Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) afflicts 12-69% lupus patients. Even with the best available therapies, complete response is achieved in only 10-85% of patients. The risk of nephritis and its poor outcomes is significantly higher in blacks. To gain better understanding of the pathogenesis specific for LN, biopsy samples from LN and other glomerulopathies (controls) were evaluated for differential gene expression levels.
Methods: Patients with LN meeting ACR SLE criteria and controls consented to donate additional samples during a clinically indicated renal biopsy. Forty-one LN and 8 control samples were analyzed after rRNA was depleted from total RNA. Libraries were prepared and sequenced with Illumina HiSeq 2500 and mapped onto the human genome. Differentially expressed genes (DEG) were selected by DESeq2. Signaling Pathway Impact Analysis identified pathways enriched for DEGs that were mapped to the Reactome database. Key transcripts were correlated with clinical and histologic measures. LN samples were scored using the NIH activity (AI) and chronicity indices (CI).
Results: Demographics and glomerular involvement are listed in Table 1.
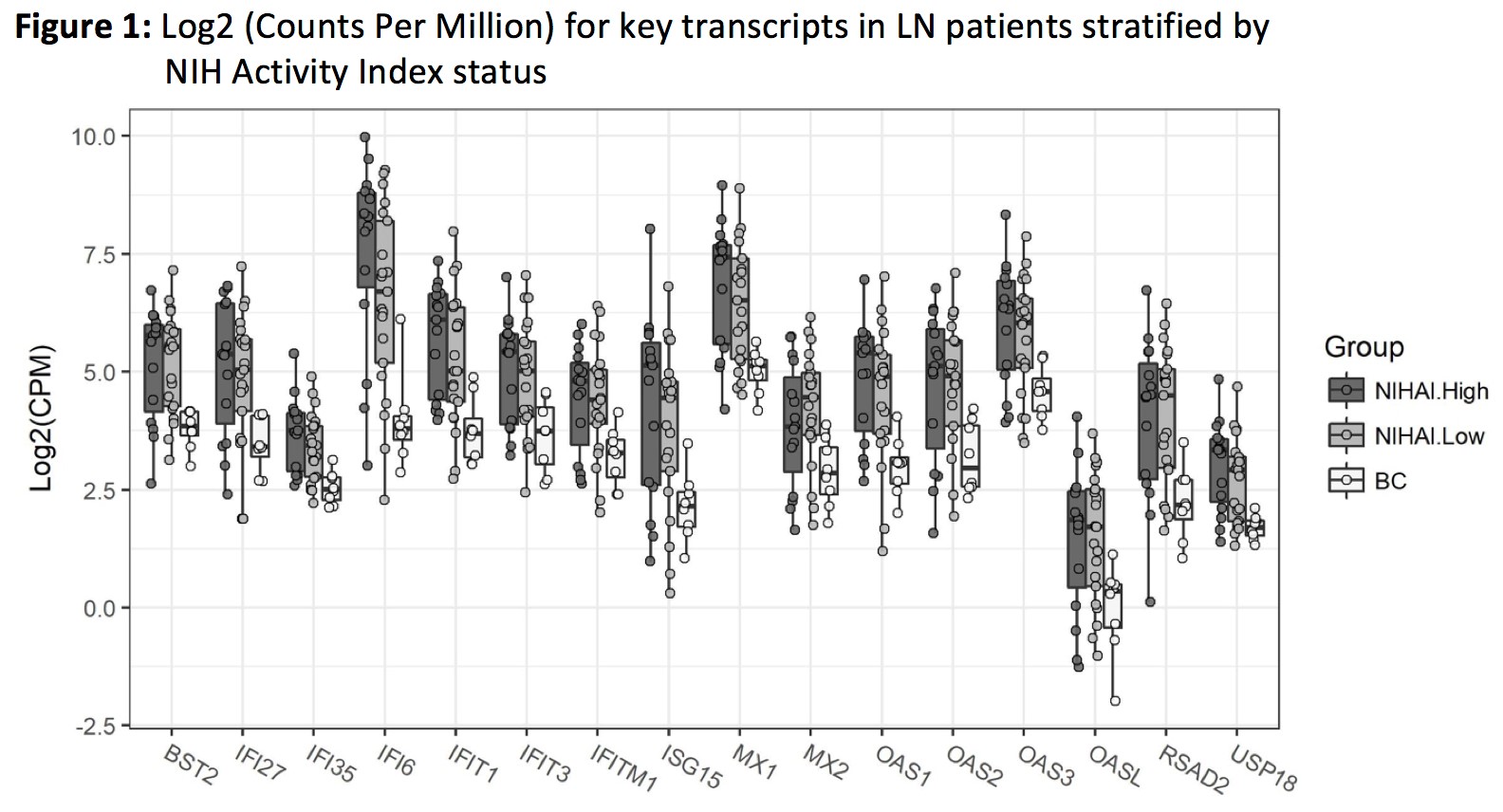
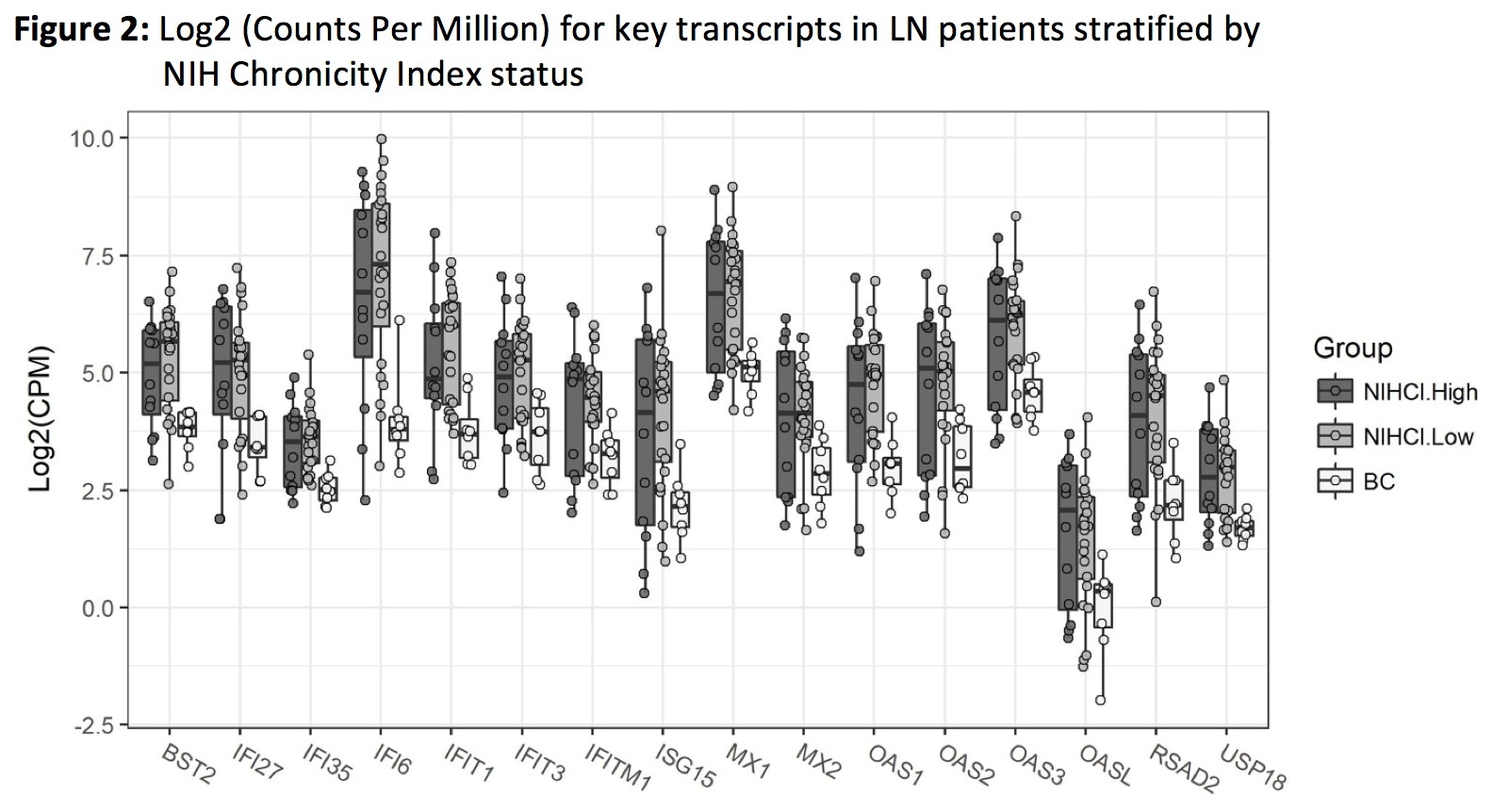
