Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Diagnosis and accurate measurement of disease activity in adult-onset Still¡¯s disease (AOSD) are still challenging due to its heterogeneous clinical manifestations and the lack of serological markers. A few serological markers, such as ferritin, C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin (IL)-18 have been suggested but their clinical role is limited. IL-37 is a novel anti-inflammatory cytokine belonging to IL-1 cytokine family. However, there has been no study on the role of IL-37 in AOSD patients.
Objectives: We aimed to investigate the role of IL-37 as a disease activity marker of patients with AOSD.
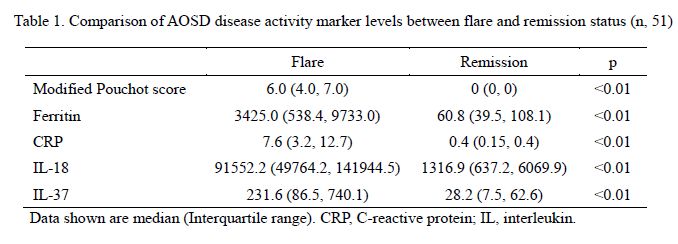
Methods: A total of 51 patients meeting the Yamaguchi criteria were recruited at a single university hospital. Patients¡¯ clinical data and additional laboratory study including serum IL-18 and IL-37 were acquired both at the definite disease flare status (defined as modified Pouchot score 4 or more) and at the definite disease remission status (with modified Pouchot score 2 or less without significant clinical symptoms for more than a month). AOSD disease activity markers were compared between flare and remission status by Wilcoxon signed rank test and their correlation were evaluated by Spearman¡¯s correlation test.
Results: The mean age of study population was 48.8 ¡¾ 2.0. The mean interval between flare and remission was 7.2 ¡¾ 0.6 months. There were significantly higher levels of modified Pouchot score, serum ferritin, CRP, IL-18 and IL-37 level in flare status compared to remission (p<0.01) supporting their roles as disease activity markers. IL-37 level positively correlated with other AOSD disease activity markers including modified Pouchot score, CRP, and ferritin at flare status. The sensitivity and specificity of IL-37 for the disease flare status were 80 % and 82 %, respectively, at a cut-off value of 82.1 pg/mL. The AUC for IL-37 was 0.85 (95% confidence interval of 0.78-0.93). IL-18 level showed highest correlation with ferritin level at flare status (Spearman¡¯s Rho = 0.632, p<0.01). In contrast, IL-37 level had highest correlation with CRP level at flare status (Spearman¡¯s Rho = 0.574, p<0.01). And, there was no significant correlation between IL-18 and IL-37 levels (p=0.13). These differences in the presentation of interactive relationship between cytokines and other disease activity markers suggest the different role of IL-37 from that of IL-18 in activated AOSD status.
Conclusion: IL-37 can be used as an efficient disease activity marker in AOSD patients. And, it has a distinctive role as disease activity marker and inflammatory modulator in AOSD patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nam SW, Kang S, Kim H, Ahn GY, Kim MJ, Yoo DH. Interleukin-37 As an Independent Disease Activity Marker of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-37-as-an-independent-disease-activity-marker-of-adult-onset-stills-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-37-as-an-independent-disease-activity-marker-of-adult-onset-stills-disease/