Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
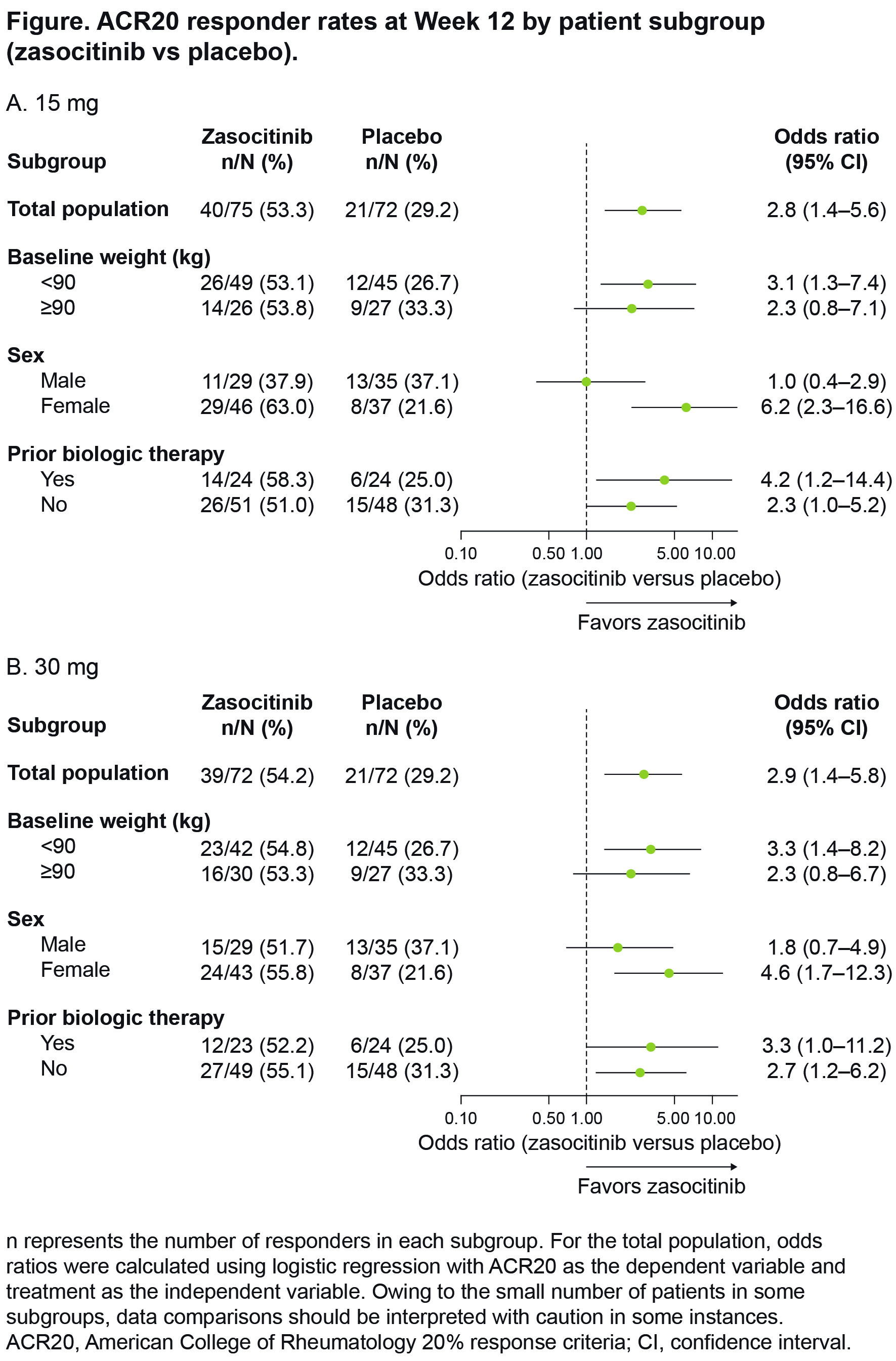
Background/Purpose: Zasocitinib (TAK-279) is a potent, highly selective, oral allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor. In a recent phase 2b trial in active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) (NCT05153148), zasocitinib achieved a greater ACR20 response at 15 mg and 30 mg doses compared with placebo (53.3% and 54.2%, respectively, versus 29.2%, each p = 0.002) at Week 12 (primary endpoint) and was well tolerated.1 Here, we evaluate the impact of body weight, sex and previous biologic use on the efficacy of zasocitinib (15 mg and 30 mg) versus placebo.
Methods: This was a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Eligible patients were aged ≥ 18 years, had PsA symptoms for ≥ 6 months before screening, met CASPAR criteria, and had ≥ 3 tender and ≥ 3 swollen joint counts at enrollment despite previous use of non-steroidal anti‑inflammatory drugs or conventional or biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Patients were randomized 1:1:1:1 to receive placebo or zasocitinib (5 mg, 15 mg or 30 mg) orally once daily for 12 weeks. Subgroup analyses (pooled and group-level data) were performed on ACR20 response (Week 12) according to body weight (< 90kg and ≥ 90kg), sex and previous biologic use. Patients with missing ACR20 data at Week 12 were imputed as non-responders. Differences in ACR20 responder rates between zasocitinib and placebo groups were assessed using Mantel–Haenszel tests adjusting for randomization stratification factors. Odds ratios (ORs) were obtained using a logistic regression model with treatment as the independent variable. Subgroup analyses were pre-specified except for body weight (post hoc).
Results: Overall, 290 patients were randomized and treated; 245 completed 12 weeks of treatment. Baseline characteristics were comparable across treatment groups; however, the proportion of females was higher in zasocitinib 15 mg and 30 mg groups versus placebo (61.3% and 59.7%, respectively, versus 51.4%). Pooled analysis of the zasocitinib 15 mg and 30 mg groups (n = 147) showed that patients treated with zasocitinib were more likely to achieve ACR20 across subgroups than placebo (OR [95% confidence interval; CI]: < 90kg 3.2 [1.5–7.0], ≥ 90kg 2.3 [0.9–6.0]; males 1.4 [0.6–3.2], females 5.3 [2.2–13.0]; previous biologics 3.7 [1.3–11.0], no previous biologics 2.5 [1.2–5.1]), although body weight of ≥ 90kg and male subgroups did not differ statistically. Similar trends for these variables were observed when the two treatment groups were considered separately (Figure).
Conclusion: In patients with active PsA, ACR20 response was higher in patients treated with 15 mg or 30 mg doses of zasocitinib than with placebo regardless of body weight, sex or previous exposure to biologics.
Reference:
1. Kivitz A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2023; 75 (Suppl 9).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eder L, Muensterman E, van der Heijde D, Kivitz A, Trivedi M, Hong T, Rehman M, Weng H, Chen J, Baraliakos X. Influence of Patient Baseline Characteristics on Zasocitinib (TAK-279) Efficacy, a Selective Oral Tyrosine Kinase 2 Inhibitor: A Randomized Phase 2b Trial in Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-patient-baseline-characteristics-on-zasocitinib-tak-279-efficacy-a-selective-oral-tyrosine-kinase-2-inhibitor-a-randomized-phase-2b-trial-in-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-patient-baseline-characteristics-on-zasocitinib-tak-279-efficacy-a-selective-oral-tyrosine-kinase-2-inhibitor-a-randomized-phase-2b-trial-in-psoriatic-arthritis/