Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Vasculitis Poster III: Immunosuppressive Therapy in Giant Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) and leflunomide (LEF) are used as adjunct immunosuppressants and corticosteroid sparing agents in treatment of Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA), but the efficacy is poorly investigated. The aim of this study was to compare efficacy, safety and drug survival between MTX and LEF in the treatment of GCA.
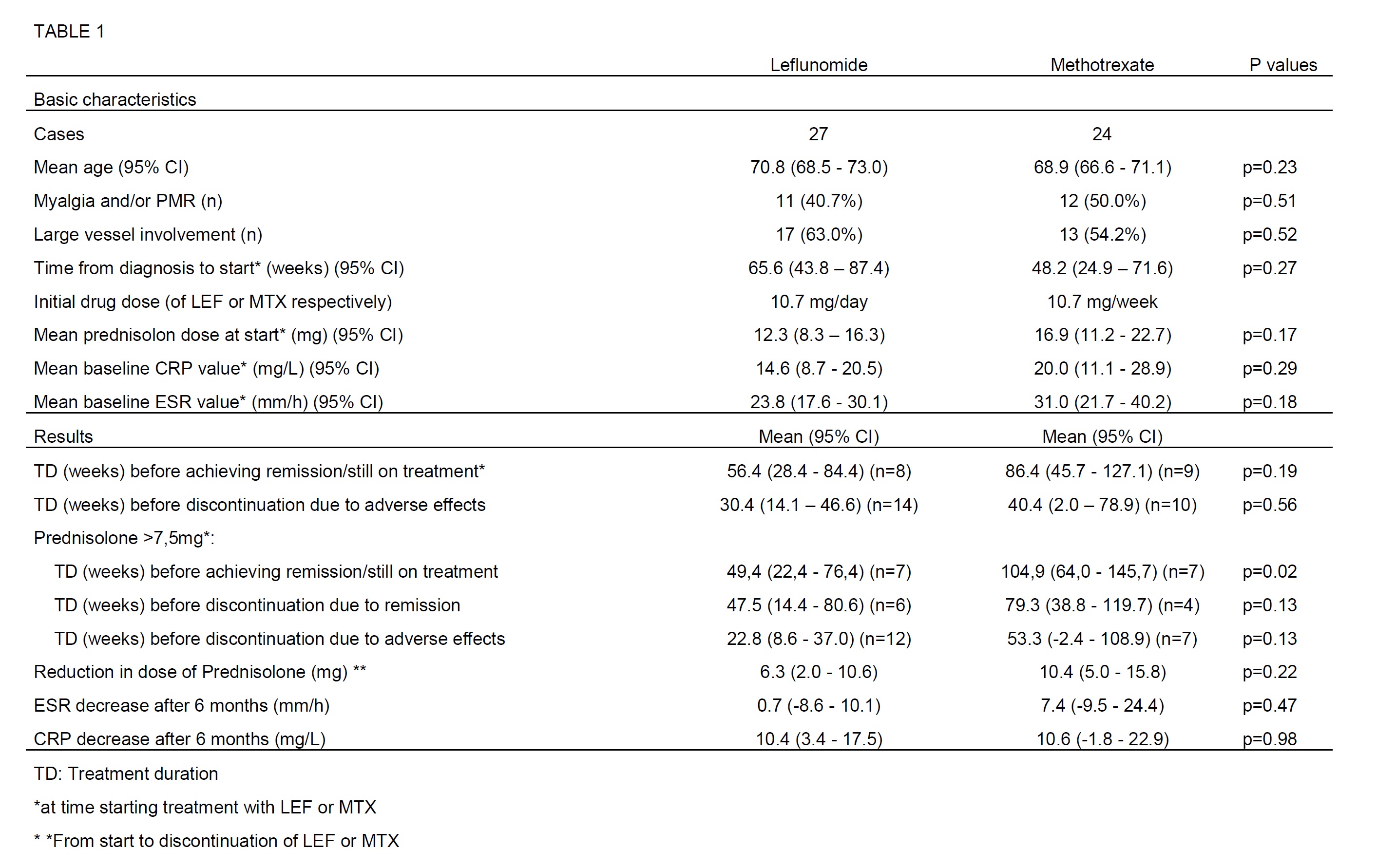
Methods: During 2007-2017 all patients diagnosed with GCA at the Department of Rheumatology were included in a hospital-based retrospective study. All patients receiving MTX and/or LEF due to insufficiency and/or adverse effects of treatment with Prednisolone were identified. Duration of treatment, causes of discontinuation and changes in Prednisolone dose, Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were registered. Concomitant myalgia and/or polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) and large vessel involvement (LVI) (involvement of aorta and its primary and secondary branches) were noted. Remission was defined as doctor’s opinion of clinical remission and a Prednisolone dose ≤5mg/day. Baseline Prednisolone dose and CRP values were unevenly distributed between the groups. Therefore the effect in patients with a Prednisolone dose >7.5 mg at start of treatment were analyzed separately, interpreted as a group of patients with higher disease activity. Student-t test was used to compare means and Chi-square test to compare categorical variables. All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS statistical package version 23.