Pathways enriched for DEGs were only identified for those driven by interferon (IFN): a/b signaling, IFN signaling, and cytokine signaling. Transcripts that overlapped between all 3 of these pathways are presented in Figs. 1 and 2. Interferon pathway expression levels were increased in LN compared to controls for DEG identified transcripts. Key pathways were consistent with or without HIV-infected controls compared to LN. Expression levels for interferon induced transcripts (IIGTs) were persistently elevated in LN patients as compared to controls regardless of degree of LN activity or chronicity (represented by NIHAI high (score>8, range 0-17) vs. low and NIHCI high (score>4, range 2-10) vs. low.
Conclusion: IIGTs are differentially upregulated in LN compared to controls. Within LN, IIGTs are not markedly different between high and low levels of histologic activity or damage. The observation that interferon persists in low activity and high damage LN biopsy samples may represent an opportunity to improve response and outcomes using agents that selectively target IFN pathways.
Table 1: Demographics and glomerular involvement
|
|
Lupus Nephritis n=41
|
Controls n=8
|
||
|
Demographics
|
Gender n, (%)
|
female
|
32 (78.1)
|
4 (50)
|
|
male
|
9 (21.9)
|
4 (50)
|
||
|
Race n, (%)
|
black
|
37 (90.2)
|
5 (62.5)
|
|
|
white
|
2 (4.9)
|
3 (37.5)
|
||
|
other
|
2 (4.9)
|
0 (0)
