Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor under investigation for treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). We examined tofacitinib efficacy in patients (pts) with active PsA.
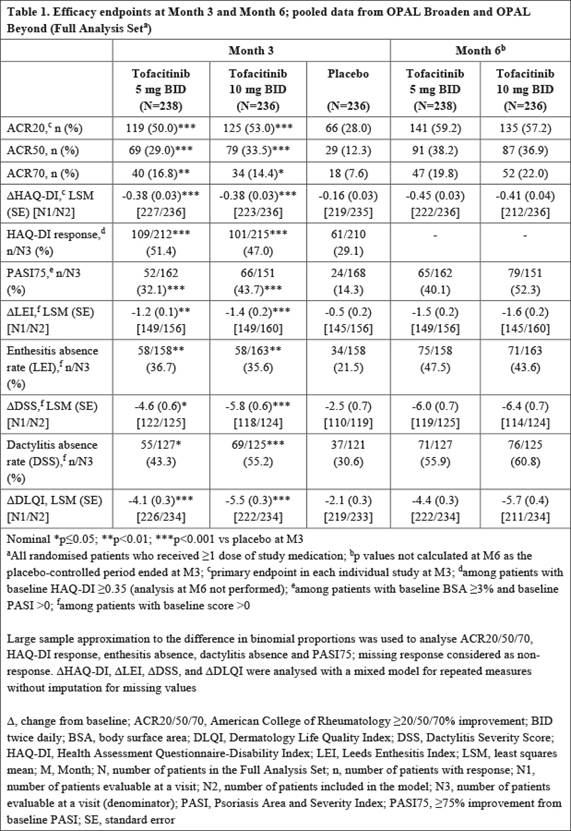
Methods: Data were pooled from 2 placebo (PBO)-controlled, double-blind, multicenter, global Phase 3 studies (OPAL Broaden [N=422; 12 months; NCT01877668]; OPAL Beyond [N=394; 6 months; NCT01882439]). Pts had active PsA and either inadequate response (IR) to ≥1 conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (csDMARD) and were tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi)-naïve (OPAL Broaden), or had IR to ≥1 TNFi (OPAL Beyond). Pts were randomized to tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID), 10 mg BID, adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneous injection once every 2 weeks (OPAL Broaden only), or PBO, and a single, stable csDMARD. PBO pts moved to tofacitinib 5 mg or 10 mg BID at Month (M)3. Endpoints included ACR20/50/70 response rates (≥20%/≥50%/≥70% improvement), change from baseline (D) in Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), HAQ-DI response (decrease from baseline [BL] of ≥0.35), ≥75% improvement from BL in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI75), D Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI) and enthesitis absence, D Dactylitis Severity Score (DSS) and dactylitis absence, and Δ Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). Tofacitinib 5 mg and 10 mg BID data (to M6) and PBO data (to M3), were pooled. Significance was declared at p≤0.05 without correction for multiplicity.
Results: In total, 238, 236 and 236 pts received tofacitinib 5 mg BID, 10 mg BID, or placebo, respectively. Pts were white (94.2%) and female (55.4%) with ≥5 peripheral swollen or tender joints (98.0%), enthesitis (LEI>0; 67.5%), dactylitis (DSS>0; 52.5%), psoriatic body surface area ≥3% (67.7%), and C-reactive protein levels >2.87 mg/L (62.5%) at BL. Mean age was 49.1 years; mean PsA duration was 8.0 years. Significant improvements vs PBO at M3 were seen for peripheral arthritis and physical function endpoints for tofacitinib 5 mg and 10 mg BID: ACR20, ACR50, ACR70, DHAQ-DI, and HAQ-DI response (Table 1). Significant improvements in psoriasis, enthesitis, and dactylitis endpoints vs PBO were seen for tofacitinib 5 mg and 10 mg BID at M3: PASI75, DLEI, enthesitis absence (using LEI), DDSS, dactylitis absence (using DSS), and ΔDLQI (Table 1). Efficacy was maintained or further improved at M6.
Conclusion: In a pooled analysis of csDMARD-IR/TNFi-naïve and TNFi-IR pts, tofacitinib 5 mg and 10 mg BID improved peripheral arthritis and physical function, psoriasis, enthesitis, and dactylitis vs PBO at M3.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nash P, Coates LC, Fleischmann R, Papp K, Gomez-Reino JJ, Kanik KS, Wang C, Wu J, Hendrikx T, Ports WC. Integrated Efficacy Analysis of Tofacitinib, an Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-efficacy-analysis-of-tofacitinib-an-oral-janus-kinase-inhibitor-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-efficacy-analysis-of-tofacitinib-an-oral-janus-kinase-inhibitor-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/