Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: B Cell Biology and Targets in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Rituximab is used for the treatment of juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) with variable success. Some of this variability is presumed to be related to the effectiveness of tissue B cell depletion. Forming new B cells requires B cell receptor recombination and the formation of KREC. The KREC does not replicate with B cell divisions. The recombination site on chromosomal DNA is known as the joining code (JC). The ratio of JC: KREC determined by qRT-PCR estimates the number of B cell divisions that have occurred in a B cell population. BAFF is a cytokine produced by activated macrophages and dendritic cell to promote B cell survival and proliferation. We hypothesized that Rituximab treated JDM who have near complete tissue B cell depletion will have a low JC to KRECs ratio and increased soluble BAFF level, which is associated with a more effective response to Rituximab.
Methods:
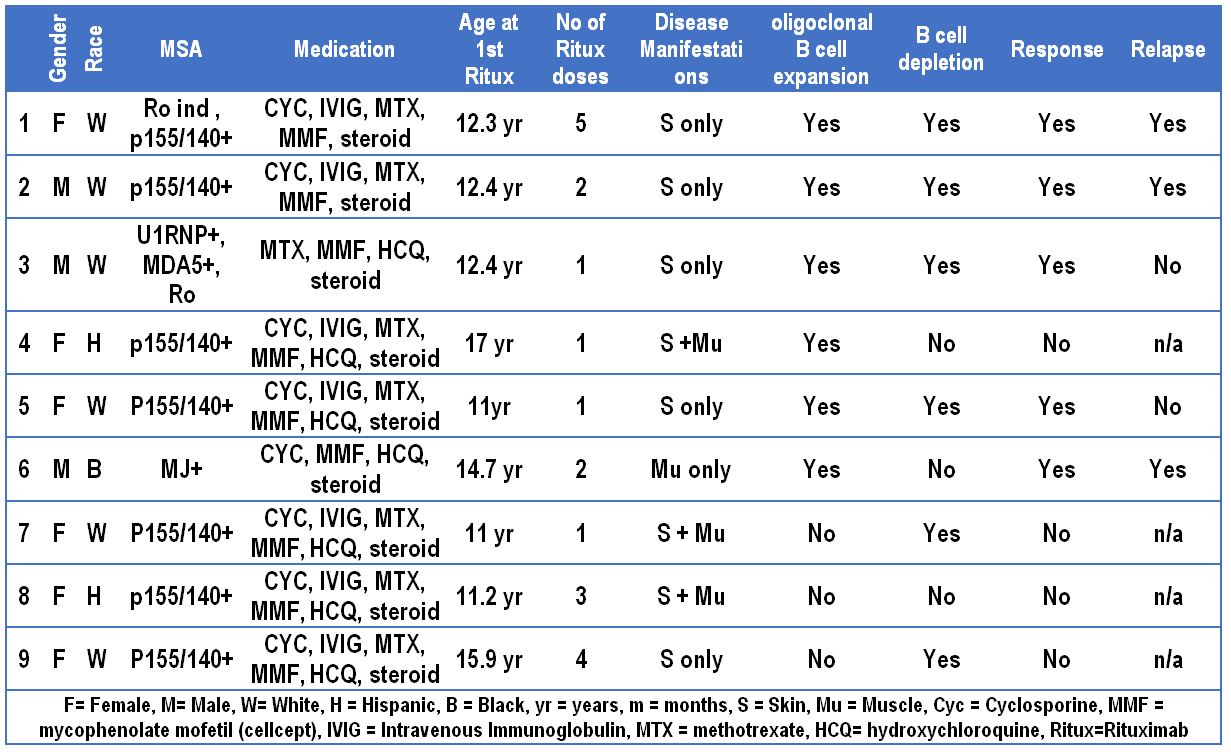
This is an IRB approved, retrospective pilot study conducted at Lurie Children’s Hospital. We included 9 JDM patients (mean age 12.5 ± 2.2 years). Their demographics are presented in Table 1. We measured JC and KREC qRT-PCR from serial PBMC stored (-80oC) in the CureJM Center Repository. BAFF level was measured using Mesoscale® technology. We defined oligoclonal B cell expansion as a JC:KRECs ratio of 8 or more before Rituximab therapy. A JC:KREC ratio of 2.5 or less on the first detectable sample post-Rituximab was considered as an evidence of good B cell depletion. A good response to therapy was defined as improvement of the Disease Activity Score (DAS) by at least 2 points on two consecutive visits. This study is supported by a grant from CARRA.
