Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Leflunomide (LEF) is a DMARD commonly used safely and effectively in rheumatoid arthritis. The experience with LEF in SLE is mainly based on what has been reported in cases or case series 1, with only one clinical trial evaluating its efficacy in extrarenal manifestations 2.
The purpose of our study is to assess the efficacy and safety of LEF in the treatment of SLE patients as well as to investigate if there are any clinical characteristics that correlate with a better response to treatment and, thus, identify the subgroup of patients that would benefit most from it.
Methods: Retrospective observational study. Medical records of all patients diagnosed with SLE (1997 ACR criteria) were reviewed and those who had received LEF were selected. Patients were evaluated for safety and efficacy after 4.9±3.2 months of therapy. Demographic and clinical data were collected. Variables were analyzed using SPSS 25 (IBM®) by descriptive statistics and cross-tabs if qualitative, the comparison of means by the Student’s t-test and correlations by Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
Results: Thirty-five patients were included, with a mean age of 52.2±14.7 years and 15.1±13 years since SLE diagnosis. The indication for LEF was arthritis in 34 patients (94.7%), relapsing polychondritis in 1 (2.9%). Age at LEF initiation was 48.3±14.7 years. The dose started was 20mg/day in 20 patients (57.1%), 10mg/day in 13 (37.1%). Seventeen patients (48.7%) went into joint remission after the initiation of LEF, and glucocorticoids (GC) could be withdrawn in 7 (20%). In 7 patients (20%) LEF was withdrawn before the first efficacy evaluation. The different adverse effects, as well as the demographic and clinical data of the patients are detailed in Table 1. We did not find any serious adverse effect or any case of subcutaneous lupus attributed to LEF. Our patients SLE baseline activity was mild–moderate: SLEDAI 6.3±3.1, normal average C3 and C4. Pre-LEF, 10 patients had positive DNA, 7 low C3, and 6 low C4. Failed treatments before LEF and treatments received concomitantly are detailed in Figure 1. In Figure 2, a statistically significant pre- and post-LEF decrease in physician global assessment (PGA), SLEDAI and ESR was observed, a non-significant one in dsDNA and GC values, as well as a non-significant increase in C3 and C4.
No correlation was found between the maximum dose of GC ever used, as an indicator of disease severity, and a better response in any parameters (ESR, CPR, PGA, dsDNA, C3, C4) pre- and post-LEF, or with going or not into joint remission. Neither was found a correlation between achieving remission or not, and the different demographic, clinical or treatment characteristics of patients, which does not allow to discern which subgroup of patients would benefit most from LEF treatment.
Nowadays, 15 patiens continue taking LEF (42.8%), with a mean treatment time of 4.4±3.9 years.
Conclusion: Treatment with LEF in SLE seems to be an effective and safe option, particularly for joint symptoms, with significant improvement observed in PGA, SLEDAI and ESR, as well as a 48.6% of joint remission after its onset.
 Table 1: Demographic and clinical characteristics of the 35 included patients.
Table 1: Demographic and clinical characteristics of the 35 included patients.
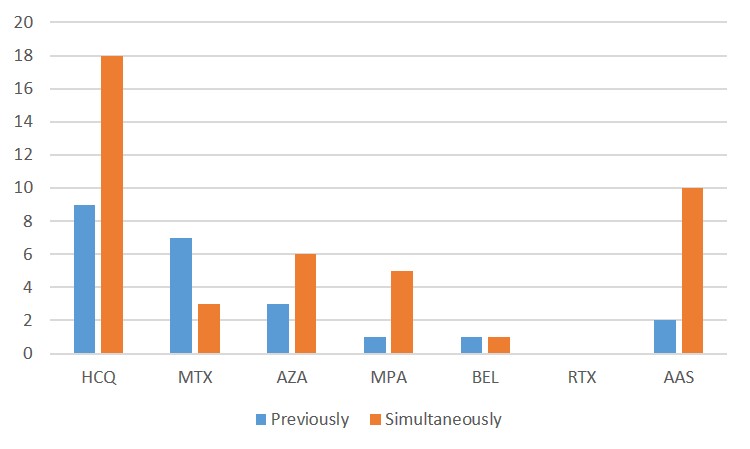 Figure 1: Previous and concomitant treatments to LEF. A treatment is reported as “previously” if it was stopped before LEF was started and “simultaneously” if it was started or maintained at the same time as LEF. HCQ: hydroxychloroquine; MTX: methotrex-ate; AZA: azathioprine; MPA: mycophenolic acid; BEL: belimumab; RTX: rituximab; AAS: acetylsalicylic acid.
