Session Information
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Clinical Aspects: Novel Biomarkers and Other Measurements of Disease Activity
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose : Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have an elevated risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD). Like active RA, atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process. There are indications that aortic inflammation in atherosclerosis can be detected on an 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography scan (18F-FDG-PET/CT).
Objective: To quantify 18F-FDG uptake in large arteries of RA patients using PET/CT, as potential reflection of vascular wall inflammation in areas of atherosclerosis, and its association with disease activity in patients with RA as compared to controls.
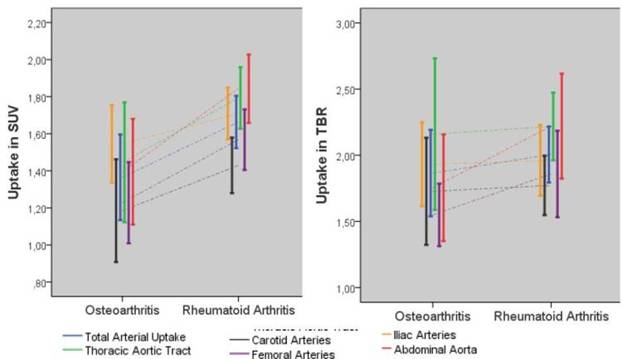
Methods : 18F-FDG-PET/CT scan was performed in patients with active RA (DAS28 > 4.0; n=29) and in controls with osteoarthritis (n=11). Semi-quantitative FDG-uptake was determined by calculation of the mean standardized uptake value (SUV) and tissue-to-background ratio (TBR) using 18F-FDG activity in the vena cava as background. One volume of interest (VOI) of an arterial segments with maximum 18F-FDG uptake was used for SUV calculation (focal arterial uptake). Total arterial uptake was estimated by using the mean of all focal arterial uptakes in all arteries.
Results : Focal as well as total arterial uptake of 18F-FDG was the highest in patients with RA. SUV was significantly higher in RA for the thoracic aortic tract, the abdominal aorta and the femoral arteries as compared to OA controls. C-reactive protein was associated with an increased total arterial uptake as well as an increased focal arterial uptake in the thoracic aortic tract, the abdominal aorta, the iliac arteries and the femoral arteries. DAS28 >2,6 was also correlated to total arterial uptake and uptake in the thoracic aortic tract, the abdominal aorta and the iliac arteries. There were no significant differences in TBR between RA and OA.
Conclusion: Increased focal vascular wall uptake of 18F-FDG as sign of vascular inflammation was found in several arterial segments of RA patients. C-reactive protein and clinical RA activity were correlated with 18F-FDG uptake in most of these arteries. Overall, total arterial uptake was higher in RA patients and it was correlated with C-reactive protein and disease activity. The lack of differences in TBR measurements requires further study.
Disclosure:
R. Agca,
None;
A. M. van Sijl,
None;
Y. M. Smulders,
None;
A. E. Voskuyl,
None;
C. J. van der Laken,
None;
R. Boellaard,
None;
K. J. D. F. Lensen,
None;
M. T. Nurmohamed,
AbbVie,
2.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-vascular-wall-inflammation-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-as-measured-by-an-18f-fdg-petct-scan/