Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster II: Psoriatic Arthritis I (1329–1363)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Many patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) experience back pain and stiffness indicative of axial involvement [1]. The prevalence of axial involvement varies between 25-70% [2]. Ixekizumab (IXE), a monoclonal antibody with high affinity for IL17-A, has been studied in Phase 3 trials in patients with PsA (SPIRIT-P1 [Biologic-naïve; NCT01695239] and SPIRIT-P2 [Inadequate response or intolerant to 1 or 2 TNF inhibitors (TNFi); NCT02349295]) [3] [4]. The objective of this analysis was to determine the efficacy of IXE up to 52 weeks (Wks) in reducing axial symptoms and improving quality of life in patients with active PsA presenting with symptoms indicative of axial involvement.
Methods: This post-hoc analysis included data from two subpopulations of patients with PsA (pooled SPIRIT-P1 and -P2). Symptoms indicative of axial involvement were defined as Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) Q2 (back pain) ≥4, and an average of Q5 + Q6 (intensity and duration of morning stiffness in the spine) ≥4 at baseline. Patients included in the sensitivity analysis subgroup 1 were, in addition to the above-mentioned criteria, < 45 years of age, while patients included in sensitivity analysis subgroup 2 were aged < 45 but had also elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) ( > 5 mg/l) at baseline. Efficacy of IXE was analysed using BASDAI questions, total BASDAI, mBASDAI (without Q3), and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) change from baseline, as well as BASDAI50 response and Short-Form-36 physical component summary (SF-36 PCS) improvement, at Wks 16, 24 and 52. Treatment comparison was done using logistic regression for BASDAI50, and analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model for other endpoints. Missing data for binary and continuous endpoints were imputed by non-responder imputation and modified baseline carried forward (mBOCF), respectively.
Results: A total of 313 patients (placebo (PBO), N=151; IXE Q4W, N=162) met the overall analysis inclusion criteria. Baseline values for BASDAI and ASDAS related endpoints were balanced across treatment arms (Table). Improvement in axial symptoms were significantly greater in patients treated with IXE compared to PBO at Wks 16 and 24 (Figure). Improvement in quality of life (QoL) measures (SF-36 PCS) were also significantly greater in patients treated with IXE compared to PBO at Wks 16 and 24 (Table). Similar results were observed for patients < 45 years, and in patients < 45 years with CRP > 5 mg/l at baseline (sensitivity analysis, data not shown).
Conclusion: IXE is effective in reducing axial symptoms and improving QoL in patients with active PsA presenting with symptoms indicative of axial involvement.
References
1. Yap KS. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(11)
2. Feld J. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14
3. Orbai A. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020[online]
4. Genovese MC. Rheumatol. 2018;57(11)
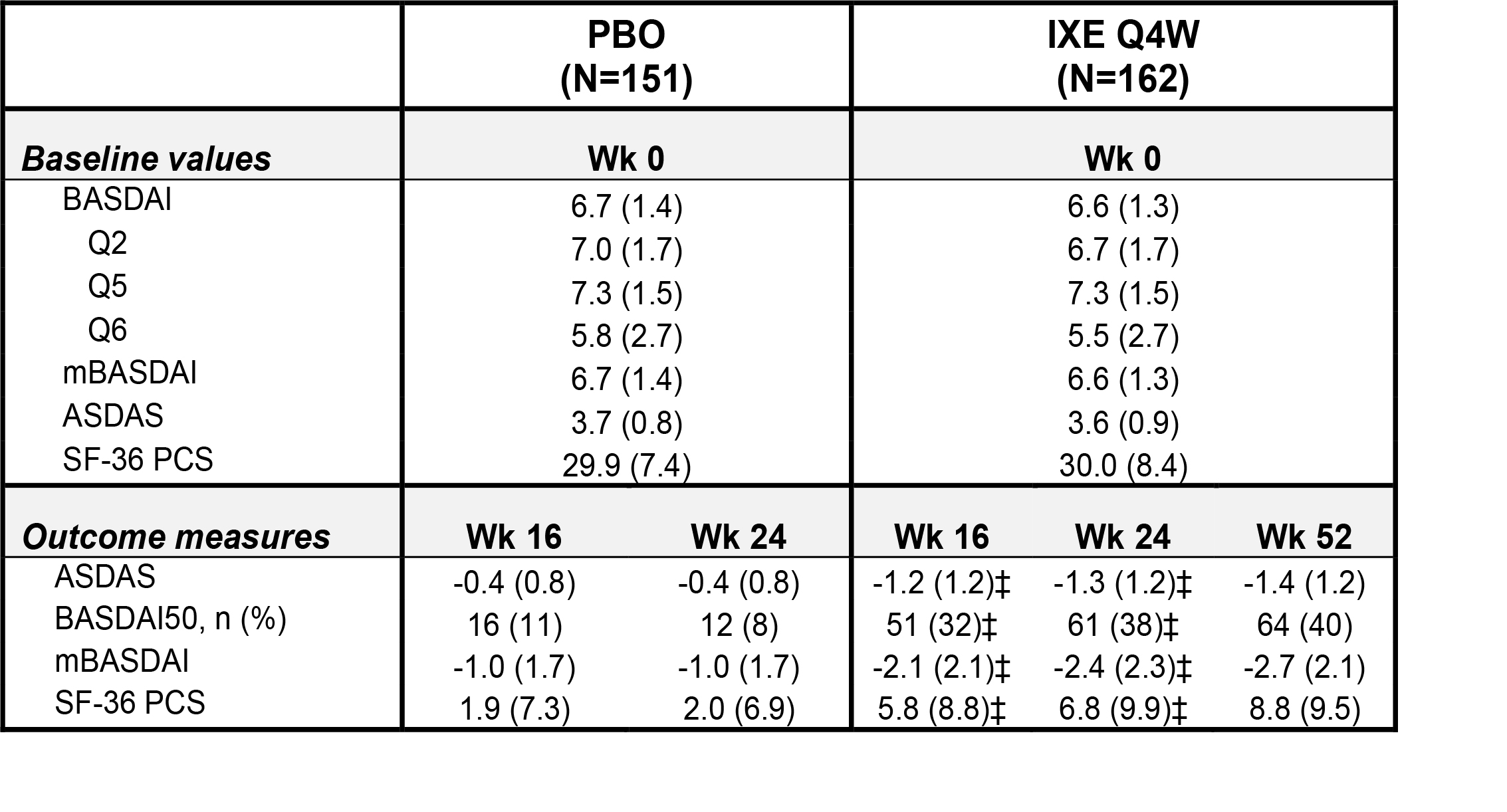 Table. Baseline values and change from baseline (mBOCF) in the overall analysis population at Wks 16, 24 and 52 for BASDAI and ASDAS related endpoints in patients with PsA and axial pain. Data presented as mean (SD) unless otherwise specified. ‡p < 0.001 vs PBO.
Table. Baseline values and change from baseline (mBOCF) in the overall analysis population at Wks 16, 24 and 52 for BASDAI and ASDAS related endpoints in patients with PsA and axial pain. Data presented as mean (SD) unless otherwise specified. ‡p < 0.001 vs PBO.
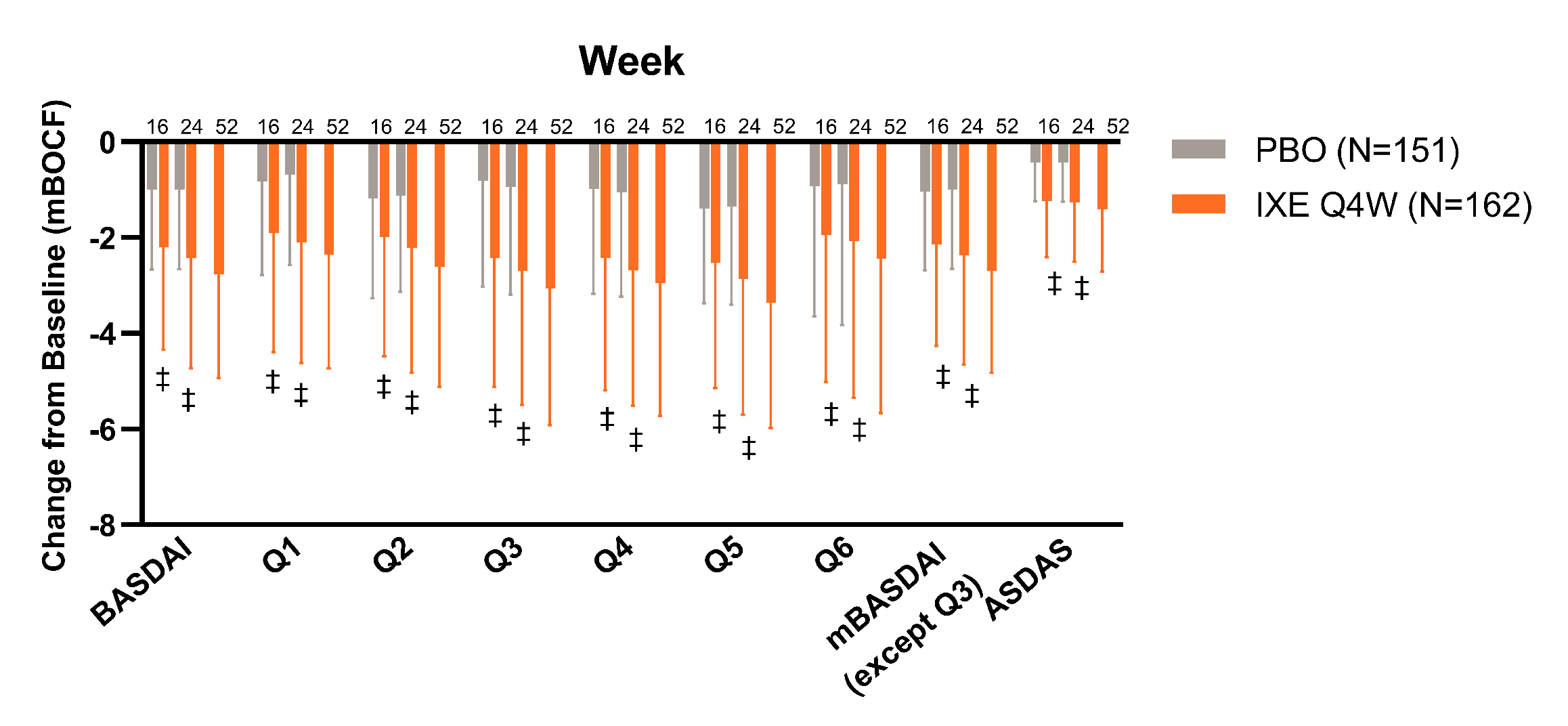 Figure. Change from baseline (mBOCF) in BASDAI and ASDAS related endpoints in patients with PsA and axial pain in the overall analysis population. Data presented as mean (SD). ‡p < 0.001 vs PBO.
Figure. Change from baseline (mBOCF) in BASDAI and ASDAS related endpoints in patients with PsA and axial pain in the overall analysis population. Data presented as mean (SD). ‡p < 0.001 vs PBO.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deodhar A, Gladman D, Bolce R, Sandoval D, Park S, Liu-Leage S, Nash P, Poddubnyy D. Ixekizumab Efficacy in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Presenting with Symptoms Indicative of Axial Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-efficacy-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-presenting-with-symptoms-indicative-of-axial-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-efficacy-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-presenting-with-symptoms-indicative-of-axial-involvement/
