Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Joints with different sizes (e.g. small and large joints) and anatomical locations (upper and lower extremities) can be affected in psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Our aim was to explore the effect of these different joint patterns on patient reported outcomes (PROs) in a patient population presenting with mono-oligoarthritis.
Methods: PsArt-ID (Psoriatic Arthritis- International Database) is a multicentre registry aiming to understand the disease characteristics of PsA in real life. From that registry, 387/1670 patients who had oligo-monoarthritis in cross sectional assessment were included. Mono-oligoarthritis was defined as having 1-4 joints that were tender and swollen in the same assessment. The joints were categorized according to their size (small and large) and location (upper and lower extremity). Patients who had combination of these joints were excluded. PROs (health assessment questionnaire, pain score, patient global assessment (PGA), fatigue, morning stiffness), physician global assessment, C-reactive protein (CRP) were compared based on the joint patterns. Analysis was made by categorizing according to joint counts (1-2 joints and 3-4 joints).
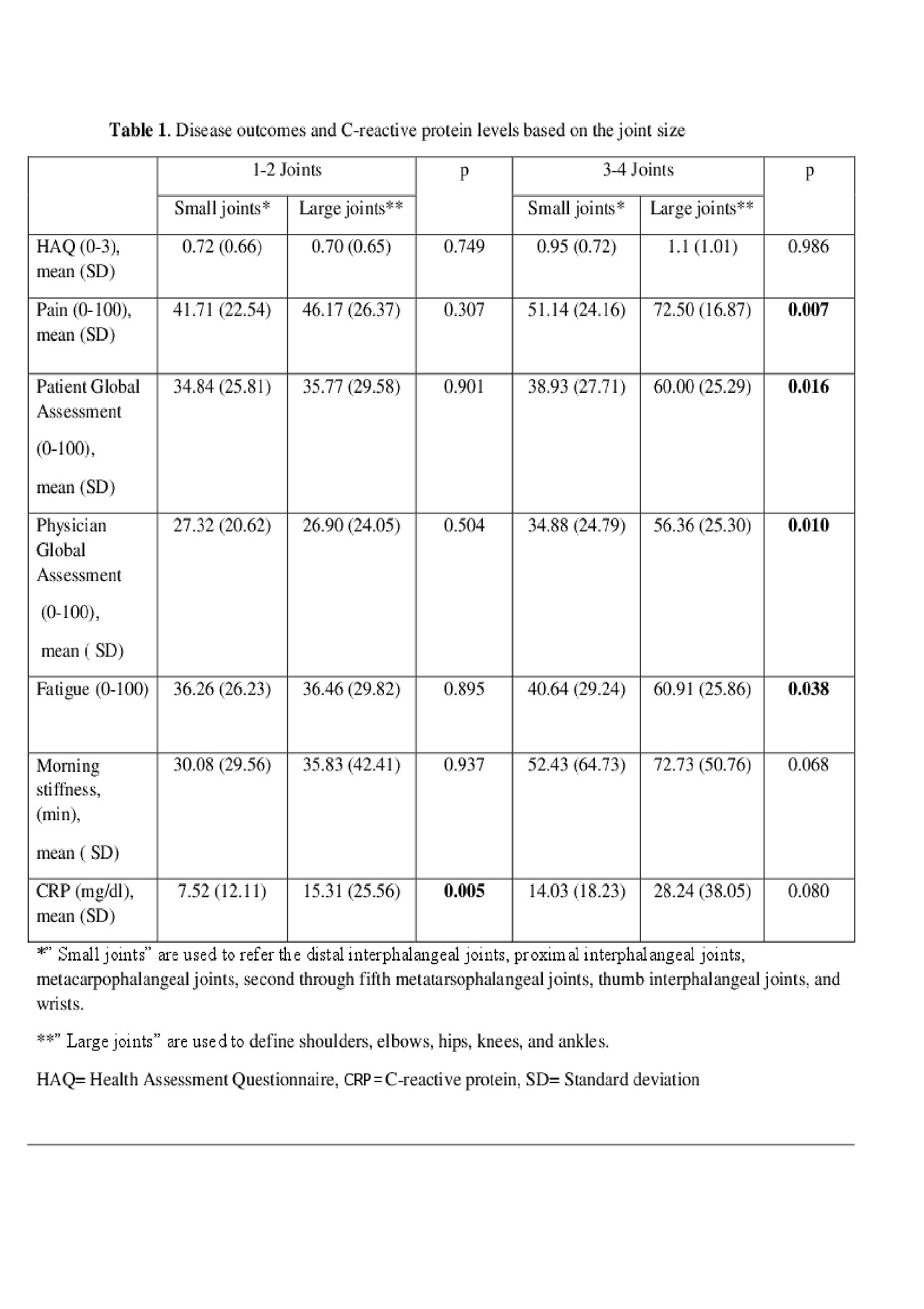
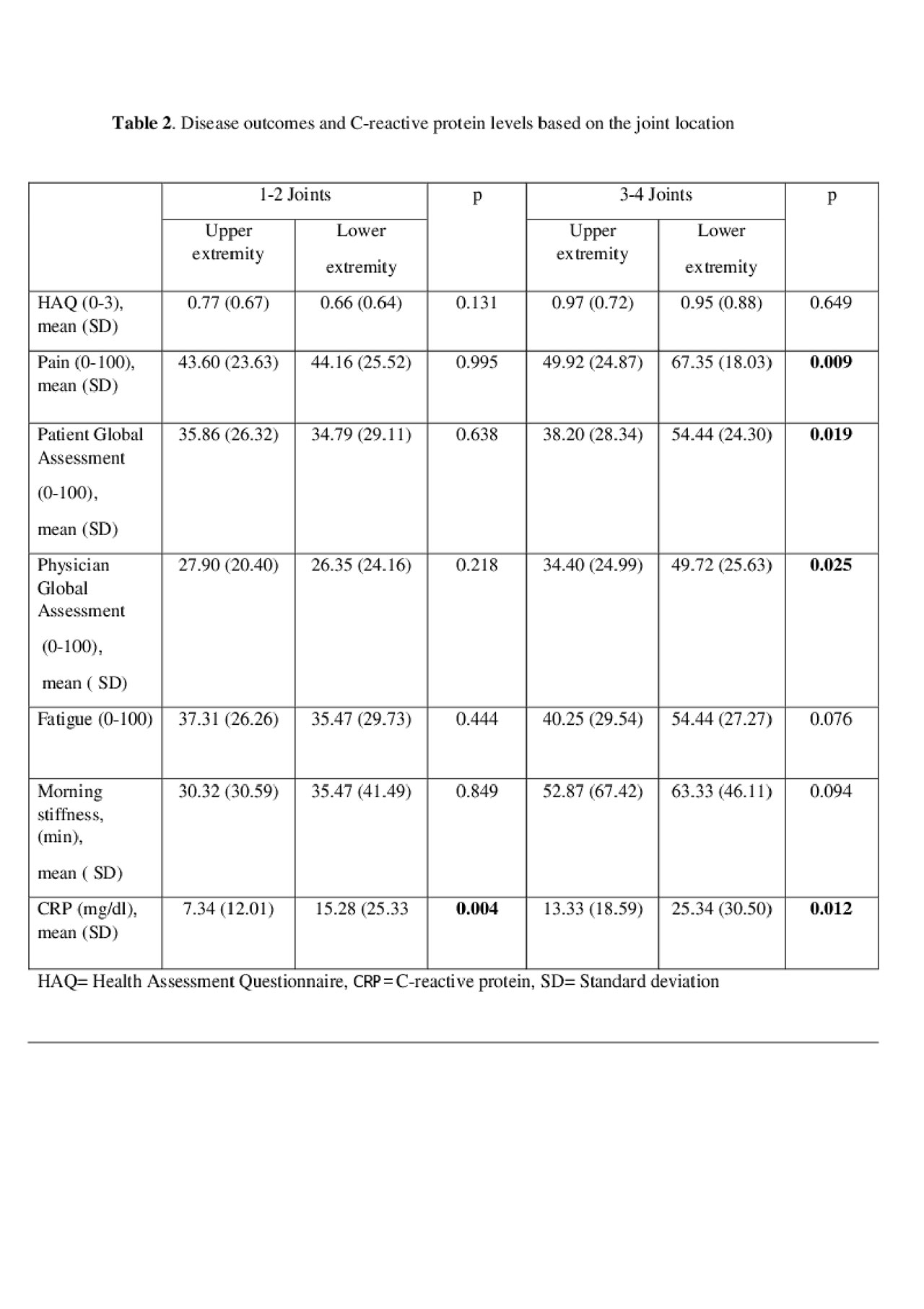
