Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Common symptoms of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) include fatigue, spinal pain, stiffness, and sleep problems, which can impair health-related quality of life. Ixekizumab (IXE) treatment shows efficacy in active non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA).1 The objective of this study was to assess fatigue, spinal pain, stiffness, and sleep with IXE treatment versus placebo in patients (pts) with active nr-axSpA up to 16 and 52 weeks.
Methods: In COAST-X, pts with active nr-axSpA were randomized to 52 weeks of double-blind IXE 80 mg once every 4 weeks (Q4W) or every 2 weeks (Q2W), or placebo. Data were collected from baseline to Week 52.
Results: At Week 16, IXE Q4W significantly improved fatigue, spinal pain, and stiffness, and IXE Q2W improved spinal pain, spinal pain at night, and stiffness vs placebo (Table). At Week 52, IXE Q4W significantly improved stiffness, and IXE Q2W improved spinal pain, spinal pain at night, and stiffness vs placebo. Numeric improvements in sleep were not significant vs placebo. Week 1, and up to Week 16, IXE Q4W and Q2W significantly reduced spinal pain and stiffness vs PBO; stiffness was significantly reduced vs placebo up to Week 52 (Figure).
Conclusion: IXE Q4W and/or Q2W significantly improved spinal pain, spinal pain at night, and stiffness vs placebo at 16 and 52 weeks in pts with nr-axSpA. IXE Q4W also improved fatigue at 16 weeks in these pts. Numerical improvements in sleep were not significant vs placebo.
Reference:
1. Deodhar A, et al. Lancet. 2020;395(10217):53-64.
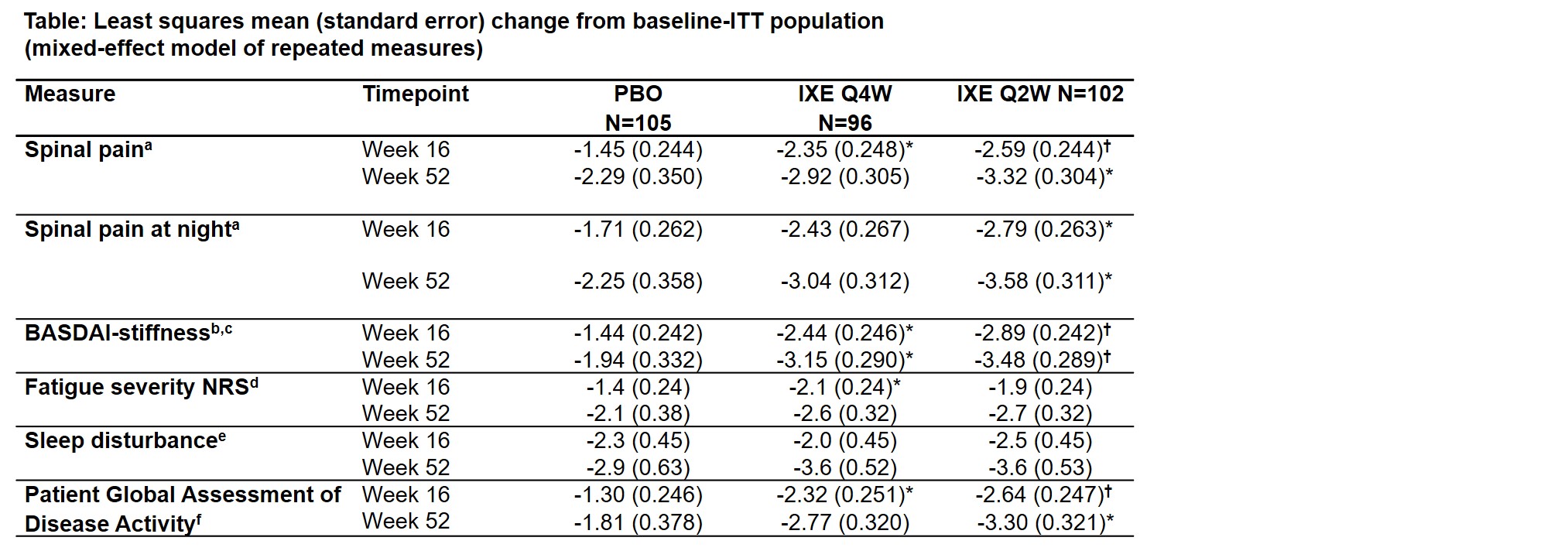 *P < .05 vs PBO; †P≤.001 vs PBO. ITT population: all randomized pts. Pts needing rescue treatment after Week 16 per investigator could switch to open-label IXE Q2W; observations at visits thereafter not included in analyses. Baseline values similar across treatments. Numerical improvements in BASDAI-fatigue not significant vs PBO. ᵃScored 0 (no pain) to 10 (most severe pain) on NRS ᵇMean score BASDAI questions 5 (intensity) and 6 (duration) ᶜScored 1–10 on NRS ᵈScored 0 (no fatigue) to 10 (as bad as you can imagine) ᵉJenkins Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire scored 0 to 20: each of 4 items scored 0 (0 days) to 5 (22–30 days) ᶠScored 0 (not active) to 10 (very active) on NRS BASDAI=Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BL=baseline; ITT=intent-to-treat IXE=Ixekizumab; N=number of pts in ITT population; NRS=numeric rating scale; PBO=placebo; pt=patient; Q2W=every 2 weeks; Q4W=every 4 weeks; vs=versus; wk=week.