|
||
|
Glomerular involvement
|
Biopsy (years)
|
mean age at biopsy
|
34.1
|
43.3
|
|
Duration (years)
|
SLE
|
8.7
|
|
|
|
Lupus Nephritis n, (%)
|
class II
|
6 (14.6)
|
|
|
|
class III
|
10 (24.4)
|
|
||
|
class IV
|
20 (48.8)
|
|
||
|
class V
|
26 (63.4)
|
|
||
|
class VI
|
4 (9.8)
|
|
||
|
Other Glomerulopathies n, (%)
|
HIV associated nephropathy
|
|
2 (25)
|
|
|
focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
|
|
2 (25)
|
||
|
IgA nephropathy
|
|
2 (25)
|
||
|
minimal change disease
|
|
1 (12.5)
|
||
|
thrombotic microangiopathy
|
|
1 (12.5)
|
||
|
diabetic nephropathy
|
|
1 (12.5)
|
||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lim SS, Farris AB, Guennel T, Wang S, Cobb J, Sinibaldi D, Jenks S, Sanz I, Guo X, Illei G, Shen K, Battle M, Wei C, White W. Interferon Induced Gene Transcripts Are Differentially Upregulated in the Kidney of Lupus Nephritis Patients Irrespective of Activity or Damage [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interferon-induced-gene-transcripts-are-differentially-upregulated-in-the-kidney-of-lupus-nephritis-patients-irrespective-of-activity-or-damage/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interferon-induced-gene-transcripts-are-differentially-upregulated-in-the-kidney-of-lupus-nephritis-patients-irrespective-of-activity-or-damage/