Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
TNFα inhibitors (TNFi) can be immunogenic in patients with autoimmune diseases. B-cell activating factor transgenic mice (BAFFtg) are a model of autoimmune disease since they present with lupus and Sjögren-like manifestations. Prolonged treatment with TNFi in this model leads to anti-drug antibodies (ADA). In humans, low dose Methotrexate (MTX) diminishes immunization against TNFi. MTX favors the release of adenosine monophosphate (AMP), which, via the CD73 ectoenzyme will be transformed in adenosine, a powerful immune-regulatory mediator. We thus sought to investigate the role of MTX in BAFFtg mice to identify the mechanism of action involved in this tolerance.
Methods:
BAFFtg mice treated with adalimumab or etanercept for 52 weeks with or without MTX for 3 consecutive days starting the day of TNFi, were studied. Drug concentration and ADA were monitored with Theradiag® assays. WT and BAFFtg mice splenocytes and B1 peritoneal cells were compared for surface markers either involved in MTX-related purinergic metabolism (CD73 CD39) or B-cell regulatory function (IL-10 or Breg precursors: CD21hi CD24hi CD23+ cells). Detection of adenosine on sorted B-cells was performed using mass spectrometry-coupled with HPLC.
Results:
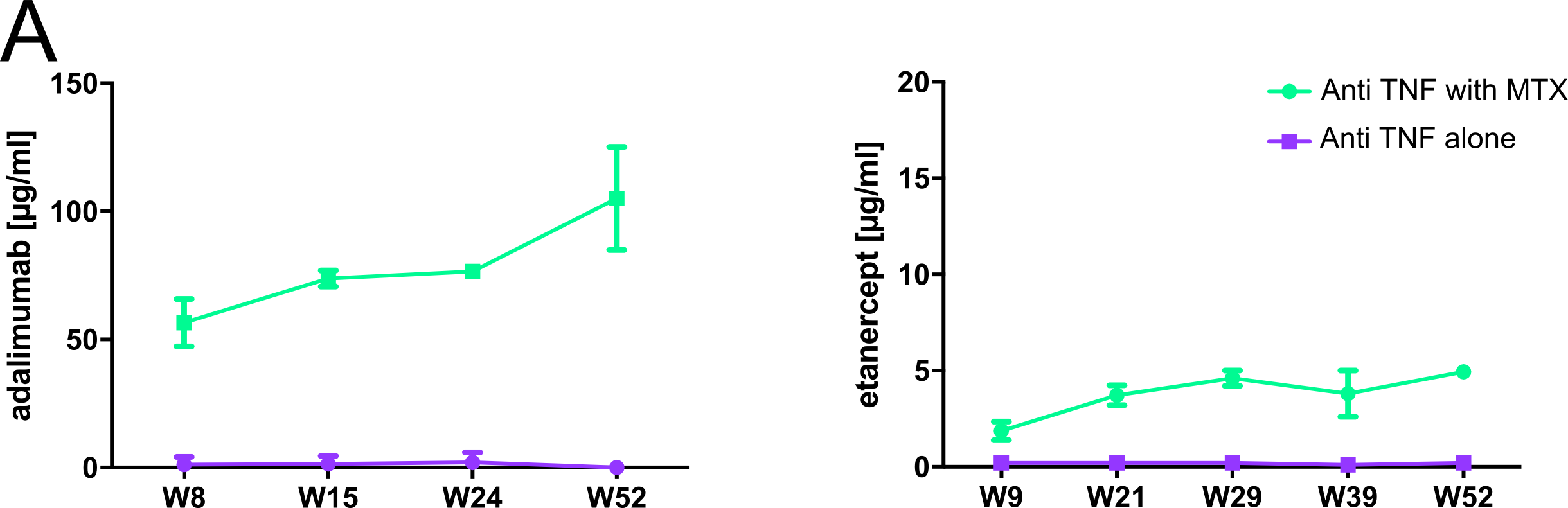
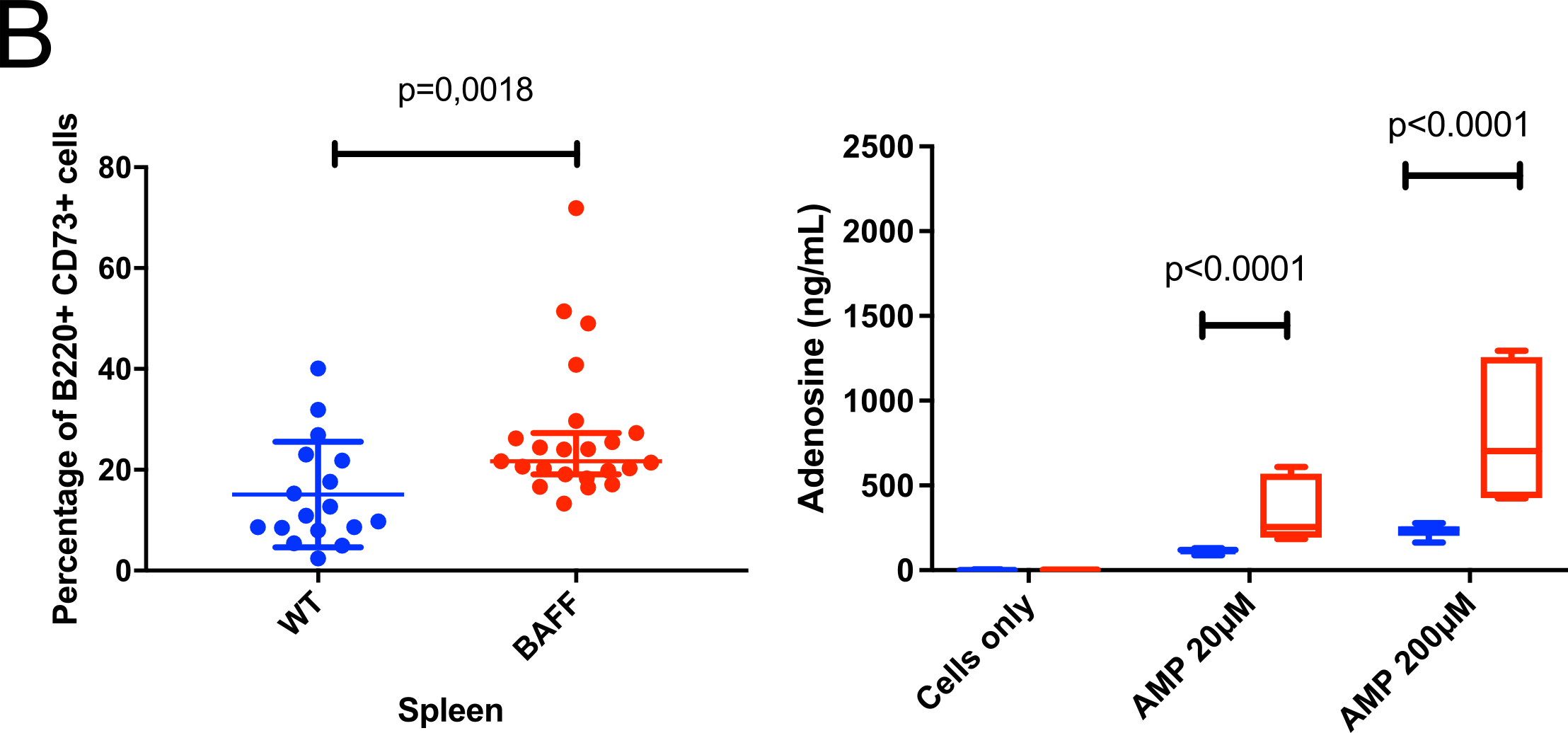