Results:
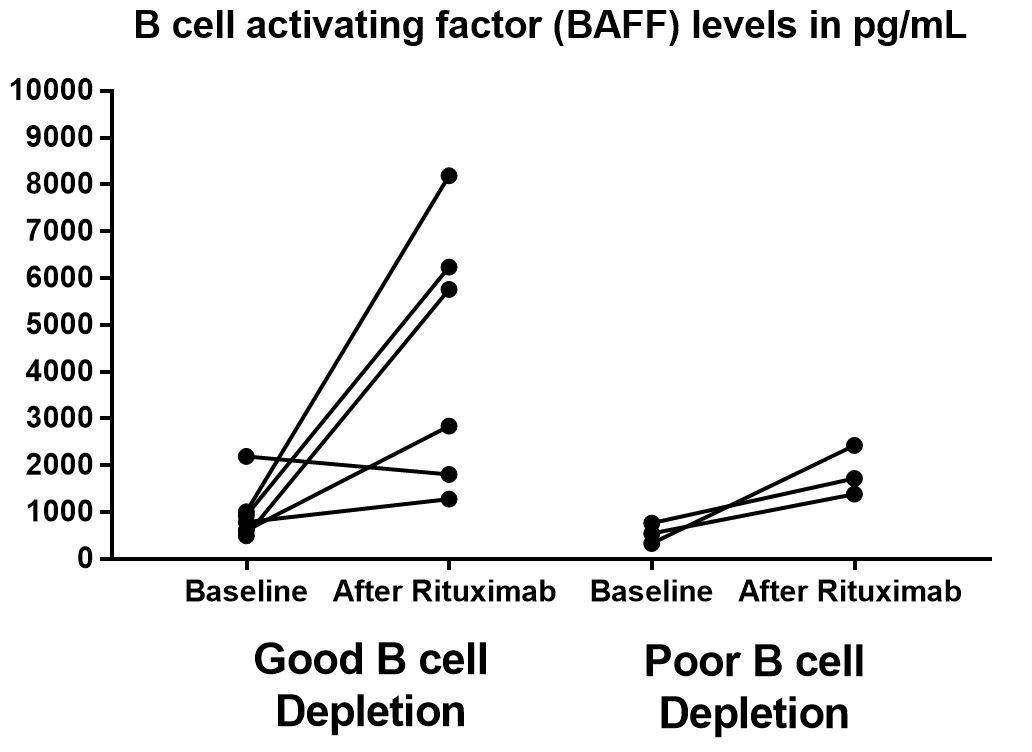
6 out 9 JDM had evidence of oligoclonal B cell expansion prior to Rituximab use. Of those 6 subjects, 4 had good B cell depletion and responded well to Rituximab therapy. On the other hand, 1 out of 2 subjects with poor B cells depletion had a lack of response to Rituximab. All JDM without oligoclonal B cell expansion had a poor response to Rituximab therapy (Table 1). Although serum BAFF level increased in almost all subjects after Rituximab therapy, subjects with poor B cell depletion appeared to have only a minor increase (Fig 1).
Conclusion:
Children with JDM who demonstrate oligoclonal B cell expansion prior to the use of Rituximab have a more favorable outcome. If this finding is confirmed, KREC PCR may serve as a selection criterion for Rituximab therapy. BAFF levels increase after Rituximab therapy, which may contribute to disease flare and may provide a therapeutic target. Limitations of this pilot study include the low numbers of subjects, which requires validation in additional cohorts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
khojah A, Hans V, Marin W, Morgan GA, Pachman LM. Kappa-Deleting Recombination Excision Circles (KREC) in B Cells and Serum B Cell Activating Factor (BAFF): Possible Aids in Predicting Juvenile Dermatomyositis Response to Rituximab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kappa-deleting-recombination-excision-circles-krec-in-b-cells-and-serum-b-cell-activating-factor-baff-possible-aids-in-predicting-juvenile-dermatomyositis-response-to-rituximab/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kappa-deleting-recombination-excision-circles-krec-in-b-cells-and-serum-b-cell-activating-factor-baff-possible-aids-in-predicting-juvenile-dermatomyositis-response-to-rituximab/