Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2227–2256) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: SpA Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In patients with mono/oligoarticular psoriatic arthritis (PsA), swelling or tenderness of specific joints can be associated with poorer patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and physician global assessment1. We hypothesize that location of affected entheseal points may also have differential impact on PROs or time to enthesitis resolution with guselkumab (GUS). The objectives of this post-hoc analysis were: (1) to describe the distribution of affected entheseal points in patients with active polyarticular PsA; (2) to evaluate the impact of anatomical location of enthesitis and Leeds enthesitis index (LEI) score on patient-reported pain (PtP), patient global assessment (PtGA), and functional status; and (3) to compare the time to resolution of each entheseal point following treatment with GUS.
Methods: This post-hoc analysis used pooled data from adults with active PsA, despite standard therapies, from the DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 studies who were randomized to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) or at W0, W4, then Q8W. Only patients with baseline enthesitis were included (N=473). Proportions of patients with enthesitis were determined for each entheseal point assessed by LEI score. Longitudinal impact of LEI score and location of individual entheseal points on PtP, PtGA, and health assessment questionnaire disability index (HAQ-DI), upon adjusting for potential confounders (age, sex, body mass index, prior use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, baseline PsA duration, swollen joint count, tender joint count), was assessed with mixed models for repeated measures through W52. Time to resolution of enthesitis at each anatomical location was assessed with Kaplan-Meier survival analysis.
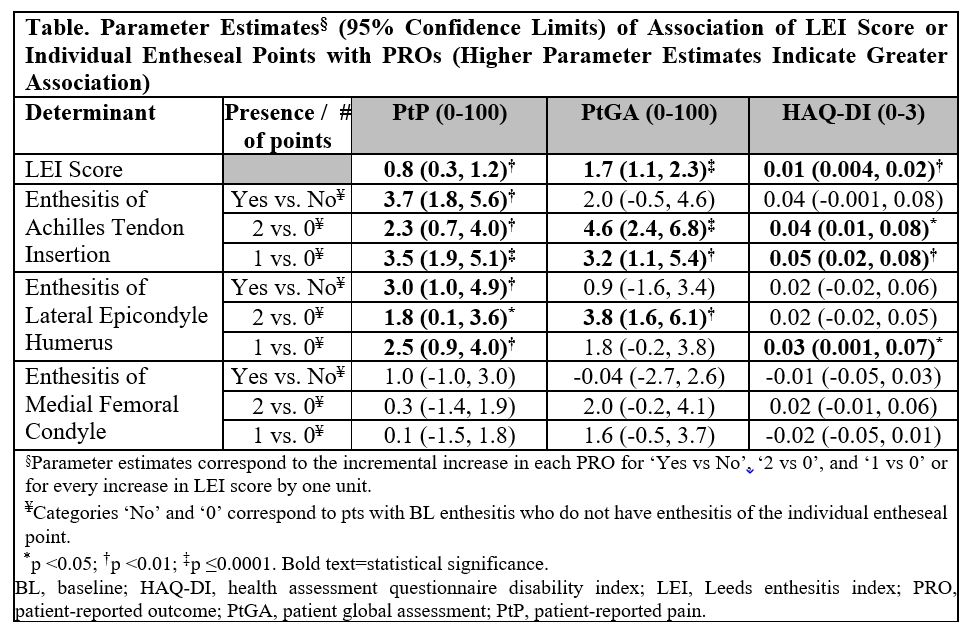
