Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:30PM-1:45PM
Background/Purpose: Goflikicept (GFC; RPH-104) is a novel fusion protein inhibiting interleukin-1 (IL-1). This study aimed to investigate its efficacy and safety in IL-1β-driven monogenic autoinflammatory disorder of Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF).
Methods: Adult patients with FMF who were resistant or intolerant to colchicine and had ongoing attacks were randomized in the international, multicenter phase 2 double-blinded study to receive GFC subcutaneously in a dose of 160 mg (day 0), 80 mg (day 7), 80 mg (day 14), and 80 mg every 2 weeks (q2w) thereafter or matching injections of placebo for 16 weeks. Marker attack was defined as the combination of Physician Global Assessment (PGA) ≥2 and CRP >10 mg/l. If the marker FMF attack was not resolved or a recurrent attack occurred, the patients were unblinded, and those on placebo switched to GFC. The primary endpoint was a proportion of patients with complete treatment response (marker attack resolution and development of no new attacks).
Results: In total, 28 patients were randomized. Of them, 24 patients completed the study per protocol, 4 patients discontinued treatment prematurely, and 3 of them were in the GFC arm: 1 due to prohibited treatment; 1 due to lack of efficacy; 1 due to an adverse event (AE). The complete response was achieved in 9 (64.3%) patients in the GFC arm and in 1 (7.1%) patient in the placebo arm (p=0.004). No recurrent attack occurred after switching from placebo to GFC in 12 of 13 patients (92%). Minimal or no disease activity (PGA < 2) and CRP decrease ≤10 mg/l were achieved in the majority of patients in the GFC arm but not in the placebo arm (Fig. 1, Fig. 2). At least one AE was reported in 11 (78.6%) patients in the GFC arm, in 3 (21.4%) patients in the placebo arm, and in 8 (61.5%) patients who were switched from placebo to GFC. The majority of AEs were mild to moderate in severity. In one patient (switched from placebo to GFC), there was a serious AE of inflammation during the safety follow-up period. In one of the GFC arm patients, diarrhea led to premature treatment discontinuation. GFC treatment was safe and overall well tolerated. Safety profile of GFC was consistent with other IL-1 inhibitors; no new safety signals were reported.
Conclusion: GFC provided a significant improvement in the disease activity of colchicine-refractory/intolerant FMF patients compared to placebo, and its safety profile was similar to other IL-1 inhibitors.
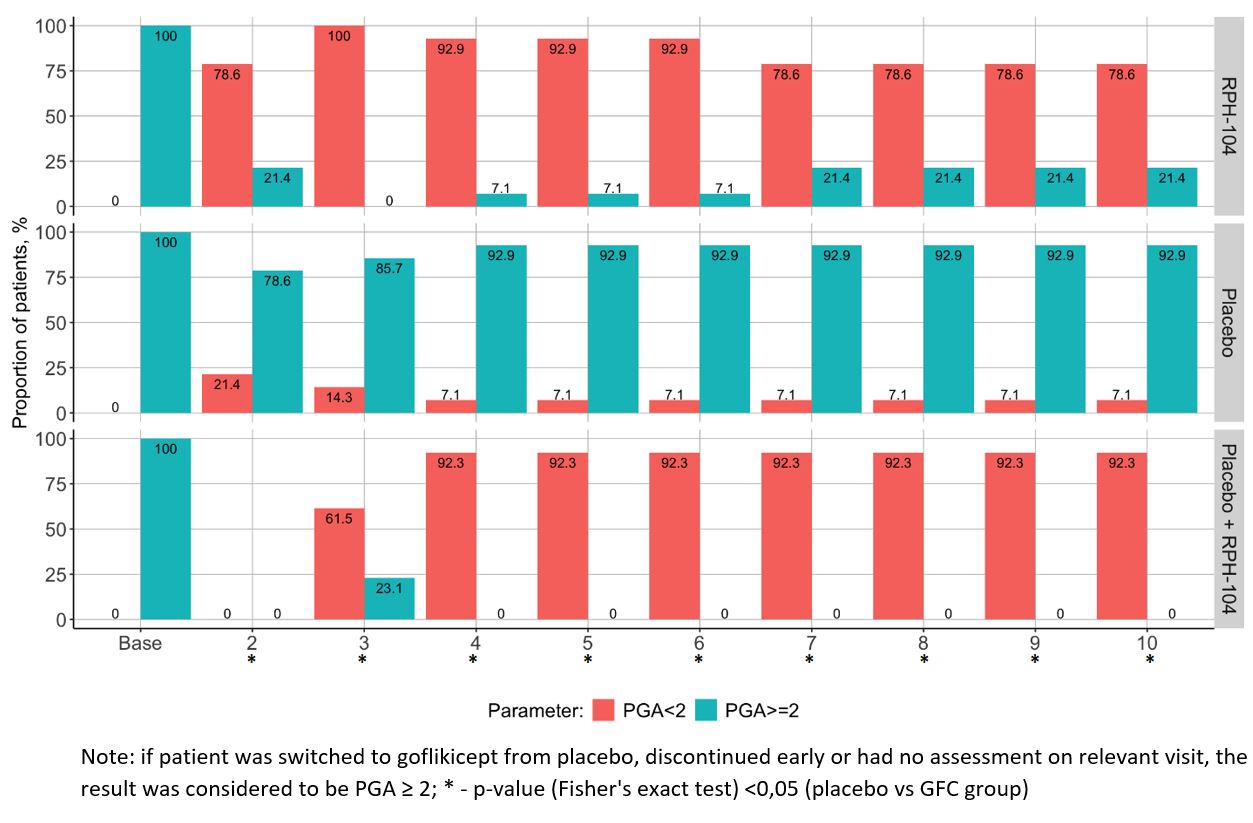 Figure 1. Proportion of subjects with minimal disease activity/ inactive disease (PGA score < 2) during the treatment period
Figure 1. Proportion of subjects with minimal disease activity/ inactive disease (PGA score < 2) during the treatment period
.jpg) Figure 2. Proportion of subjects with CRP ≤ 10 mg/L during the treatment period
Figure 2. Proportion of subjects with CRP ≤ 10 mg/L during the treatment period
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Uhanova O, Ugurlu s, Kostik M, Sarkisyan T, Yeghiazaryan A, Lysenko L, Rameev V, Karadag O, Vardanyan V, Yazisiz V, Sotnikova T, Podsvirov V, Egorova A, Bukhanova D, Grishin S, Tuncel T, Samsonov M, Gul A. Interim Results of a Randomized Placebo Controlled Study of IL-1 Inhibitor Goflikicept in Patients With Familial Mediterranean Fever [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interim-results-of-a-randomized-placebo-controlled-study-of-il-1-inhibitor-goflikicept-in-patients-with-familial-mediterranean-fever/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interim-results-of-a-randomized-placebo-controlled-study-of-il-1-inhibitor-goflikicept-in-patients-with-familial-mediterranean-fever/
