Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: B Cell Biology and Targets in Autoimmune Disease - Poster I: SLE and Sjögren's
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Recent research indicates that lipid rafts play an important role during B-cell activation and could be defective in patients with primary Sjӧgren’s syndrome (pSS). No previous comparisons between the lipid raft profile in patients with lupus (SLE), SLE and secondary Sjӧgren’s syndrome (SLE/SS) and pSS are available. Our study aimed to: 1. identify peripheral B and T cell abnormalities in patients with pSS compared to SLE and SS/SLE patients and correlate them with immune phenotype with clinical features and serological abnormalities. 2. investigate lipid raft expression in different B cell populations and their correlations with disease activity scores (ESSDAI and BILAG).
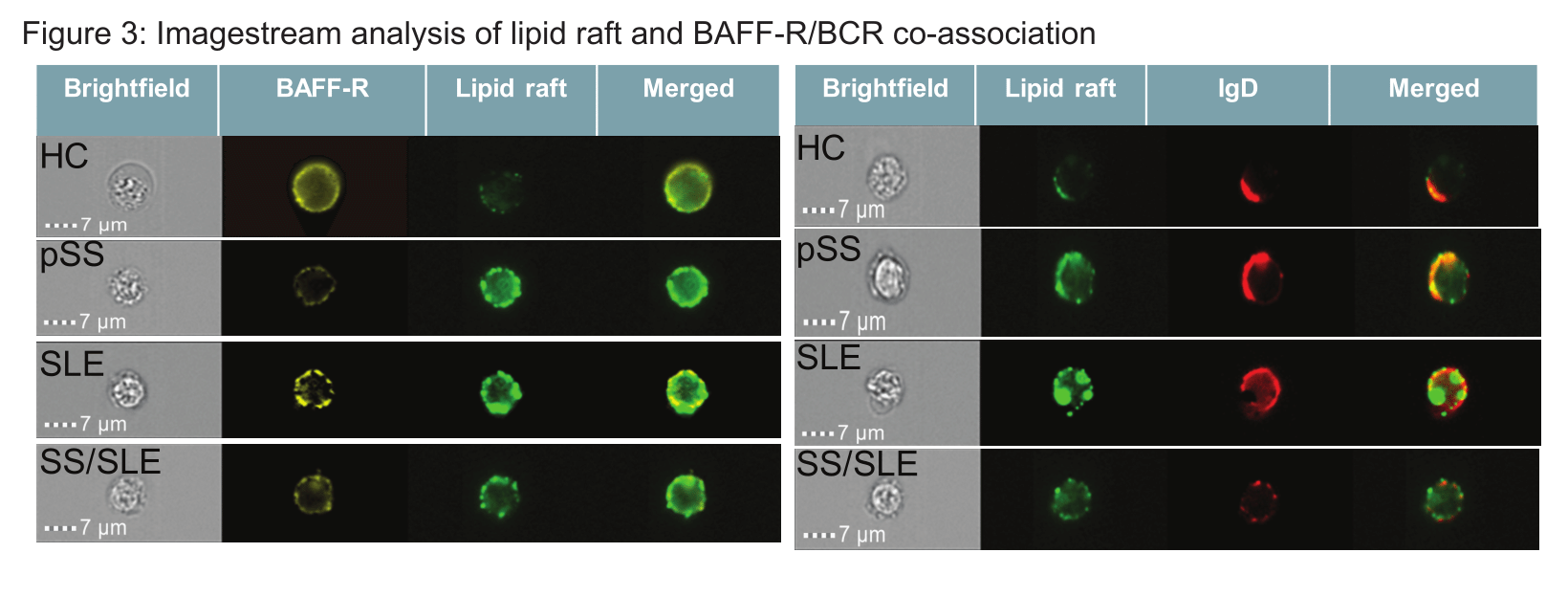
Methods: Blood samples and clinical and laboratory parameters from 34 patients with pSS, SLE and SS/SLE and 13 age/sex matched healthy controls (HC) were obtained. We used flow-cytometry to perform B-cell immunophenotyping and analysis of lipid-raft expression (marker of B-cell activation). In vitro cultures assessed lipid-raft expression in response to BAFF. We used ImageStream cytometry to characterise the interaction between lipid rafts and IgD and BAFF receptor (BAFF-R).
