Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE) is a high affinity monoclonal antibody that selectively targets interleukin-17A. Up to 24 weeks, IXE was superior to placebo (PBO) in improving health related quality of life of patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and previous inadequate response to TNF inhibitors (TNFi) in a phase 3 trial (SPIRIT-P2; NCT02349295).1 Herein, we report the Week 52 interim patient-reported outcome (PROs) findings of IXE treatment during the Extension Period (EP) of SPIRIT-P2.
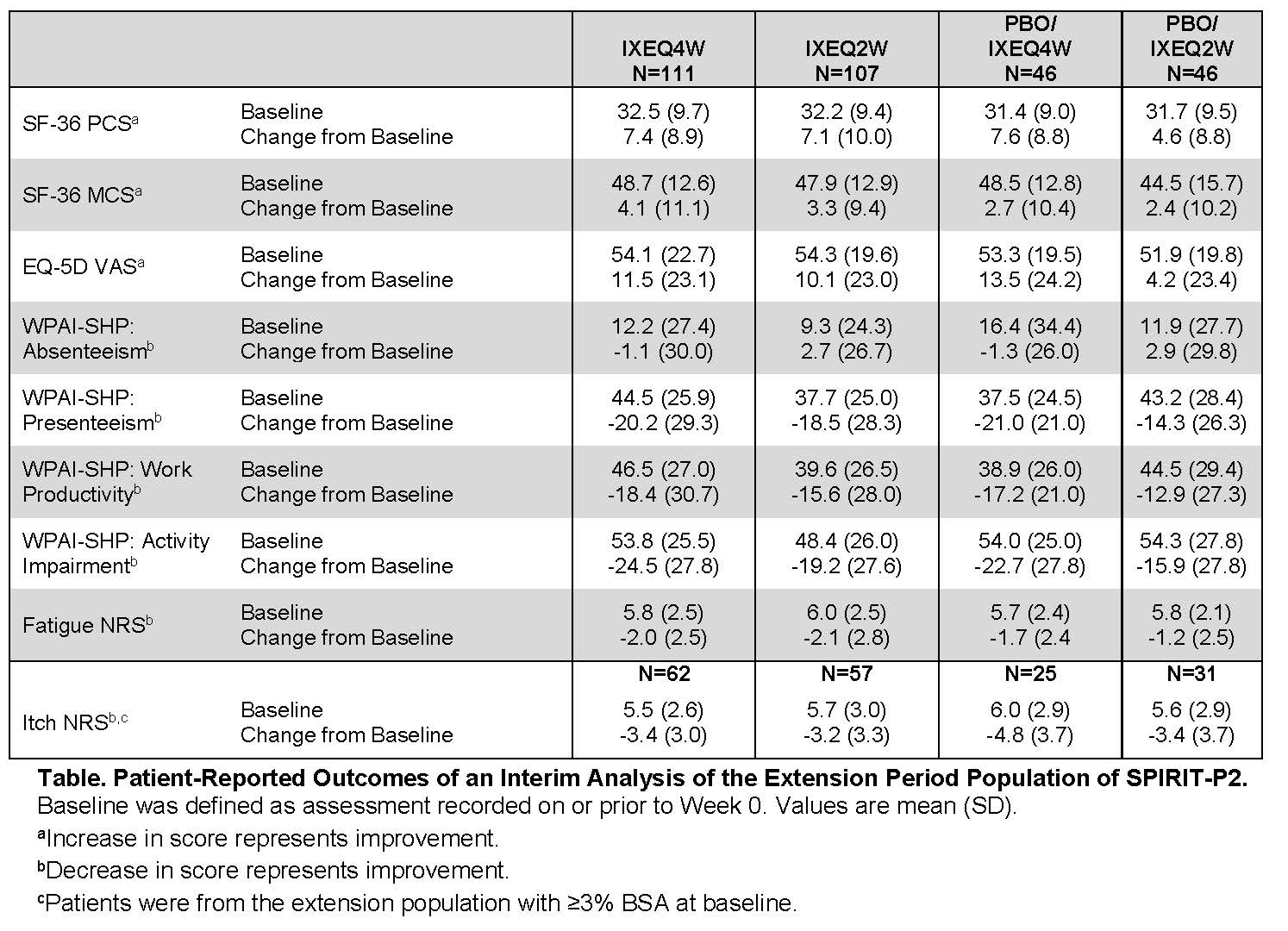
Methods: All 363 patients entering SPIRIT-P2 had an inadequate response to or were intolerant to TNFi. During the Double-Blind Treatment Period (DBTP; Weeks 0-24), patients were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to subcutaneous administration of either 80 mg IXE every 4 weeks (Q4W; N=122) or 2 weeks (Q2W; N=123) following a 160 mg starting dose at Week 0 or PBO (N=118). Of these, 310 patients completed the DBTP and entered the EP (Weeks 24-156). Patients randomized to IXE at Week 0 continued the same dose regimen in the EP. PBO patients were re-randomized (1:1) to IXE Q4W or Q2W at Week 16 (inadequate responders) or Week 24 and received a 160 mg starting dose. At baseline and Week 52, the following PROs were assessed: Short Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36) Physical Component Summary (PCS) and Mental Component Summary (MCS), European Quality of Life 5 Dimensions Visual Analog Scale (EQ-5D VAS; 0-100 scale), Work Productivity and Activity Impairment-Specific Health Problem (WPAI-SHP; absenteeism, presenteeism, work productivity, and activity impairment), fatigue Numeric Rating Scale (NRS; 0 [no fatigue]-10 [as bad as you can imagine] scale), and the itch NRS (0 [no itch]-10 [worst itch imaginable] scale). The fatigue NRS has not been validated. Itch NRS was assessed in patients with baseline psoriatic lesion involving ≥3% body surface area (BSA; N=175). All analyses were performed on the EP population. Change in PRO measures from baseline at Week 52 were summarized using descriptive statistics. Missing values were imputed by modified baseline observation carried forward.
Results: Mean baseline (Week 0) scores of PROs indicated that the EP population had impaired physical and mental function, quality of life, and work productivity (Table). Patients receiving IXE up to 52 weeks reported improvements in SF-36 (PCS and MCS), EQ-5D VAS, WPAI-SHP (presenteeism, work productivity, and activity impairment), and fatigue NRS (Table). For PsA patients with ≥3% BSA baseline psoriasis, improvements in itch NRS were observed for patients receiving IXE up to 52 weeks.
Conclusion: In patients with active PsA and previous inadequate response to TNF-i, IXE provided sustained improvement up to 52 weeks in all measured PROs, including physical and mental function, quality of life, work productivity, fatigue, and itch (≥3% BSA psoriasis).
1. Kavanaugh et al. EULAR. 2017 June 17; Madrid, Spain; [abstract SAT0446]
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kavanaugh A, Marzo-Ortega H, Vender R, Birt J, Adams D, Benichou O, Lin CY, Nash P. Ixekizumab Improves Patient-Reported Outcomes through 52 Weeks in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis and Previous Inadequate Response to Tumor Necrosis Factor-Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-improves-patient-reported-outcomes-through-52-weeks-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-and-previous-inadequate-response-to-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-improves-patient-reported-outcomes-through-52-weeks-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-and-previous-inadequate-response-to-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors/