Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In patients (pts) with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and inadequate response or intolerance to conventional synthetic DMARD (csDMARD), use of a biologic DMARD (bDMARD) is often recommended.1 Multiple bDMARD treatments are available, and head-to-head trials comparing their safety and efficacy provide valuable information to physicians in choosing the best bDMARD for each pt. SPIRIT-H2H is the first completed large head-to-head (H2H) superiority study in active PsA.2 The study demonstrated superiority at Week 24 of ixekizumab (IXE), an IL-17A antagonist, over adalimumab (ADA), a TNF inhibitor, on a combined endpoint. Improvement in individual American College of Rheumatology (ACR) components is presented.
Methods: Data from the SPIRIT-H2H (NCT03151551) (Phase 3b/4, 52-week, multicenter study) were evaluated. All pts met Classification for Psoriatic Arthritis criteria and are bDMARD-naïve with inadequate response to csDMARD, active PsA (≥3 tender joints [TJ] and ≥3 swollen joints [SJ]), and plaque psoriasis (PsO; body surface area [BSA] ≥3%). Pts were randomized (1:1, stratified by baseline concomitant csDMARD and moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis) to IXE or ADA on-label PsA or PsO dosing based on the absence/presence of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis (defined: BSA ≥10% + Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] ≥12 + static Physician Global Assessment ≥3). All pts could remain on stable dose of csDMARD. A blinded assessor counted TJ (68) and SJ (66). Other ACR components analyzed included C-reactive protein (CRP) and those completed by the unblinded pt and investigator: HAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), joint pain by visual analog scale (VAS), Physician’s and Pt’s Global Assessments. The primary outcome was the percentage of pts meeting ≥50% or ≥70% improvement in each ACR component at Week 24 and is summarized by treatment groups. Logistic regression analysis was used to detect any treatment group differences at Week 24 on intent-to-treat population. Missing data were imputed using the nonresponder imputation method.
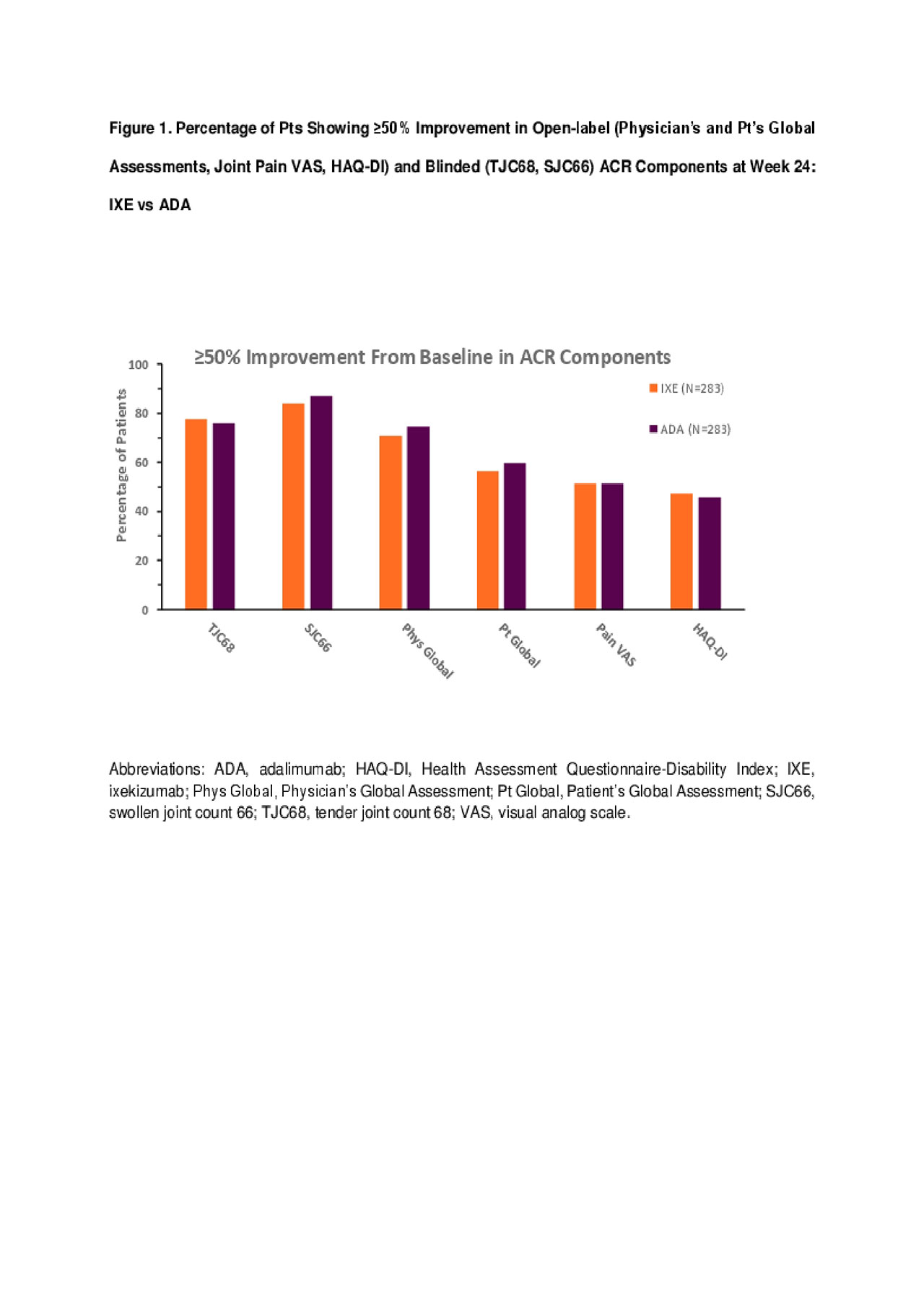
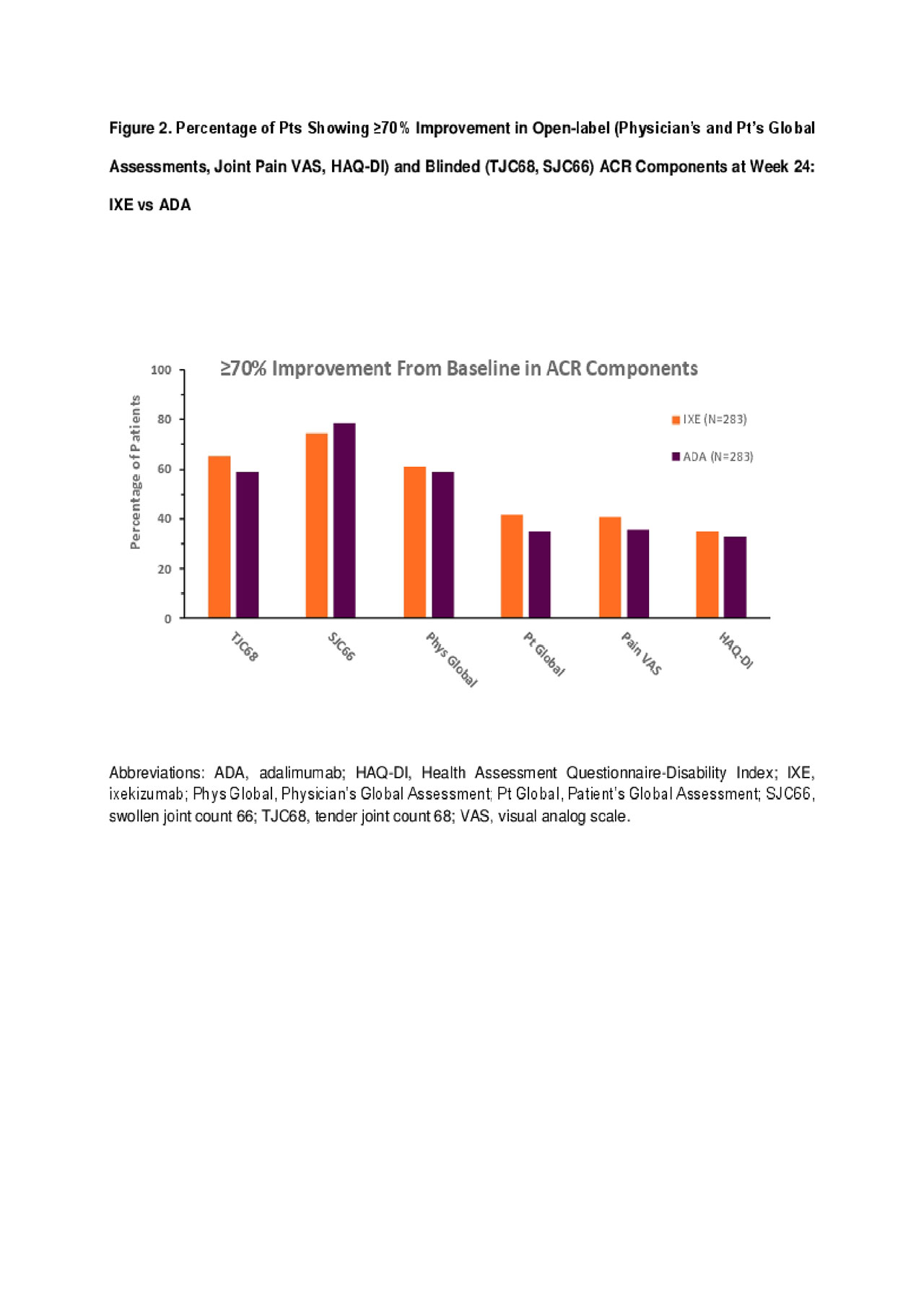
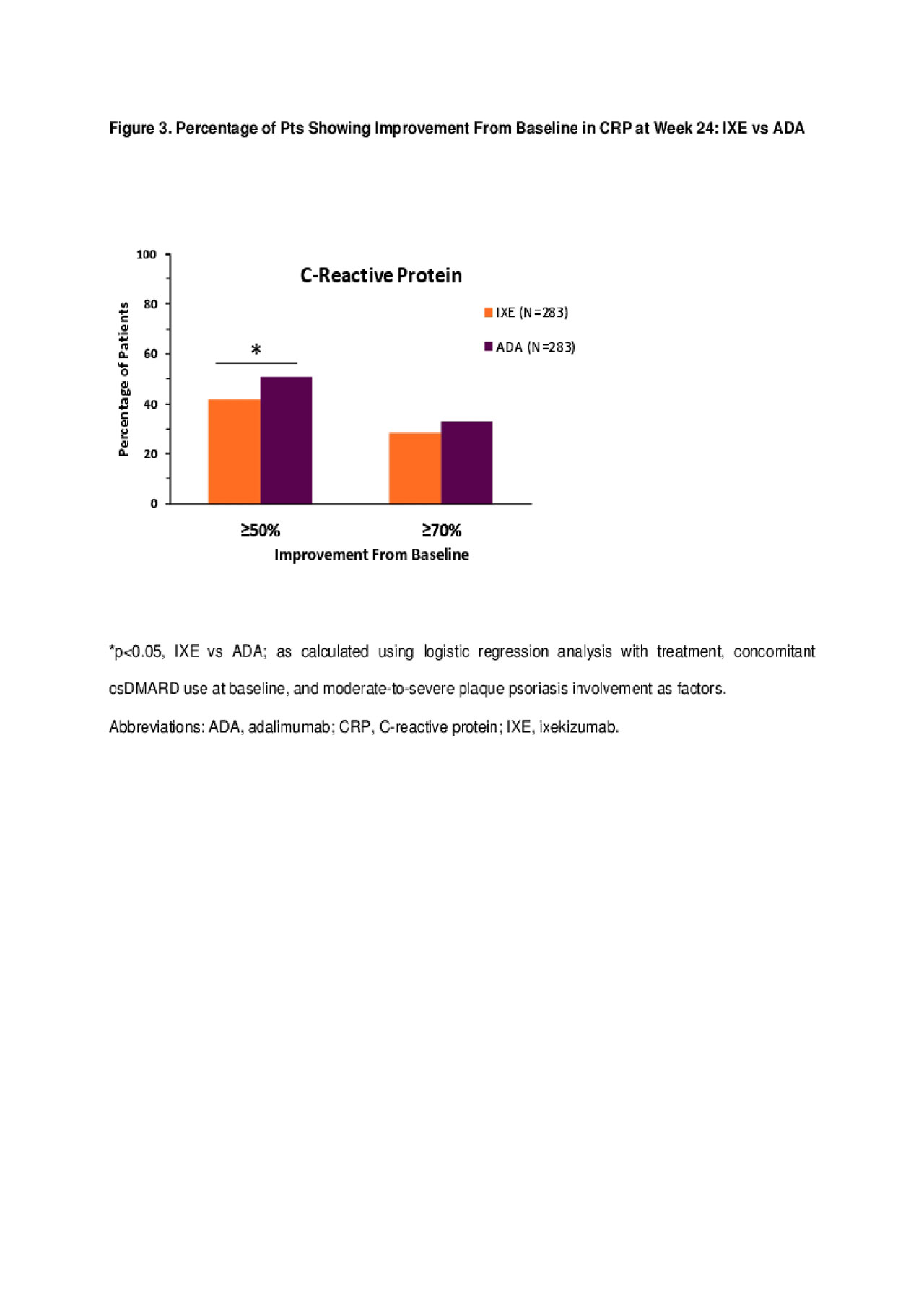
Results: 566 pts were randomized (283 in each arm) with baseline demographics and disease characteristics generally well balanced between groups. IXE and ADA provided comparable efficacy as measured by the percentage of pts achieving ≥50% improvement from baseline at Week 24 for ACR components (Figure 1) other than CRP, where significantly more pts treated with ADA had ≥50% improvement compared with IXE (p< .05). No significant differences in the percentage of pts achieving ≥70% improvement from baseline in all ACR components, including CRP, were observed between IXE and ADA groups (Figures 2-3), for both open-label and blinded outcome measures.
Conclusion: In biologic-naïve PsA pts, IXE has comparable efficacy to ADA at Week 24 as determined by the percentage of pts achieving ≥50% or ≥70% improvement in clinical components and in pt-reported outcomes of ACR.
- Singh JA, et al. Arth Rheum 2019; 71:5-32
- Available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT03151551?term=spirit-h2h&rank=1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Husni M, Gowin K, Gellett A, Trevelin Sprabery A, Helt C, Geneus V, Rossini M. Ixekizumab Demonstrates Improvement Comparable to Adalimumab Across ACR Components in Biologic-Naïve Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-demonstrates-improvement-comparable-to-adalimumab-across-acr-components-in-biologic-naive-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-demonstrates-improvement-comparable-to-adalimumab-across-acr-components-in-biologic-naive-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/