Figure 1: Previous and concomitant treatments to LEF. A treatment is reported as “previously” if it was stopped before LEF was started and “simultaneously” if it was started or maintained at the same time as LEF. HCQ: hydroxychloroquine; MTX: methotrex-ate; AZA: azathioprine; MPA: mycophenolic acid; BEL: belimumab; RTX: rituximab; AAS: acetylsalicylic acid.
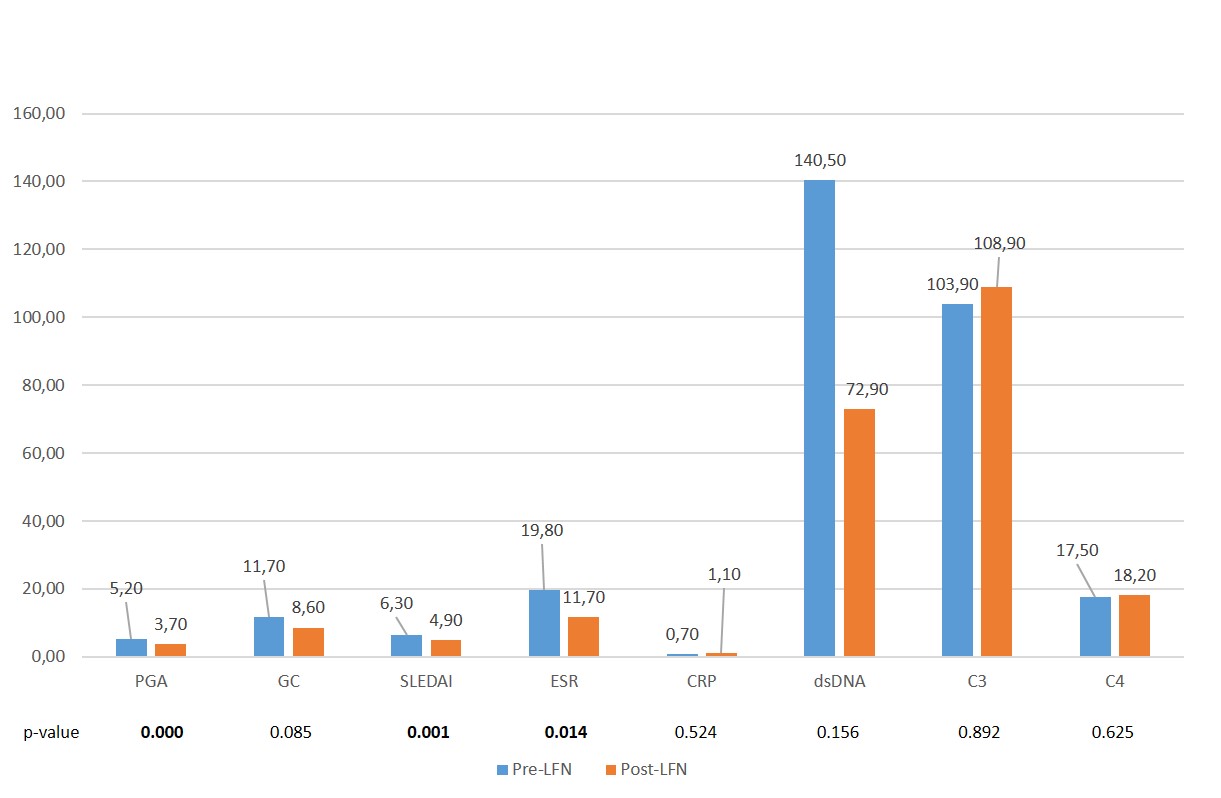 Figure 2: Value changes in different parameters before and after LEF. PGA: physician global assessment, GC: glucocorticoids, SLEDAI: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-Reactive Protein; dsDNA: double-stranded DNA; C3: complement C3; C4; complement C4.
Figure 2: Value changes in different parameters before and after LEF. PGA: physician global assessment, GC: glucocorticoids, SLEDAI: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-Reactive Protein; dsDNA: double-stranded DNA; C3: complement C3; C4; complement C4.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Carrión-Barberà I, Salman Monte T, Polino L, Mejía M, Ciria M, Pérez-García C, Rodríguez E, Monfort J. Leflunomide: A Safe and Effective Alternative in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-a-safe-and-effective-alternative-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-a-safe-and-effective-alternative-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/
