Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1434–1466) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with psoriasis (PsO), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) are at increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) due to systemic inflammation and cardiometabolic burden. Secukinumab, a fully human interleukin (IL)-17A inhibitor, has demonstrated long-term efficacy and safety across multiple indications. We assessed the 5-year incidence of MACE and baseline cardiovascular (CV) risk factors in patients with and without CV risk factors who were treated with secukinumab in the real-world SERENA study.
Methods: SERENA (CAIN457A3403) is a non-interventional, prospective real-world study conducted across 19 countries in patients with moderate to severe chronic PsO, PsA, or radiographic axSpA (r-axSpA), who received secukinumab for ≥16 weeks before enrollment. MACE were defined using MedDRA v26.1 (including myocardial infarction, stroke, and CV death). Exposure-adjusted incidence rates (EAIRs) were calculated per 100 patient-years (PY). Descriptive comparisons of CV risk factors (age ≥60 years, BMI ≥30 kg/m², disease duration ≥15 years, and diabetes) were performed between patients with and without MACE. No formal statistical comparisons were made.
Results: Among 2927 patients (PsO: 1842; PsA: 579; r-axSpA: 506), 35 MACE were reported during 9679 PY: 24 in PsO, 7 in PsA, and 4 in r-axSpA. EAIRs were 0.39 (95% CI: 0.25 – 0.58), 0.38 (0.15 – 0.78), and 0.23 (0.06 – 0.60) per 100 PY, respectively; equivalent to 3.9, 3.8, and 2.3 events per 1000 PY. These rates are lower than those reported in biologic-naïve psoriatic disease cohorts (14.5–16.4/1000 PY),1,2 as well as in patients with and without prior biologic experience: 7.4/1000 PY in PsA and 6.0/1000 PY in axSpA3. Among patients who experienced MACE, 42.9% were ≥60 years old, 31.4% were obese, 34.3% had long-standing disease (≥15 years), and 17.1% had diabetes vs 9.3% in non-MACE patients. Most events occurred in individuals with traditional CV risk factors, however there was no meaningful difference in baseline characteristics compared to patients who did not experience MACE (Table 1). No multivariable analysis was conducted due to the low event count.
Conclusion: These results support the favorable long-term CV safety profile of secukinumab in patients with PsO, PsA, and axSpA. Over five years of treatment in a real-world setting, MACE were infrequent, and incidence rates remained low and stable across indications, including patients with baseline CV risk. The lower observed incidence than that reported in biologic-naïve cohorts,1-3 is in line with the hypothesis that IL-17A inhibition with secukinumab may help reduce the incidence of MACE in these populations.
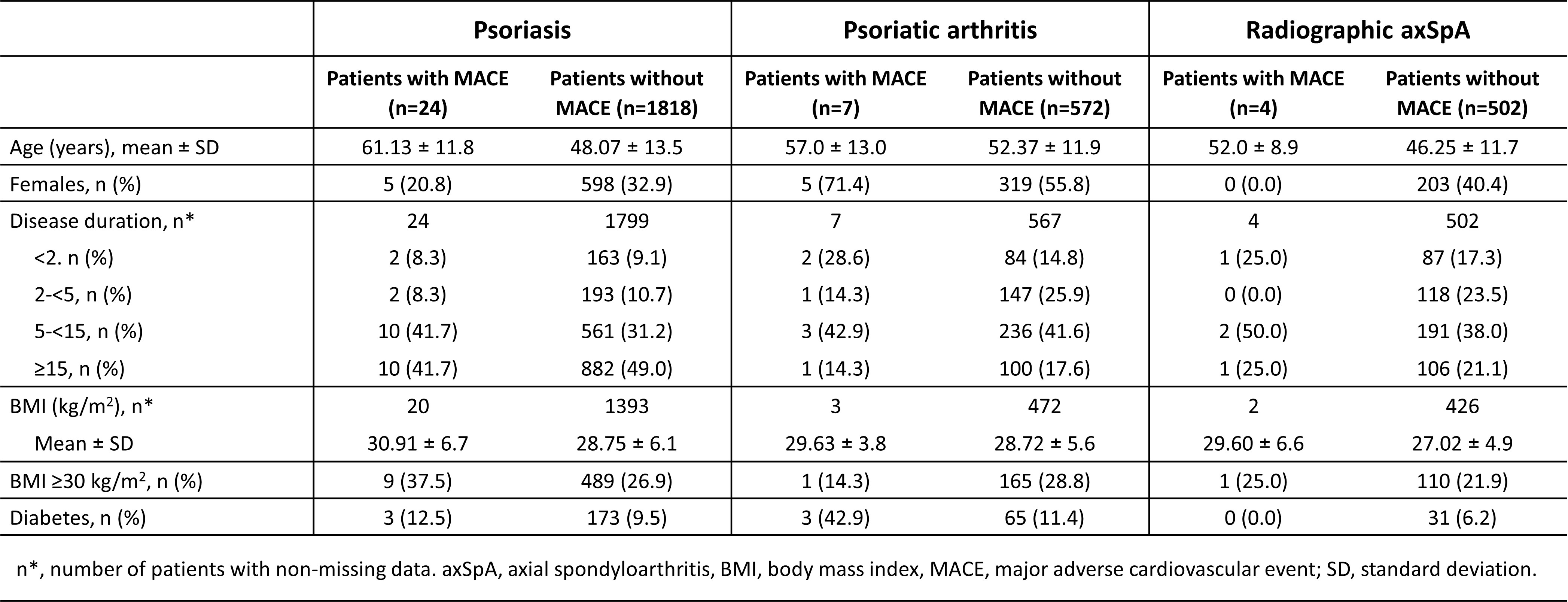 Table 1. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics
Table 1. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiltz U, Sfikakis P, Bounas A, Gullick N, LESPESSAILLES E, Brandt-Juergens J, Rashkov R, Vizcaya C, Clemens A, Gómez L, Hoyt K, Bao W, Gaffney K. Incidence of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE) in Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients With and Without Cardiovascular Risk Factors Treated With Secukinumab: Five-Year Safety Data from the Real-World SERENA Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-major-adverse-cardiovascular-events-mace-in-psoriasis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-with-and-without-cardiovascular-risk-factors-treated-with-secukinumab-fi/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-major-adverse-cardiovascular-events-mace-in-psoriasis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-with-and-without-cardiovascular-risk-factors-treated-with-secukinumab-fi/
