Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy IV: Biomarkers
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. A novel automated quantification method for RA MRI-detected pathology using statistical shape modelling technology (RAMRIQ) provides a tool that may be even more responsive than the sensitive RAMRIS semi-quantitative standard.1 We aimed to determine if early changes in RAMRIQ were predictive of subsequent MRI and radiographic damage progression in a study of tofacitinib for the treatment of early RA in methotrexate-naïve patients with minimal radiographic progression.
Methods: We used data from an exploratory, Phase 2 randomized controlled trial comparing tofacitinib, methotrexate, and the combination (n=109) in early active RA.1 All patients met ACR classification criteria for active RA. MRI was performed at baseline, 1, 3, 6, and 12 months. A single centralized reader read all MRI data; data for each patient were randomized by time point, and read in the same sitting. We examined changes in synovitis, osteitis and erosions for RAMRIQ and RAMRIS at 1 and 3 months and performed univariate analyses on their relationship to RAMRIS, RAMRIQ, and radiographic progression (modified total Sharp score [mTSS]) at 12 months.
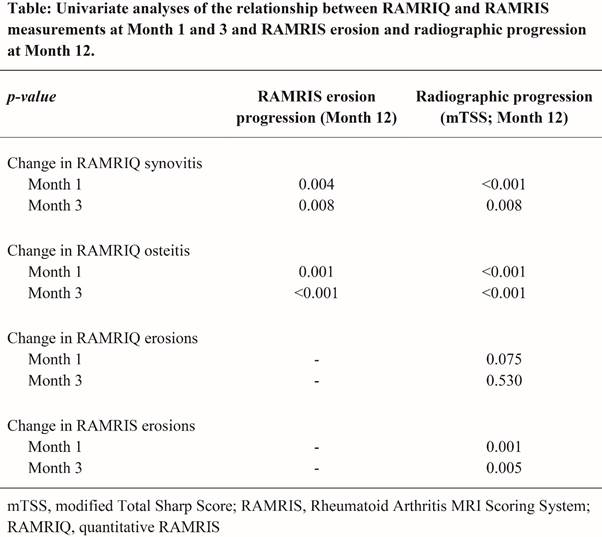
Results: Reduction in RAMRIQ synovitis and osteitis at 1 and 3 months were significantly associated with reduction in RAMRIS erosion progression at 12 months (Table). Improvement in RAMRIQ synovitis and osteitis at 1 and 3 months were also associated with reduction in radiographic progression at 12 months, while RAMRIQ erosions at 1 and 3 months were not significantly associated with radiographic progression (Table). Early changes in RAMRIS erosion at 1 and 3 months were associated with radiographic progression at 12 months (Table). Treatment with tofacitinib alone or in combination with methotrexate was also associated with reduced progression in RAMRIS erosions (p=0.017 and p=0.007, respectively).
Conclusion: In this study, sensitive automated detection demonstrated that change in synovitis and osteitis predict subsequent RAMRIS erosion and radiographic progression. Treatment with tofacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate was also highly predictive of no progression of erosive damage. Because of its enhanced sensitivity, novel quantitative imaging analysis has the potential to change RA clinical trial design where assessing structural damage is an objective. Reference:
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Conaghan PG, Bowes MA, Østergaard M, Guillard G, Chapman D, Stein A, Andrews J, Xie Z, Koenig A, Soma K, Wilkinson B. Inflammation Detected with Modern Sensitive MRI Analysis Demonstrates That Therapeutic Response As Early As One Month Predicts 12-Month Radiographic Progression: Data from a Study Using Tofacitinib and Methotrexate in Early RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammation-detected-with-modern-sensitive-mri-analysis-demonstrates-that-therapeutic-response-as-early-as-one-month-predicts-12-month-radiographic-progression-data-from-a-study-using-tofacitinib-an/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammation-detected-with-modern-sensitive-mri-analysis-demonstrates-that-therapeutic-response-as-early-as-one-month-predicts-12-month-radiographic-progression-data-from-a-study-using-tofacitinib-an/