*P < .05 vs PBO; †P≤.001 vs PBO. ITT population: all randomized pts. Pts needing rescue treatment after Week 16 per investigator could switch to open-label IXE Q2W; observations at visits thereafter not included in analyses. Baseline values similar across treatments. Numerical improvements in BASDAI-fatigue not significant vs PBO. ᵃScored 0 (no pain) to 10 (most severe pain) on NRS ᵇMean score BASDAI questions 5 (intensity) and 6 (duration) ᶜScored 1–10 on NRS ᵈScored 0 (no fatigue) to 10 (as bad as you can imagine) ᵉJenkins Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire scored 0 to 20: each of 4 items scored 0 (0 days) to 5 (22–30 days) ᶠScored 0 (not active) to 10 (very active) on NRS BASDAI=Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BL=baseline; ITT=intent-to-treat IXE=Ixekizumab; N=number of pts in ITT population; NRS=numeric rating scale; PBO=placebo; pt=patient; Q2W=every 2 weeks; Q4W=every 4 weeks; vs=versus; wk=week.
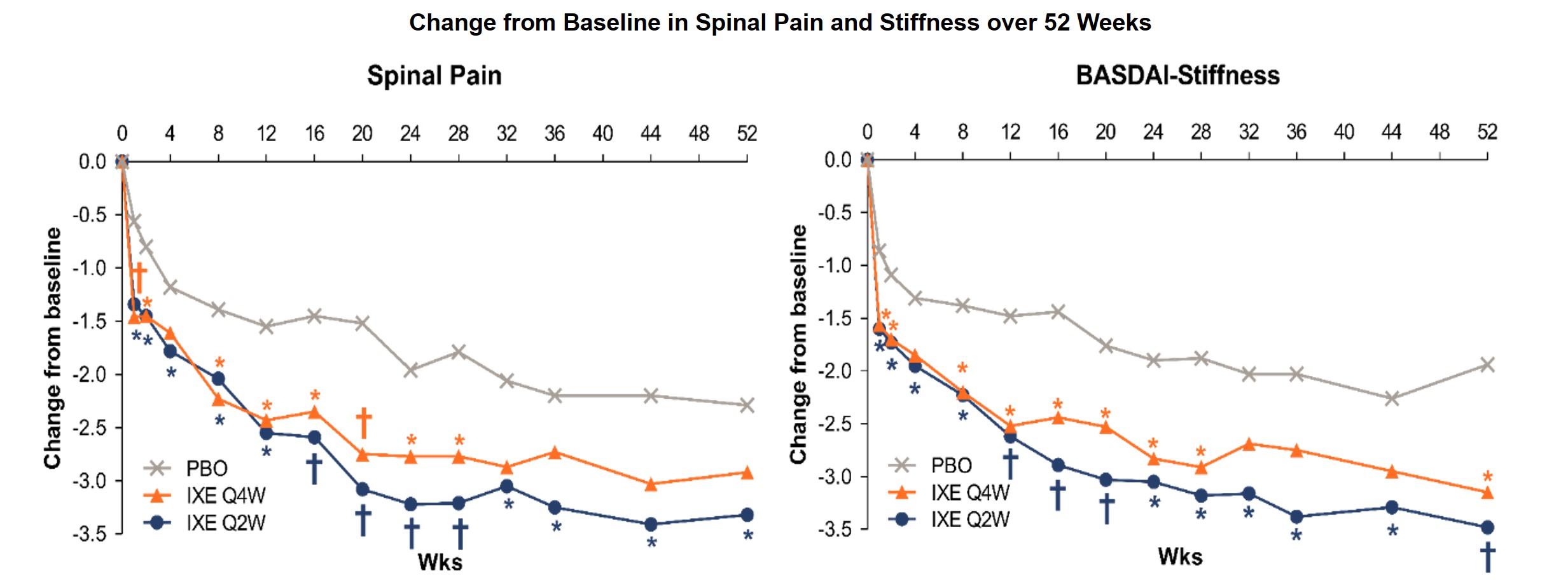 *P < .05 vs PBO; †P≤.001 vs PBO. Significant differences between placebo and IXE Q4W and IXE Q2W are shown by orange and blue symbols, respectively. Changes from BL (Least squares mean) up to Wk 52 were analysed using MMRM analysis in the ITT population, which included all randomized pts. BASDAI=Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BL=baseline; ITT=intent-to-treat IXE=Ixekizumab; MMRM=mixed-effects model of repeated measures; PBO=placebo; pt=patient; Q2W=every 2 weeks; Q4W=every 4 weeks; vs=versus; wk=week
*P < .05 vs PBO; †P≤.001 vs PBO. Significant differences between placebo and IXE Q4W and IXE Q2W are shown by orange and blue symbols, respectively. Changes from BL (Least squares mean) up to Wk 52 were analysed using MMRM analysis in the ITT population, which included all randomized pts. BASDAI=Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BL=baseline; ITT=intent-to-treat IXE=Ixekizumab; MMRM=mixed-effects model of repeated measures; PBO=placebo; pt=patient; Q2W=every 2 weeks; Q4W=every 4 weeks; vs=versus; wk=week
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Deodhar A, Rahman P, Marzo-Ortega H, Strand V, Hunter T, Adams D, Sandoval D, Kronbergs A, Zhu B, Leung A, Liu-Leage S, Navarro-Compán V. Ixekizumab Treatment Improves Fatigue, Spinal Pain, Stiffness, and Sleep in Patients with Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-treatment-improves-fatigue-spinal-pain-stiffness-and-sleep-in-patients-with-nonradiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-treatment-improves-fatigue-spinal-pain-stiffness-and-sleep-in-patients-with-nonradiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/
