Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster III: Biosimilars and New Compounds
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: CT-P10 is a biosimilar of the reference rituximab (RTX) and has been approved by several regulatory agencies including EMA. Pharmacokinetic and therapeutic equivalence from phase III study (NCT02149121) in rheumatoid arthritis has been reported previously1,2. The objective of this report is to evaluate radiographic joint damage progression and its association with disease activity states in terms of disease activity score by 28 joint counts (DAS28) based on C reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), clinical disease activity index (CDAI) and simplified disease activity index (SDAI) for 48 weeks.
Methods: Patients with RA were randomized to CT-P10 or RTX (US or EU sourced rituximab) groups and received 2 courses of either CT-P10 or RTX at weeks 0 and 24. Radiographic progression was evaluated using the van der Heijde modified Sharp Scoring system (SvdH). The smallest detectable difference (SDD) was calculated to define radiographic non-progressor (defined as change in SvdH lesser than or equal to SDD at Week 48)3. The proportions of patients achieving remission or low disease activity (LDA) and, moderate disease activity (MDA) or high disease activity (HDA) in terms of DAS28, CDAI, and SDAI were compared at weeks 24 and 48.
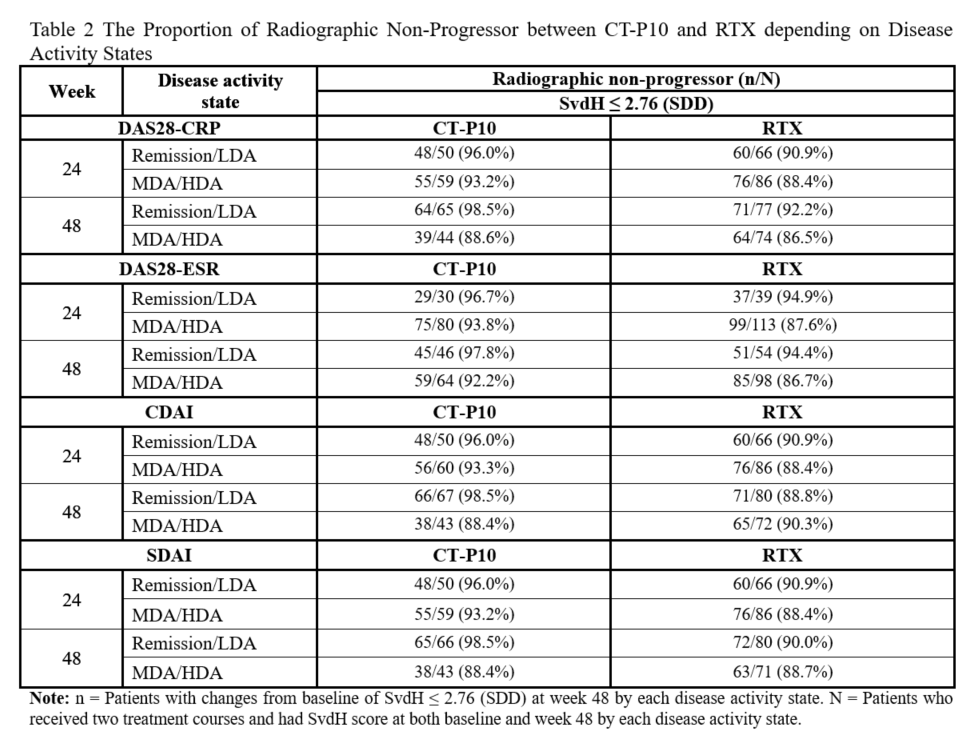
Results: The mean (standard deviation) increase from baseline in SvdH score was similar between CT-P10 and RTX (1.85 [9.03] vs 1.24 [2.98]) at Week 48. Comparable proportion of radiographic non-progression was observed between CT-P10 and RTX; 94.5% vs. 89.5% based on calculated SDD (SvdH equal to 2.76). The proportion of patients with remission or LDA and, MDA or HDA was generally comparable between CT-P10 and RTX at weeks 24 and 48 for various disease activity indices (DAS28-CRP, DAS28-ESR, CDAI, SDAI) (Table 1). The proportion of radiographic non-progressors was comparable between two groups within each disease activity state with an increasing trend as disease activity improved (Table 2).
Conclusion: Comparable disease activity and effect of inhibition for joint damage progression were shown between CT-P10 and RTX groups. The evaluation of radiographic progression with disease activity states by DAS28, CDAI and SDAI showed a trend of higher proportion of radiographic non-progressors in Remission or LDA than that of MDA or HDA.
Reference
1. Yoo et al. (2016), Arthritis Rheumatol 68(Suppl 10): 2037-9.
2. Shim et al. (2017), Arthritis Rheumatol 69(Suppl 10): 3447-9.
3. Bruynesteyn et al. (2005), Ann Rheum Dis 64:179-182.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Suh CH, Yoo DH, Park W, Shim SC, Lee SJ, Bae YJ, Han SE, Lee SM. Joint Damage Progression According to Disease Activity States in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with CT-P10 and Reference Rituximab: Up to 48 Weeks Results from Phase III Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/joint-damage-progression-according-to-disease-activity-states-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-ct-p10-and-reference-rituximab-up-to-48-weeks-results-from-phase-iii-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/joint-damage-progression-according-to-disease-activity-states-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-ct-p10-and-reference-rituximab-up-to-48-weeks-results-from-phase-iii-study/