Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) involves inflammation of the joint synovium where synovial cells (FLS) are the target for T cell activated cytokines for pannus formation. The T cell secreted cytokines (IL-17A, IL-22 and TNF-α) signal through the JAK family of tyrosine kinases. Activated JAKs recruit and activate STATs, which in turn drive gene transcription. IL-17A, IL-22 and TNF-α play leading roles in PsA but their regulatory role on JAK-STAT signaling for pannus formation remains largely unknown. Here we have addressed (A) whether these key regulatory cytokines induce phosphorylation of STAT3 and thus regulates (i) FLS proliferation and (ii) IL-6, IL-8 and MMP3 production by FLS. (B) Can a JAK-STAT inhibitor (Tofacitinib) inhibit this process and thus brakes pannus formation induced by TNF-α, IL-17 and IL-22.
Methods: Methods: FLS were isolated from synovial tissue biopsies of PsA, RA and OA (n=5, for each). They were cultured in presence or absence of tofacitinib (50nM) with TNF-α (20ng/mL), IL-17A (100ng/mL) or IL-22 (100ng/mL); supernatants were collected on the day 5. ELISAs were performed for IL-6, IL-8 and MMP-3 with ELISA kits (PeproTech). MTT assay was done for proliferation. Immunoblot studies of FLS lysates were done to identify for STAT3/ phospho-STAT3.
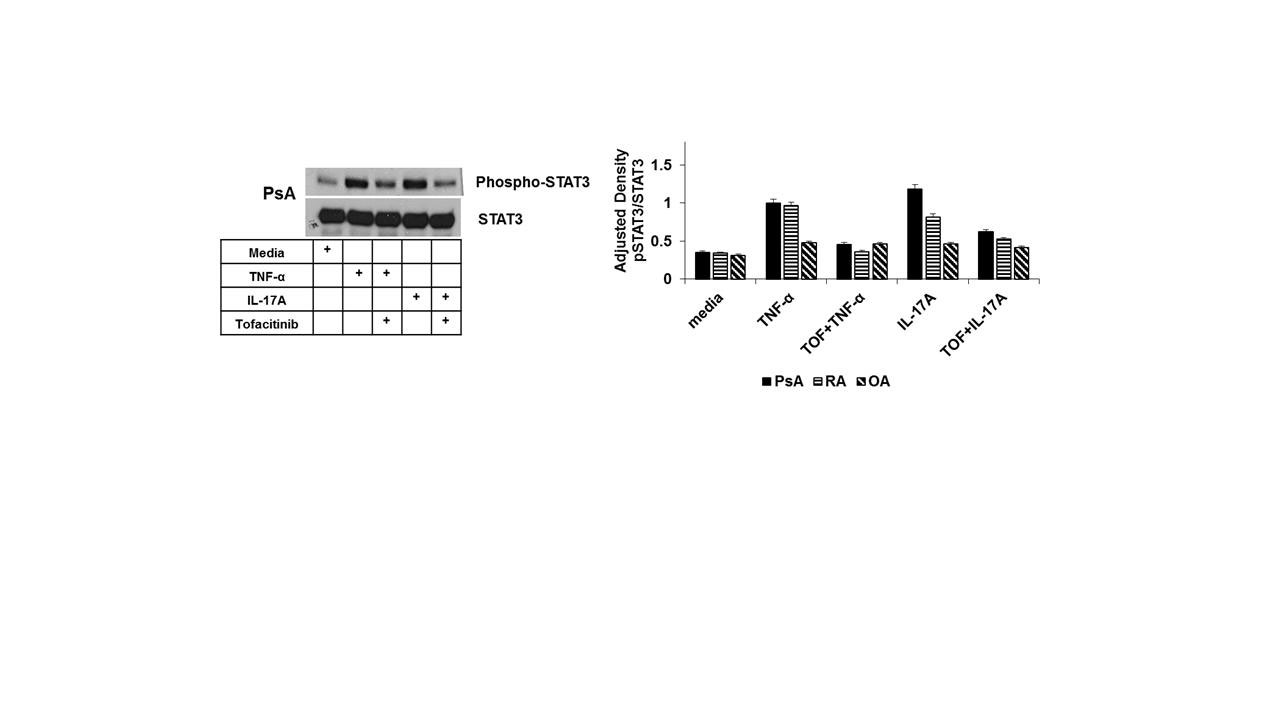
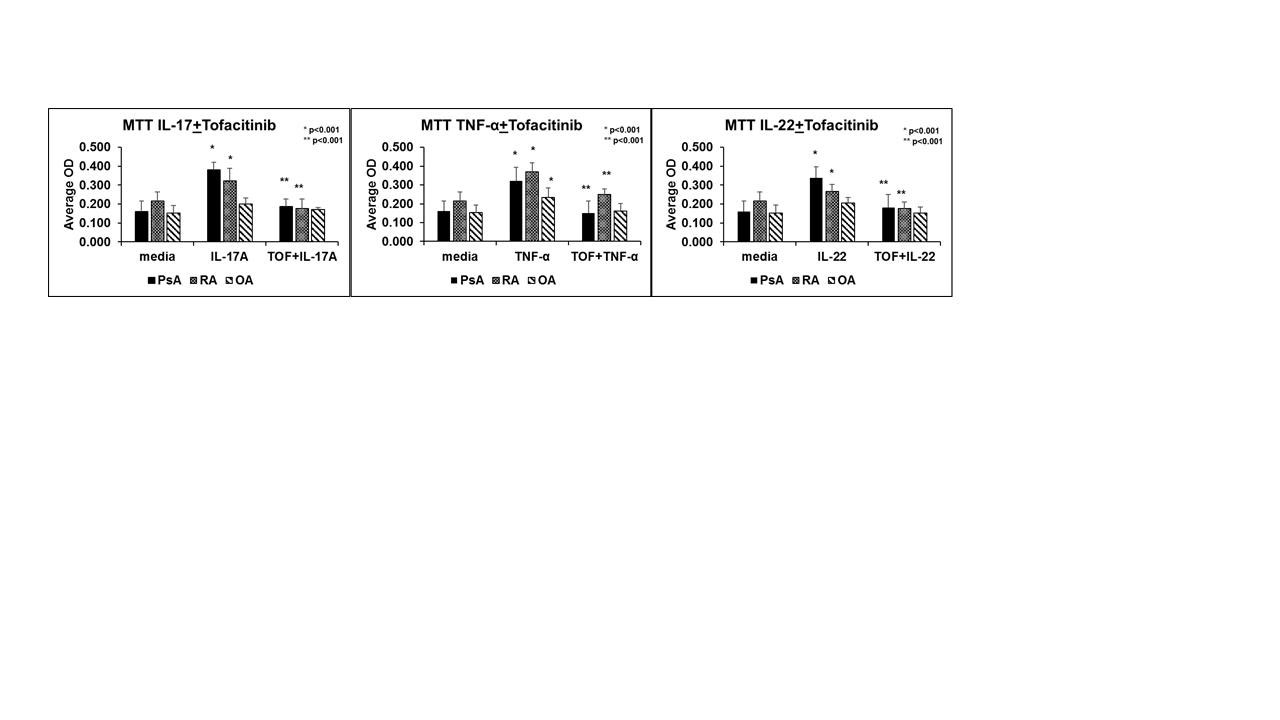
