Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The value of biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) in SpA is well recognized but global access to these treatments can be limited due to high cost and other factors. This study explores variation in the use of bDMARDs in SpA across countries and to what extent socio-economic (SE) factors may explain variation.
Methods: Patients fulfilling the ASAS SpA criteria in the multi-national, cross-sectional ASAS COMOSPA study were studied. Multi-level logistic regression models with random intercept for country were constructed with current use of bDMARDs as the dependent variable. Contribution of socio-economic factors using country health expenditures and gross domestic product (GDP) (all low vs medium/high tertiles) as independent country-level factors, was explored in models adjusted for socio-demographic as well as clinical variables known to determine bDMARD-use in SpA.
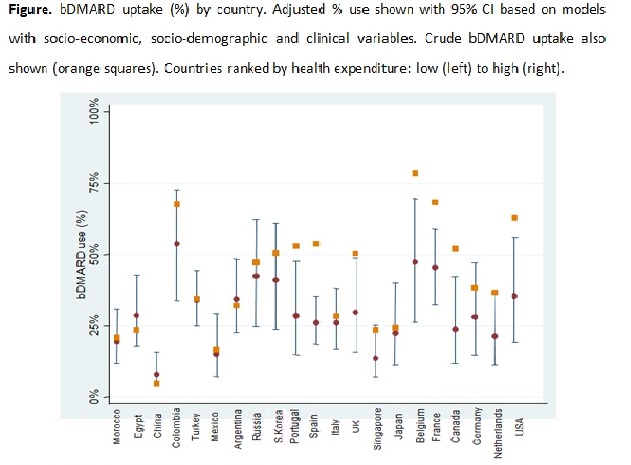
Results: In total, 3370 patients from 22 countries were included (mean [SD] age 43 [14] years; 66% male; 88% axial disease). Across countries, 1275 (38%) were bDMARD users. Crude mean bDMARD-use varied between 5% (China) to 74% (Belgium). After adjustment for relevant socio-demographic and clinical variables, important variation in bDMARD-use across countries remained (Figure, p<0.001). Country-level socio-economic factors, specifically higher health expenditures were related to higher bDMARD uptake (Table), though not meeting statistical significance (OR 1.96;95%CI 0.94,4.10). Similar findings were found with country GDP (OR 1.93;95%CI 0.91,4.06).
Conclusion: There remains important residual variation across countries in bDMARD uptake of patients with SpA followed in specialized SpA centers. This is despite adjustment of well-known factors for bDMARD use such as clinical and country-level socio-economic factors.
Table. bDMARD: univariable and multivariable analyses with socio-demographic, clinical and treatment variables as well as indicators of the country socio-economic welfare included.
|
Independent predictors |
Univariable analysis bDMARD use OR (95% CI) |
Multivariable analysis bDMARD use OR (95% CI) n=2792 |
|
Country health expenditure (high/medium vs low) |
1.71(0.84,3.50) |
1.96(0.94,4.10) |
|
Age (years) |
1.01(1.00,1.01) |
1.00(0.99,1.01) |
|
Male gender (vs females) |
1.18(1.01,1.39) |
1.26(1.04,1.53) |
|
Axial (vs peripheral) disease |
1.48(1.16,1.89) |
1.62(1.15,2.28) |
|
ASDAS (CRP based) |
0.82(0.76,0.89) |
0.80(0.73,0.87) |
|
Sacroiliitis on X-ray |
1.75(1.44,2.12) |
1.41(1.12,1.78) |
|
History of extra-articular manifestations |
1.46(1.25,1.70) |
1.31(1.08,1.58) |
|
Total NSAID score (0-100) in last 3 months |
0.99(0.99,1.00) |
0.99(0.99,1.00) |
|
Past csDMARD use |
2.31(1.96,2.73) |
2.08(1.72,2.52) |
|
Past bDMARD use |
2.64(2.13,3.28) |
2.48(1.93,3.19) |
|
Education (secondary/university vs primary) |
0.79(0.62,1.00) |
0.76(0.52,1.13) |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nikiphorou E, van der Heijde D, Norton S, Landewé RBM, Moltó A, Dougados M, van Den Bosch F, Ramiro S. Inequity in Biologic DMARD Prescription for Spa across the Globe: Results from the Multi-Centre, Cross-Sectional, ASAS Comospa Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inequity-in-biologic-dmard-prescription-for-spa-across-the-globe-results-from-the-multi-centre-cross-sectional-asas-comospa-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inequity-in-biologic-dmard-prescription-for-spa-across-the-globe-results-from-the-multi-centre-cross-sectional-asas-comospa-study/