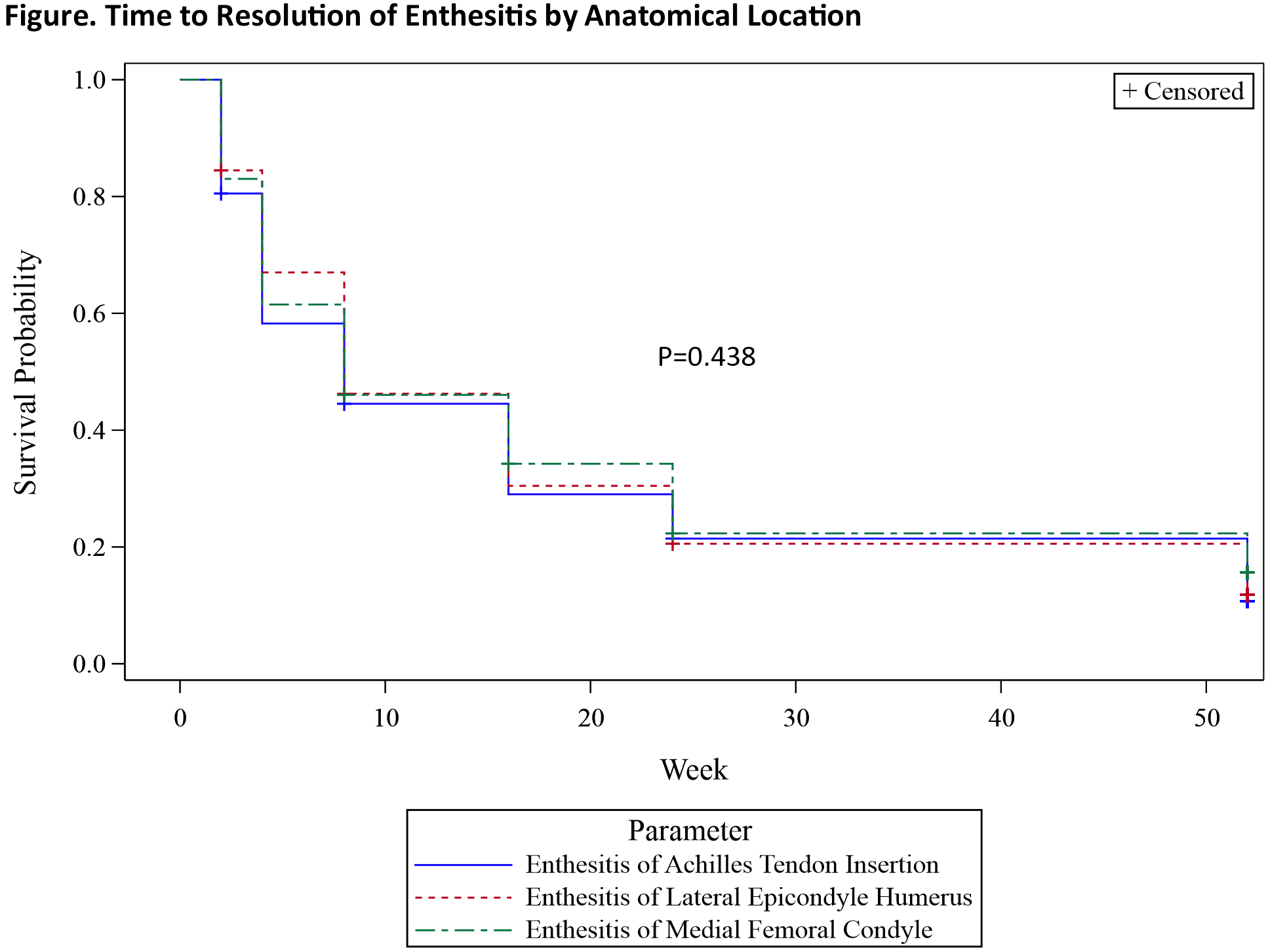
Results: Approximately half (49.5%) of GUS-randomized patients with baseline enthesitis had an LEI score of 1 or 2. The most commonly affected entheseal point was Achilles tendon insertion among both patients with baseline enthesitis and patients with an LEI score of 1 or 2. Through W52, higher baseline LEI score was associated with increased PtP, PtGA, and HAQ-DI scores (Table). Of the individual entheseal points assessed, enthesitis of Achilles tendon insertion had the greatest impact on all PROs and enthesitis of medial femoral condyle the least. Following GUS treatment, median time to enthesitis resolution was W8 for each of the three anatomical locations assessed by the LEI (Figure).
Conclusion: In this population of patients with active polyarticular PsA, Achilles tendon insertion was the most commonly affected entheseal point and more highly associated with worse PtP, PtGA, and functional status. GUS treatment was associated with rapid enthesitis resolution, including resolution of Achilles enthesitis.
References: 1. Ayan G. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020;23(8):1094-9.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates L, McInnes I, Aydin S, Kishimoto M, Mease P, Shawi M, Zimmermann M, Rampakakis E, Lavie F, McGonagle D. Individual Entheseal Points Have Differential Frequency of Involvement and Impact on Patient Reported Outcomes in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Pooled Analysis of Two Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/individual-entheseal-points-have-differential-frequency-of-involvement-and-impact-on-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-pooled-analysis-of-two-phase-3-randomized/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/individual-entheseal-points-have-differential-frequency-of-involvement-and-impact-on-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-pooled-analysis-of-two-phase-3-randomized/