Results: 1. We observed that IL-17/IL-22/TNF-α induced phosphorylation of STAT3 by 2 fold change relative to the untreated PsA FLS. PsA FLS pre-treated with tofacitinib showed decreased levels of phospho-STAT3 compared to the FLS cells not treated with tofacitinib (p< 0.01) (Fig 1). 2. We observed IL-17, TNF-α and IL-22 induced significant proliferation of PsA and RA FLS compared to the media (p< 0.001); and cells that were pre-treated with tofacitinib had significantly lower proliferation (p< 0.001) (Fig 2). 3. PsA and RA FLS stimulated with IL-17A, TNF-α or IL-22 produced significantly more IL-6 IL-8 and MMP-3 compared to media (p< 0.001) and that could be significantly reduced when these FLS were pre-treated with tofacitinib (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: The two critical events of inflammatory/proliferative process for pannus formation are: (i) FLS proliferation; (ii) IL-6, IL-8 and MMP-3 production by FLS. Here we observed: (i) IL-17A, TNF-α and IL-22 the most critical cytokines for the disease process of PsA regulate these biological functions of FLS by activating JAK-STAT kinase system (ii) Further tofacitinib a pan jAK inhibitor effectively blocked these effects. These observations support a critical role for JAK-STAT signaling pathways in PsA and provide mechanisms of actions of tofacitinib for its efficacy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raychaudhuri S, Raychaudhuri S. JAK-STAT Signaling System in Pannus Formation of Psoriatic Arthritis: A Therapeutic Target [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jak-stat-signaling-system-in-pannus-formation-of-psoriatic-arthritis-a-therapeutic-target/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jak-stat-signaling-system-in-pannus-formation-of-psoriatic-arthritis-a-therapeutic-target/