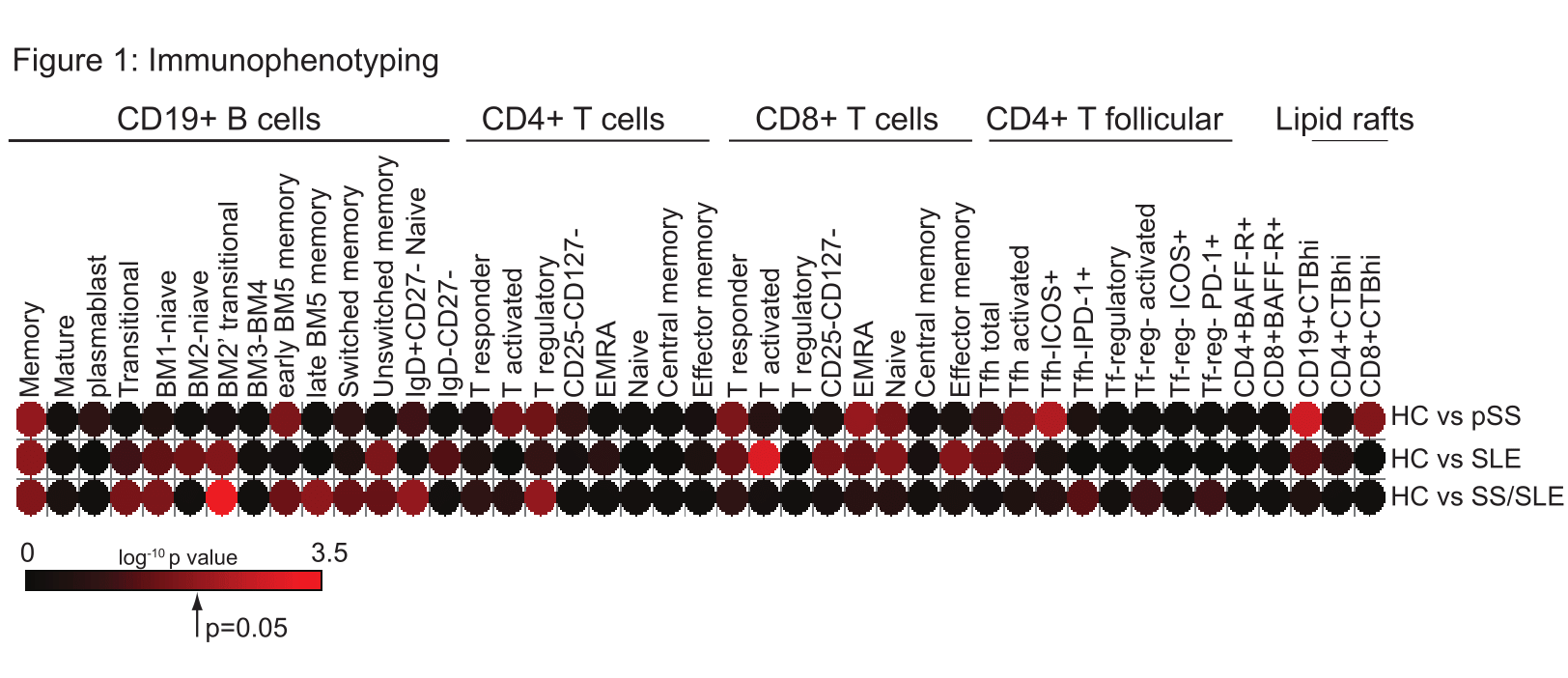
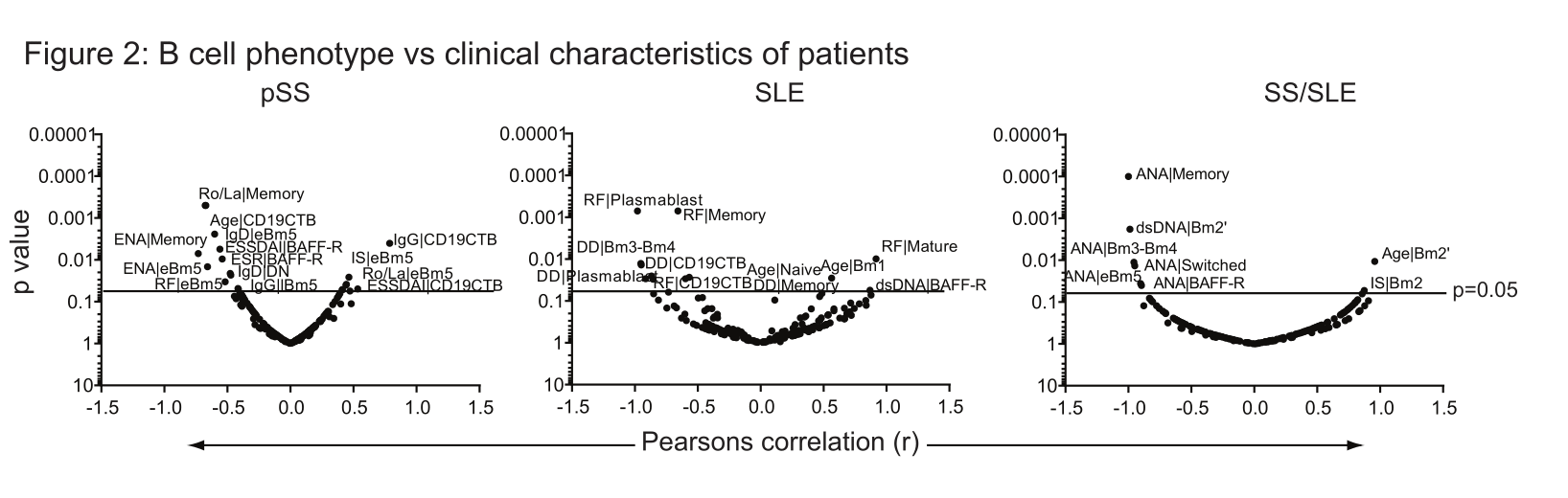
Results: Figure 1 presents the heatmaps assessing the expression of T and B cell populations in HC compared to patients with SS, SLE and SS/SLE. Lipid rafts were significantly elevated in B cells from patients with SS and SLE but not SLE/SS. Figure 2 shows the correlation between different immune cell populations and clinical and laboratory parameters. Figure 3 shows altered colocalisation of BAFF-R, Ig D and lipid rafts in patients with pSS, SLE and SS/SLE compared to HC.
Conclusion: This is the first comprehensive immunophenotype analysis performed in patients with pSS and SS/SLE, which identified that the SS/SLE patient group is immunologically distinct from pSS and SLE patients. The SS/SLE group had the most striking B cell phenotype abnormalities compared to patients with pSS or SLE (increased Bm2 cells and decreased early and late Bm5 cells). These abnormalities suggest a disturbance of B cell trafficking in the patient groups, and a possible bias towards plasma cell differentiation (as all disease groups had low memory B cells). The significant correlation between lipid raft expression and disease activity (ESSDAI score) in patients with pSS suggests abnormal B cell signalling. This could be relevant for the variability of patients’ response to biologic treatments in SLE compared to pSS, as B cell targeted monoclonal antibodies are internalised within the lipid rafts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Thompson N, Gandhi A, Radmore R, Cho S, Isenberg DA, Jury E, Ciurtin C. Increased Expression of B-Cell Lipid Rafts in Patients with Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome Correlated Positively with Disease Activity Score, Suggesting a B Cell Activated State Potentially Relevant for the Disease Pathogenesis and Response to Biologic Therapies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-expression-of-b-cell-lipid-rafts-in-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-correlated-positively-with-disease-activity-score-suggesting-a-b-cell-activated-state-potentially-releva/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-expression-of-b-cell-lipid-rafts-in-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-correlated-positively-with-disease-activity-score-suggesting-a-b-cell-activated-state-potentially-releva/