In BAFFtg mice, a short course of MTX treatment starting the day of the TNFi administration prevented immunization against TNFi and maintained drug concentration over 52 weeks (Fig A). The same experiments made in WT mice led to controversial results. BAFFtg mice splenic B-cells expressed more CD73 (median: 21.7% vs 10.9% for WT) (FigB) leading to more adenosine production (Fig B) when exposed to AMP known to be released by cells upon MTX exposure. BAFFtg splenocytes also expressed more IL-10 (B10 cells) and B1 peritoneal cells express more CD73. Tolerization with MTX further increased B10 and Breg precursors (Fig C).
Conclusion:
In BAFFtg mice, immunization against TNFi can be prevented for a year by a single course of MTX if administered concomitantly with the first TNFi injection. This supports an interaction between MTX and BAFF to prevent ADA formation. The mechanism of this specific tolerance could involve interaction between extracellular release of AMP induced by MTX and increase of CD73 in BAFFtg mice, which in turn may increase adenosine and IL-10 regulatory B cells.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bitoun S, Nocturne G, Ly B, Pascaud J, Pruvost A, Mariette X. Interaction between Methotrexate and BAFF for Preventing Immunization Against TNF-α Inhibitors By Increasing Adenosine and Regulatory B-Cell Subsets [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interaction-between-methotrexate-and-baff-for-preventing-immunization-against-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitors-by-increasing-adenosine-and-regulatory-b-cell-subsets/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interaction-between-methotrexate-and-baff-for-preventing-immunization-against-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitors-by-increasing-adenosine-and-regulatory-b-cell-subsets/