Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: With many treatments under study for SLE, a crisis in recruiting sufficient numbers of qualified patients for clinical trials has emerged. Willingness to consider trial participation may be influenced by many factors. The aim of this study was to analyze factors affecting interest in clinical trial participation using the Lupus Foundation of America’s Research Accelerated by You (RAY) registry.
Methods: RAY was created to improve understanding of lupus patient perspectives and connect patients with trial opportunities. Over 3,000 registrants have reported on lupus diagnosis, symptoms, treatments, and impacts. This analysis assessed factors associated with interest in trial participation in those with no prior trial participation. Demographics (age, time since diagnosis, education, gender, income, insurance, race and ethnicity) were compared between patients with and without interest in trial participation using T-test and chi-square analyses. Multinomial regression models reported as relative risk ratios (RRR) were fit to assess any independent contributions of demographic factors to a three-category dependent variable: interest in trial participation, no interest due to side effect concerns, and no interest due to other reasons.
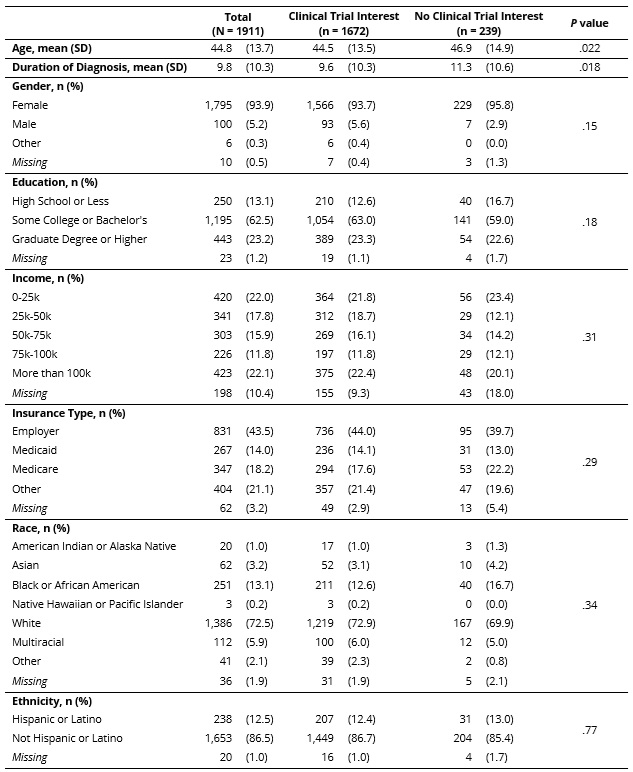
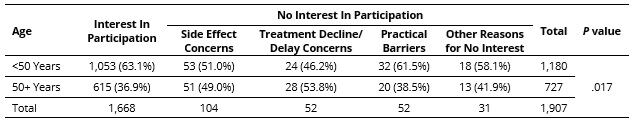
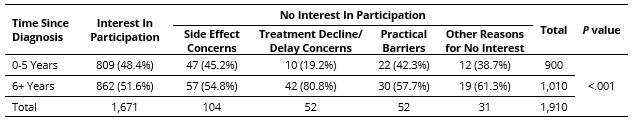
Results: Of the 1,911 RAY registrants with no prior clinical trial participation, those reporting no interest in trial participation (12.5%) were older (46.9 vs. 44.5 years, p = .022) and had longer time since diagnosis (11.3 vs. 9.6 years; p = .018) compared to those expressing interest in trials (Table 1). The proportion of older individuals (50+ years) was higher in those who were clinical trial averse due to side effect concerns (49.0%) or concerns about treatment declines/delays (53.8%) than those interested in trials (36.9%), not interested due to practical barriers (38.5%), and not interested for other reasons (41.9%; p = 0.017; Table 2). In younger patients, no reason for reticence about trial participation predominated, but a range of concerns were reported. The proportion of people with 6+ years since diagnosis was higher in trial averse patients with concerns about treatment declines/delays (80.8%) compared to other groups (51.6 – 61.3%; p < 0.001; Table 3). Multinomial logistic regression analysis showed that age 50+ years was independently associated with a 1.64-fold increase in the risk ratio of no trial interest due to side effect concerns vs. trial interest (RRR = 1.64 compared to age < 50 years; 95% CI: 1.09-2.46; p = 0.017). Time since diagnosis 6+ years was independently associated with a 1.86-fold increase in the risk ratio of no trial interest for other reasons vs. trial interest (RRR = 1.86 compared to time since diagnosis < 6 years; 95% CI: 1.27-2.71; p = 0.001).
Conclusion: Although clinical trial participation interest is high (88.6%) in RAY, addressing patient reservations about trial participation might improve enrollment at a time of plentiful trials and insufficient numbers of participants. Key issues reported by lupus patients, especially those over 50, are the potential for side effects and treatment declines/delays. However, other issues are also reported, and recruitment of younger patients might be impacted by addressing these impediments.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fisher M, Kim M, Merrill J, Agyemang S, Buie J. Interest in Clinical Trial Participation Among People with Lupus: Results from the Research Accelerated by You (RAY) Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interest-in-clinical-trial-participation-among-people-with-lupus-results-from-the-research-accelerated-by-you-ray-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interest-in-clinical-trial-participation-among-people-with-lupus-results-from-the-research-accelerated-by-you-ray-registry/