Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose :Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) die mainly of cardiovascular/cerebrovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, infections, or malignancies. In recent years, the ratio of infections and respiratory diseases associated with RA as causes of deaths has been decreasing, whereas that of malignancies increasing. A possible reason is recent changes in RA therapy, namely, elevated dose of methotrexate (MTX) or popularized biologics. Incidence of malignancies varies depending on studies because it is strongly affected by regional or racial differences among cohorts. This study is to disclose incidence and risk of malignancy in Japanese patients with RA.
Methods : Data from RA patientsregistered in a nationwide Japanese cohort database (NinJa: National Database of Rheumatic Diseases by iR-net in Japan) from 2003 to 2011 were used. To adjust difference of population composition and compare the incidence of malignancy between RA patients and general population, standardized incidence rates (SIRs) were calculated. An SIR is a ratio between actually obtained number of malignancies from the cohort and expected number estimated using incidence of age- and sex-matched Japanese population.
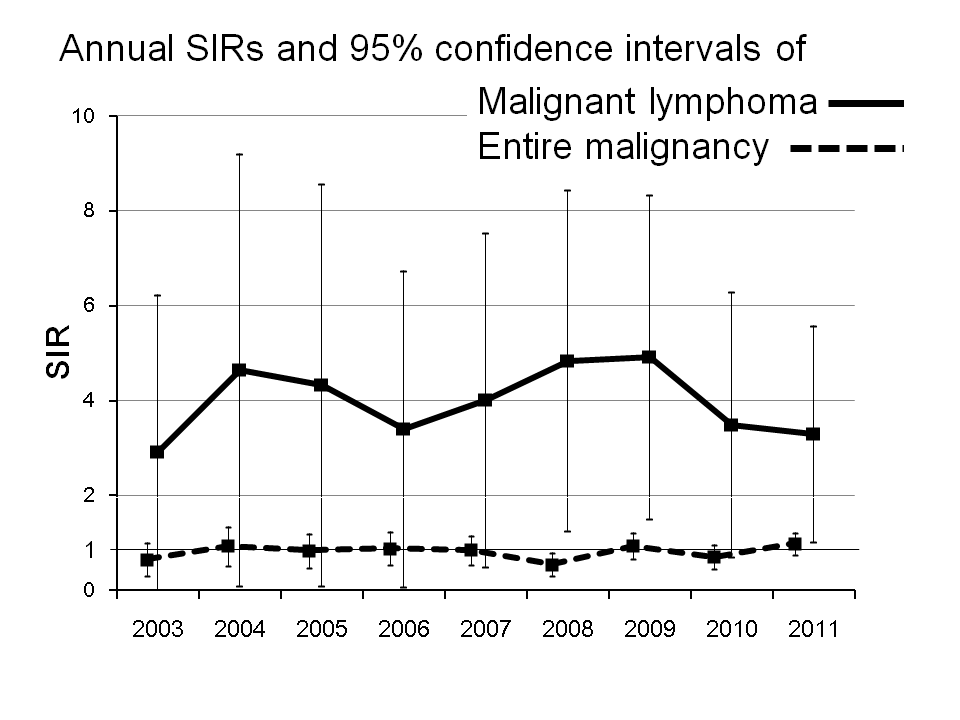
Results : In 9 years the cohort comprised of 55003 patient-years (80% females and 18% males) yielded 444 malignancies, which contained 300 (69%) females and 137 (31%) males, including 6 patients with multiple malignancies. Most frequent malignancy was lung cancer (n=71) followed by gastric (n=59) and breast cancer (n=53). SIR for entire malignancies was 0.96 (95% confidence interval 0.87-1.05), which was consistent with that in the general population. SIRs for malignant lymphoma (ML) in both sexes (SIR 4.01) and bladder cancer in females (SIR 2.80) were significantly higher, whereas several malignancies including rectal cancer in both sexes (SIR 0.49), colon cancer in females (SIR 0.89), or liver cancer in both sexes (SIR 0.28) had significantly lower SIRs. Number of patients on MTX therapy and their dose of MTX have been increasing, while annual SIRs for entire malignancies and ML remained steady (figure).
Conclusion : RA patients had no higher incidence for entire malignancies but should be cared for several malignancies including ML.
Disclosure:
A. Hashimoto,
None;
N. Chiba,
None;
J. Nishino,
None;
T. Matsui,
None;
S. Tohma,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-malignancy-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-from-a-japanese-large-observational-cohort-ninja/