Results: The mean age (SD) was 46.9 (14.24) with a mean (SD) PsA duration of 3.93 (6.03) years. For joint counts, 194 (50.1%) patients had 1, 108 (27.9%) had 2, 46 (11,9 %) had 3 and 39 (10.1%) patients had 4 joints involved. Within patients with 1-2 involved joints, size of the joints only had an impact on CRP values with large joints having higher CRP (p=0.005) (Table 1), similar to joints of the lower extremity (p= 0.004) (Table 2). None of the PROs were significant based on the size or the location, if 1-2 joints were inflamed. Within patients with 3-4 involved joints, PGA, pain, fatigue and physician global assessment were higher in patients with large joint involvement. Similarly, PGA, pain and physician global assessment was higher in patients with lower extremity involvement as well as higher CRP values.
Conclusion: For PsA patients with 3-4 joints involved, lower extremity and larger joints are associated with poorer outcomes with worse PROs, physician global assessment and higher CRP. The size and anatomical location of the joints are less important for patients with 1-2 joints in terms of the outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ayan G, Solmaz D, Bakirci S, Tinazzi I, Omma A, Küçükşahin O, Ozisler C, Yavuz S, Bayindir O, Kimyon G, Dogru A, Tarhan E, Can M, Kilic L, Duruoz M, Aksu K, Kalyoncu U, Aydin S. Large Joint and Lower Extremity Involvement Has Higher Impact on Disease Outcomes in Oligoarticular PsA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/large-joint-and-lower-extremity-involvement-has-higher-impact-on-disease-outcomes-in-oligoarticular-psa/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/large-joint-and-lower-extremity-involvement-has-higher-impact-on-disease-outcomes-in-oligoarticular-psa/