Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sirukumab (SIR), a human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the IL-6 cytokine with high affinity, has demonstrated efficacy in RA in the phase 3 SIRROUND studies. Lipid elevations have been observed with SIR, consistent with IL-6 pathway inhibition (Lancet 2017. 389:1206). A post hoc analysis evaluated the impact of SIR treatment on plasma lipids and lipid particle subtypes.
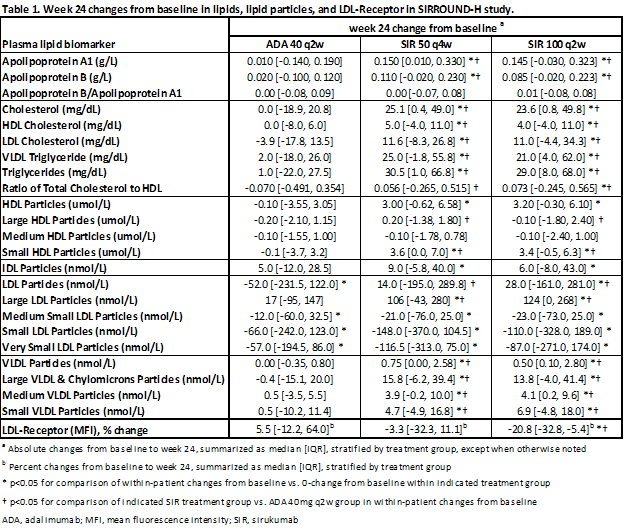
Methods: Lipids were analyzed in plasma samples obtained from RA patients in SIRROUND-H (active comparator monotherapy study; n=160, 159, and 162 for adalimumab (ADA) 40mg q2w, SIR 50mg q4w, and SIR 100mg q2w treatment groups) and SIRROUND-D (placebo(PBO)-controlled DMARD-inadequate responder (IR) study; n=293, 470, and 437 patients for PBO (excluding early escape patients), SIR 50mg q4w, and SIR 100mg q2w treatment groups). Plasma fasting levels of HDL, LDL, IDL, VLDL and their respective particle subtypes (LipoProfile® test), triglycerides, Apolipoproteins (Apo) A1 and B, and total cholesterol were measured centrally. LDL-receptor (LDL-R) levels on blood leukocytes were measured by flow cytometry in 15 (ADA 40mg q2w), 23 (SIR 50mg q4w), and 20 (SIR 100mg q2w) patients in SIRROUND-H. Significance of differences between baseline and week (Wk)24 sample data was tested using Wilcoxon signed-rank and Mann-Whitney tests (p<0.05 considered significant).
Results: Elevations in total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, IDL, VLDL and triglycerides from baseline to Wk24 were observed with SIR compared to PBO or ADA (p<0.05; Table 1 for the SIRROUND-H study). However, atherogenic indices increased slightly (total cholesterol:HDL) or remained unchanged (ApoB/ApoA1) with SIR. Increases in LDL levels with SIR were mainly due to increases in anti-atherogenic large particles, with decreases in smaller pro-atherogenic particle sizes. Increases in HDL were mainly due to increases in small anti-atherogenic particles, with decreases in medium particles. Increases in VLDL with SIR were associated with increases in all particle sizes. Results were similar for both SIR doses and both studies, with similar changes observed by Wk4 (SIRROUND-H). ADA was associated with smaller but significant decreases in very small, small, and medium LDL particles (Table 1). LDL-R levels were decreased (p=0.044) only in the SIR 100mg q2w group, but changes in LDL-R levels did not correlate to changes in lipids or lipid particles (p>0.05).
Conclusion: SIR treatment was associated with increased plasma lipid levels compared to placebo and ADA. However, atherogenic indices, which are considered more reliable lipid markers in RA (Mediators Inflamm 2012. 2012: 785946), remained unchanged or changed minimally with SIR. Changes in LDL and HDL levels with SIR were mainly due to a shift towards a more anti-atherogenic lipid profile. Despite the small sample size, modulation of LDL-R levels did not appear to be involved in the observed lipid changes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Loza M, Bili A, Daga S, Brown K, Gilbride J, Dasgupta B, Hsu B, McInnes IB. LDL and HDL Changes with Sirukumab Treatment Are Anti-Atherogenic: Results from Two Phase 3 Trials in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ldl-and-hdl-changes-with-sirukumab-treatment-are-anti-atherogenic-results-from-two-phase-3-trials-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ldl-and-hdl-changes-with-sirukumab-treatment-are-anti-atherogenic-results-from-two-phase-3-trials-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/