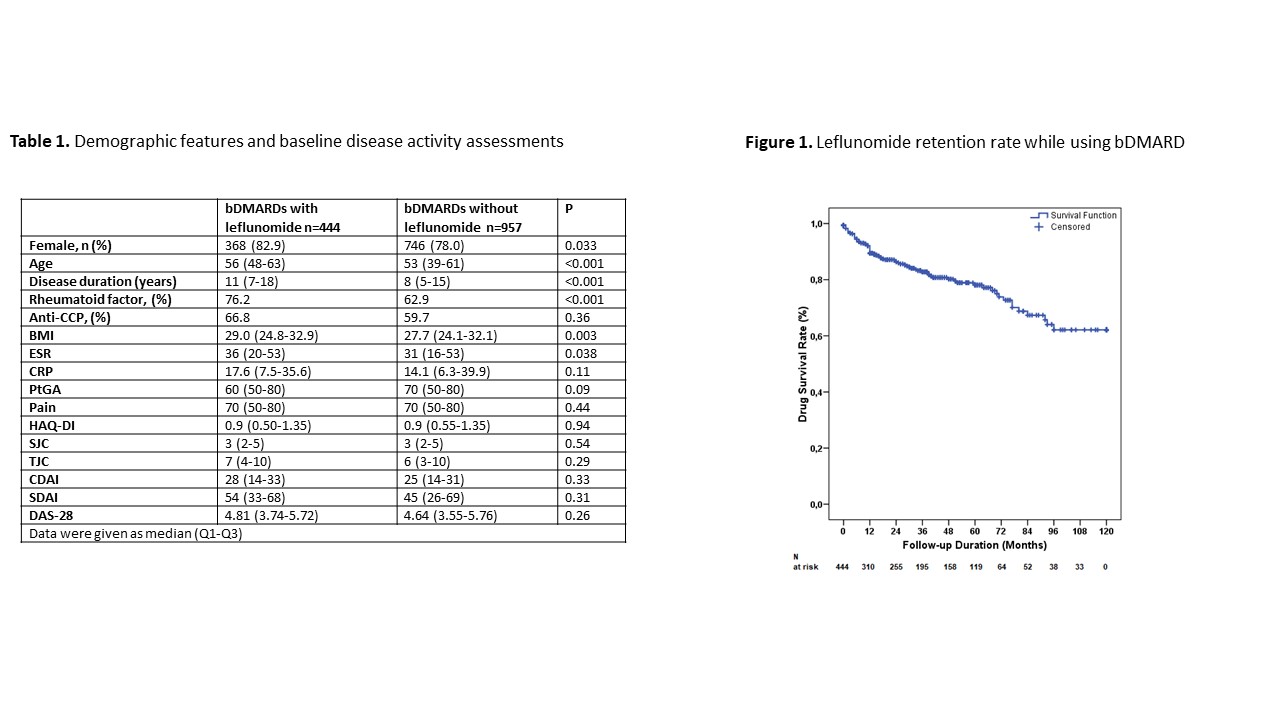
Results: Overall, 1401 patients, 444 of which (31.6%) using leflunomide with their first bDMARD were included. Demographic data and baseline disease activity are given in table 1. Initial bDMARDs in group 1 were anti-TNF drugs 275 (61.9%), abatacept 77 (17.3%), rituximab 59 (13.3%), tofacitinib 20 (4.5%), and tocilizumab 13 (2.9%). At the baseline visit leflunomide was combined with hydroxychloroquine [266 (59.9%)], methotrexate [83 (18.7%)], or sulfasalazine [67 (15.1%)]. Median (Q1-Q3) duration of treatment with leflunomide was 28 (7-54) months. DAS-28 activity state at the last visit for group 1 and group 2 were; high in 8.8% vs. 8.5%, moderate in 36.7% vs. 33.3%, low in 20.2% vs. 18.0%, and remission in 34.3% vs. 40.1% respectively (p=0.31). Median (Q1-Q3) DAS-28 score at the last visit was not significantly different between groups [3.05 (2.31-3.96) vs. 2.86 (2.18-3.82), p=0.11]. Five-year survival of bDMARDs with concomitant leflunomide was around 80% (figure 1).
Conclusion: Leflunomide was one of the major concomitant csDMARDs in our RA biological registry. It was combined with both anti-TNF and other biologics. Retention rate of bDMARDs with concomitant leflunomide was satisfactory and disease activity with leflunomide was not significantly different from that with other synthetic DMARDs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kimyon G, Kiraz S, Ertenli I, Kucuksahin O, Dalkiliç E, Bes C, Alpay Kanitez N, Kasifoglu T, Emmungil H, Coşkun BN, Yagız B, Koca SS, Cinar M, Ateş A, Akar S, Ersozlu Bakirli D, Yazisiz V, Yasar Bilge NS, Aydin Tufan M, Mercan R, Karadag O, Kelesoglu AB, Gercik O, Oz B, Akar ZA, Yılmaz S, Turan S, Pehlivan Y, Terzioglu E, Kilic L, Erten S, Tekgöz E, Tascilar K, Kalyoncu U. Leflunomide As a Concomitant DMARD Choice for the Biological Treatment Era of Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-as-a-concomitant-dmard-choice-for-the-biological-treatment-era-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-as-a-concomitant-dmard-choice-for-the-biological-treatment-era-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/