Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Limited information exists about the very early forms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). In particular, differences and responsiveness of patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in very early disease as compared to established PsA have not been investigated to date.
Methods: Cross-sectional and prospective longitudinal evaluation of PROs related to pain (VAS pain score), physical function (HAQ-DI, SF-36 physical), mental function (SF-36 mental), impact of psoriatic skin (DLQI), joint (PsAID) and global disease (VAS global) in two small prospective observational studies on secukinumab 300 mg therapy over 6 months in 20 very early disease patients (1) and 20 established PsA patients (2). Adjusted changes from baseline were estimated using linear mixed models. We performed a cluster analysis of centered and scaled PROs at baseline and 24-weeks of follow-up using Euclidean distances.
Results: While responses in pain and physical activity-related PROs to secukinumab were more pronounced in established PsA than very early disease, effects on PROs related to general health perception, as well as those related to emotional and mental well-being, were modified in a similar way in very early disease and established PsA. The absolute adjusted improvement over baseline for the specific PROs for the 2 groups of patients is presented in figure 1. Cluster analysis based on global disease activity assessment and PROs showed that baseline clusters reflected very early disease and established PsA, while during interleukin-17 inhibition these clusters were abolished and new clusters based on differential responses to physically and mentally-oriented PROs formed (figure 2).
Conclusion: Inhibition of IL-17A leads to comprehensive improvement of PROs in patients with very early musculoskeletal involvement in PsA. Most importantly, treatment restructures original clusters based on the stage of psoriatic disease and leads to the formation of clusters that reflect their post-treatment state in physical and mental-orientated PROs.
References :
1. Kampylafka E et al: Resolution of synovitis and arrest of catabolic and anabolic bone changes in patients with psoriatic arthritis by IL-17A blockade with secukinumab: results from the prospective PSARTROS study. Arthritis research & therapy 2018, 20(1):153.
2. Kampylafka E et al: Disease interception with interleukin-17 inhibition in high-risk psoriasis patients with subclinical joint inflammation-data from the prospective IVEPSA study. Arthritis research & therapy 2019, 21(1):178.
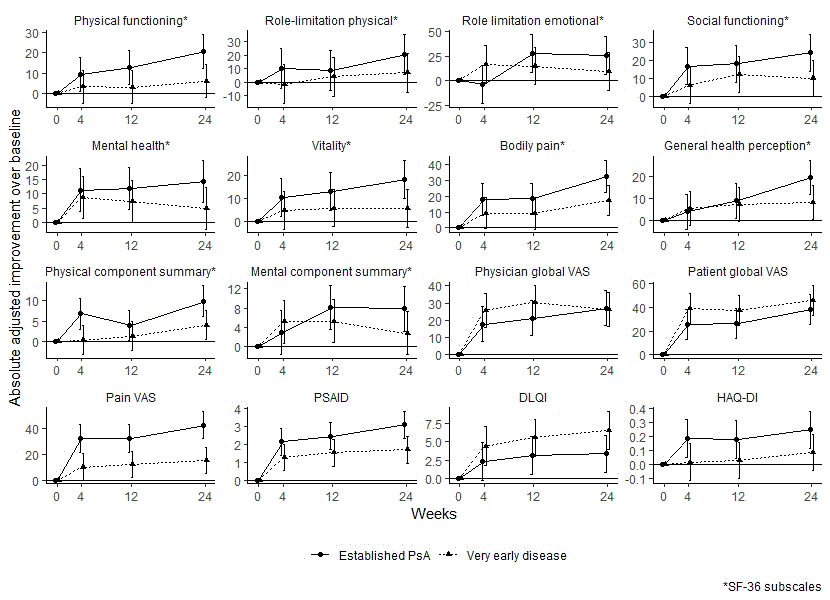 Effects of secukinumab on patient-related outcomes in patients with very early disease and established psoriatic arthritis
Effects of secukinumab on patient-related outcomes in patients with very early disease and established psoriatic arthritis
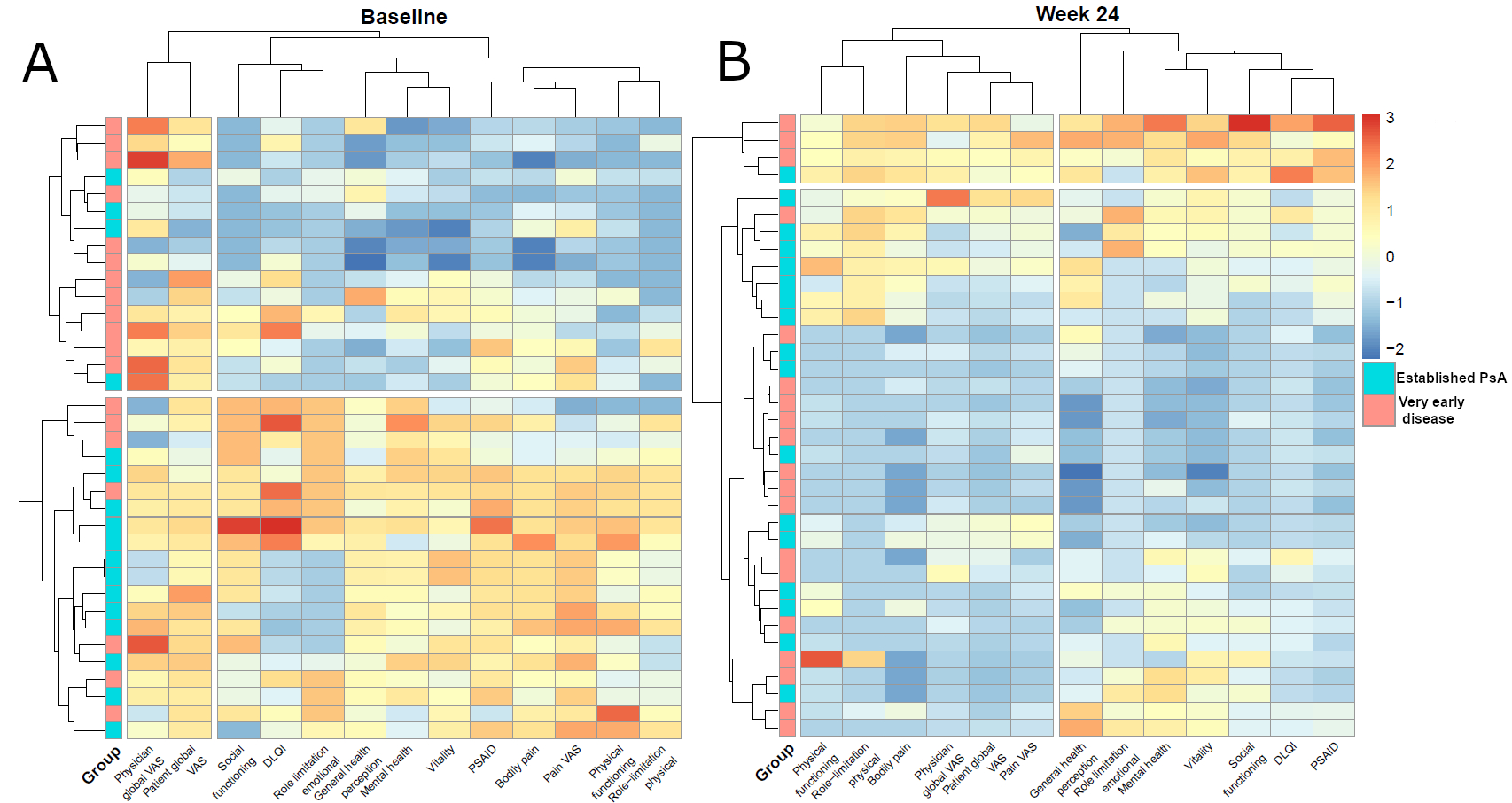 Pre- and post-treatment patient-related outcome based cluster analysis
Pre- and post-treatment patient-related outcome based cluster analysis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kampylafka E, Tascilar K, Lerchen V, Linz C, Sokolova M, Zekovic A, Kleyer A, Simon D, Rech J, Sticherling M, Schett G, Hueber A. Interleukin-17 Blockade Leads to Shifts from Stage-based Towards Response-based Disease Clusters- Comparative Data from Very Early and Established Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-17-blockade-leads-to-shifts-from-stage-based-towards-response-based-disease-clusters-comparative-data-from-very-early-and-established-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-17-blockade-leads-to-shifts-from-stage-based-towards-response-based-disease-clusters-comparative-data-from-very-early-and-established-psoriatic-arthritis/
