Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Although some global composite measures (DAPSA, DAS28) reflect musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) findings of psoriatic arthritis (PsA), there is little knowledge on how to predict whether certain joints have US active findings. We examined the relationship between composite measure score of PsA and MSUS findings for each body part, and searched for useful indicators for active MSUS findings.
Methods:
Total 98 PsA consecutive cases who fulfilled CASPAR criteria were evaluated. PASDAS, DAPSA, PASI, DAS28-CRP, DAS28-ESR, BASDAI, SDAI, CDAI, CPDAI were calculated using clinical examinations of 68 tender joints, 66 swelling joints, 6 enthesitis and 20 dactylitis. 5 body parts (hand, elbow, shoulder, knee, foot) specific PASDAS, DAPSA were also calculated. MSUS evaluated 60 joints, 16 entheses and 24 tendons. Enthesitis was assessed according to the MASEI investigating the inflammatory scores (entheseal thickening, structural changes, bursitis and vascularization) and chronic damage scores (calcifications, enthesophytes, and erosions). US findings were grouped into 7 body parts (finger, wrist, elbow, shoulder, knee, ankle, toe), and the relationship between composite measure score of PsA and MSUS findings were analyzed using Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results:
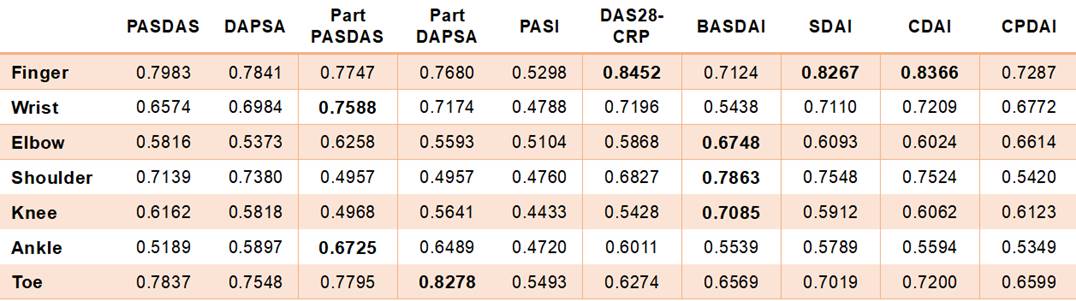
MSUS PD>=1 in joints were frequent in wrist (13.9 } 3.4%), knee (7.65 } 6.5%) and elbow (13.9 } 3.4%). MSUS enthesitis were frequent in Achilles tendon (inflammatory 18.9%, chronic 29.5%) and knee quadriceps (inflammatory 11.5%, chronic 32.8%). Composite measures predicting active MSUS findings (PD>=1 in joint or tendon, or positive for inflammatory scores of enthestis) were different among body parts (Table 1). In fingers, DAS28-CRP, SDAI, CDAI predict active MSUS findings with moderate accuracy. In wrist, ankle and toe, hand-specific PASDAS, foot-specific PASDAS or foot-specific DAPSA predict active MSUS findings than global PASDAS and DAPSA. On the other hand, in elbow, shoulder and knee, BASDAI predict active MSUS findings with the highest accuracy.
Conclusion:
Composite measures predicting active MSUS findings were different according to body parts. Parts-specific composite measure improved predicting wrist or ankle MSUS findings. Since there is laterality of arthritis or enthesitis of PsA, location specificity is considered to be important than global composite measures. BASDAI is important when considering elbow, shoulder and knee, which is presumably related to the importance of the element of enthesitis in these parts. Careful evaluation according to each part is considered important for prediction of MSUS.
Table 1: Relationship between active MSUS findings in body parts and composite measures (value = AUC).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sumitomo S, Tateishi S, Soroida Y, Shirai H, Iwai T, Ono K, Hirose J, Yoshizaki A, Asano Y, Sato S, Tanaka S, Ikeda H, Fujio K, Yamamoto K, Kanda H. Indicators for Active Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Findings of Psoriatic Arthritis Vary on Each Body Part [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/indicators-for-active-musculoskeletal-ultrasound-findings-of-psoriatic-arthritis-vary-on-each-body-part/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/indicators-for-active-musculoskeletal-ultrasound-findings-of-psoriatic-arthritis-vary-on-each-body-part/