Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Patients with autoimmune conditions are at increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) compared to the general population. It is not routine practice at UT Rheumatology to manage lipids. Since rheumatologists often play the role of PCP for patients with autoimmune diseases, they are at a unique position to modulate the CVD risk. Our aim was to increase the percentage of patients with an annual lipid panel checked to 50% and to prescribe statin therapy for LDL more than or equal to 190 or if the 10-year risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is more than or equal to 7.5%.
Methods:
Patients over 18 years of age with RA, SLE, Psoriatic arthritis, Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis were included in this study. This quality improvement project was undertaken by a single attending provider at a single clinic location. The baseline data from chart review was collected from July 2016 to August 2016. The post-intervention data was collected in 3 phases between December 2016 and May 2017. For the first phase of intervention a reminder card with a flowchart was attached to the work stations, and ASCVD risk calculator was downloaded to the providerÕs cell phone. For appropriate patients, lipid profiles were ordered and ASCVD risk calculated. If indicated, atorvastatin was prescribed. During the second intervention phase, in addition to the above the provider reviewed the daily schedule and printed appropriate lab orders for each patient the day prior to the visit.
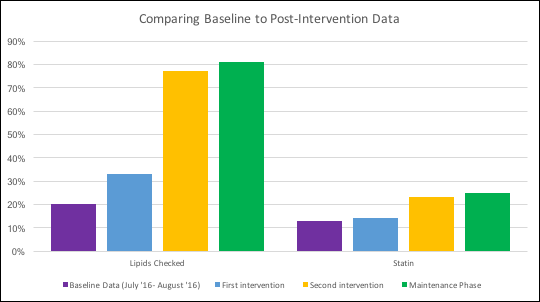
Results:
During baseline period, lipid profiles were ordered on 20% of appropriate patients (5/30) with 13% (4/30) on statins. After the first intervention, lipids were checked in 33% (12/36) with 13.8% (5/36) on statins. During the second intervention phase, lipids were checked in 77% (10/13) with 23% (3/13) on statins. During maintenance (about 3 months later), lipids were ordered on 81% (13/16) with 25% (4/16) placed on statins. It was also noted that 5 of the 65 patients in the intervention phases declined having lipid panel measured.
Conclusion:
The initial intervention did not result in significant improvement. For the second intervention, pre-clinic reviews with labs checks were performed, which increased success. Next steps will involve spread to other rheumatology providers in the clinic and interventions to increase appropriate prescribing of statins based on lipid panel results.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mohan A, Scholz B. Increasing Lipid Panel Monitoring in a Rheumatology Clinic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increasing-lipid-panel-monitoring-in-a-rheumatology-clinic/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increasing-lipid-panel-monitoring-in-a-rheumatology-clinic/