Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: There is a need for effective and safe treatment during pregnancy in women affected by chronic active inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Adequate disease control is crucial to ensure the best fetal and maternal health, and to reduce the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. Anti-TNFs are an effective therapeutic option, but because most cross the placenta they are often stopped during pregnancy. Certolizumab pegol (CZP), due to its Fc-free molecular structure, is not expected to undergo active placental transfer compared to other antibody-based anti-TNFs. This study aimed to accurately measure the level of placental transfer of CZP from mothers to infants using a highly sensitive CZP-specific assay.
Methods: CRIB (NCT02019602) was a pharmacokinetic (PK) study of pregnant women (≥30 weeks [wks] gestation) receiving commercial CZP (maintenance dose) for an approved indication; the last dose was given within 35 days prior to delivery. Blood samples were collected from mothers, umbilical cords, and infants at delivery, and infants again at Wks 4 and 8 post-delivery. CZP concentration was measured with a highly sensitive, CZP-specific electrochemiluminescence immunoassay validated in plasma (lower limit of quantification [LLOQ]=0.032 μg/mL; >10-fold lower than assays used in prior CZP PK studies).
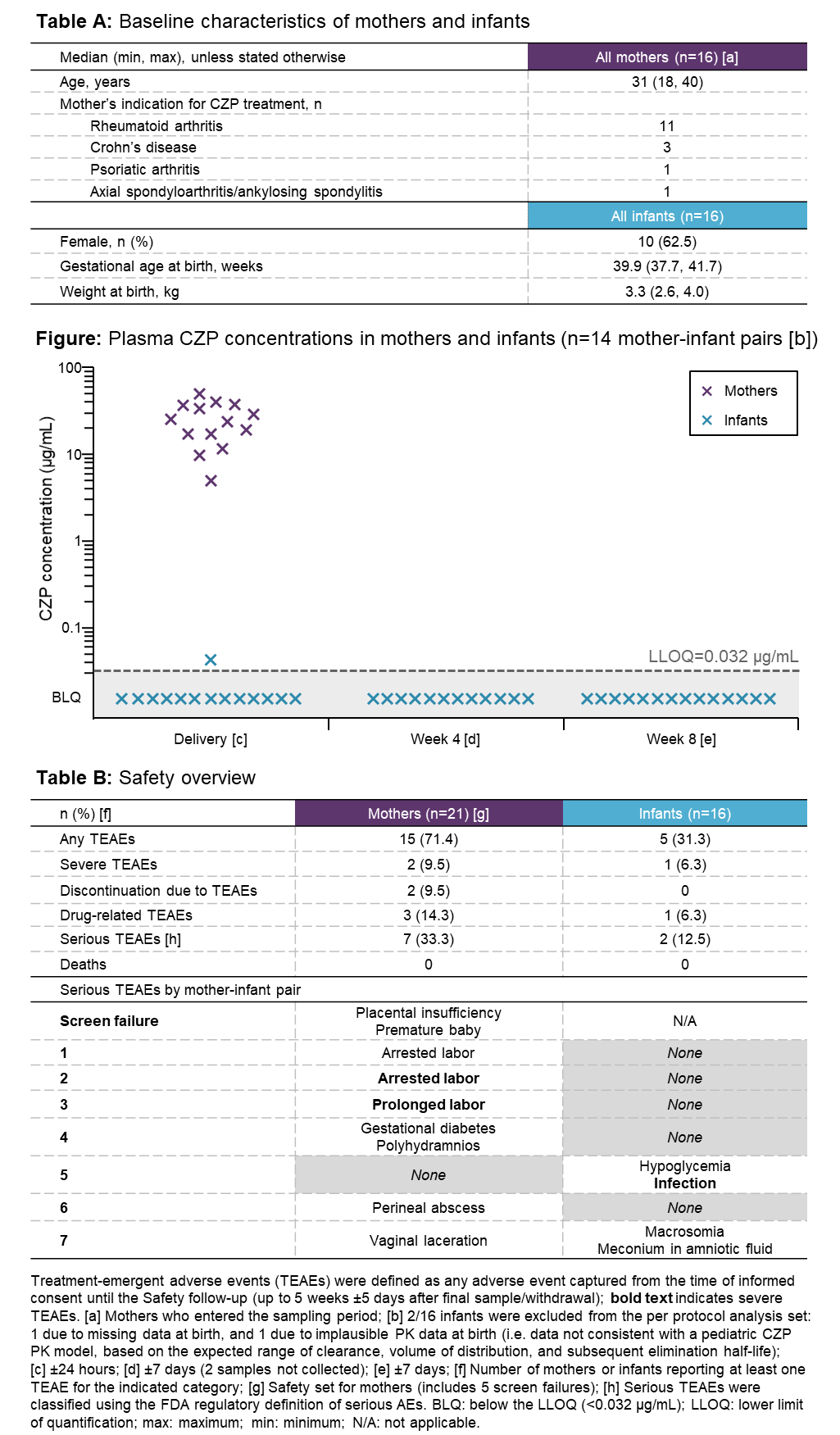
Results: Of 21 CZP-treated pregnant women screened, 16 entered the study (Table A). Maternal CZP plasma levels at delivery were within the expected therapeutic range (median [range]=24.4 [5.0–49.4] μg/mL). Of the 16 infants, 2 were excluded from the per-protocol set: 1 due to missing data at birth, and 1 due to implausible PK data (inconsistent with a pediatric CZP PK model). Of the remaining 14 infants, 13 had no quantifiable CZP level at birth (<0.032 μg/mL) and 1 had a minimal CZP level of 0.042 μg/mL (infant/mother plasma ratio=0.0009); no infants had quantifiable levels at Wks 4 and 8 (Figure). Of the 16 umbilical cord samples, 1 was excluded due to missing data; 3/15 had quantifiable CZP levels (max=0.048 μg/mL). No anti-CZP antibodies were detected in mothers, umbilical cords, or infants. The infants of CZP-exposed mothers had a safety profile consistent with that of unexposed, similar-age infants (Table B).
Conclusion: Using a highly sensitive assay, CZP levels were below LLOQ in 13/14 infant blood samples at birth, and all samples at Wks 4 and 8. This indicates no to minimal placental transfer of CZP from mothers to infants, suggesting lack of in utero fetal exposure during the third trimester. These results support continuation of CZP treatment during pregnancy, if anti-TNF therapy is considered necessary.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chakravarty E, Förger F, Abraham B, Flynn A, Moltó A, Flipo RM, van Tubergen A, Shaughnessy L, Simpson J, Teil M, Helmer E, Wang M, Mariette X. Lack of Placental Transfer of Certolizumab Pegol during Pregnancy: Results from a Prospective, Postmarketing, Multicenter, Pharmacokinetic Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lack-of-placental-transfer-of-certolizumab-pegol-during-pregnancy-results-from-a-prospective-postmarketing-multicenter-pharmacokinetic-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lack-of-placental-transfer-of-certolizumab-pegol-during-pregnancy-results-from-a-prospective-postmarketing-multicenter-pharmacokinetic-study/