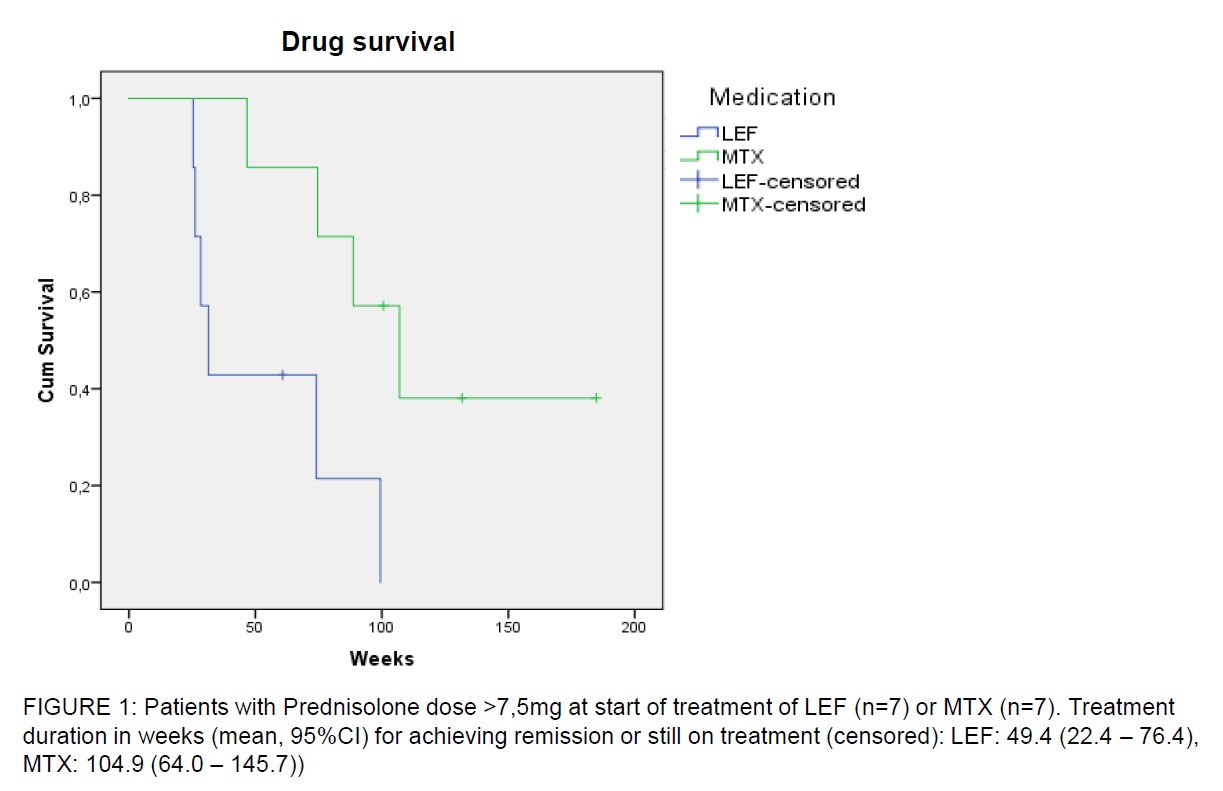
Results: 216 patients (70.4% women) were included (mean age 72.9 at time of diagnosis). Twenty-seven and 24 patients started treatment with LEF and MTX, respectively. During the treatment-period, the observed mean reduction in Prednisolone dose, ESR and CRP did not differ significantly. No significant difference between LEF and MTX in treatment duration to achieve remission/still on treatment was found (p=0.19). For patients with higher disease activity (Prednisolone >7.5mg), this difference was significant favoring LEF (p=0.02). In the same group, a non-significant difference was found in the time to discontinuation due to adverse effects (p=0.13). There were no differences in the number of adverse effects in the treatment groups, most of them mild and well known.
Conclusion: To our knowledge this is the first study to compare LEF and MTX in the treatment of GCA. Patients treated with LEF achieved remission earlier than MTX, and this difference was significant in patients with higher disease activity (p=0.02). We found no difference in tolerability and reduction in ESR and CRP after 6 months of treatment between the groups.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tengesdal S, Myklebust G. Leflunomide and Methotrexate in Treatment of Giant Cell Arteritis: Comparison of Efficacy, Safety and Drug Survival [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-and-methotrexate-in-treatment-of-giant-cell-arteritis-comparison-of-efficacy-safety-and-drug-survival/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-and-methotrexate-in-treatment-of-giant-cell-arteritis-comparison-of-efficacy-safety-and-drug-survival/