Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes I: COVID-19 (0464–0468)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 5:00PM-5:50PM
Background/Purpose: The prevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG infection was estimated at 9.7% in the Geneva population end of April 2020. (1) Immunosuppressed patients may be at increased risk of developing severe forms of COVID-19. It is unknown whether the increasing risk is due to immune-mediated diseases by themselves or to specific immunosuppressive therapies. We postulated that long-lasting cell-depleting therapies may increase the risk of severe COVID-19 more than targeted anti-cytokine therapies.
Methods: We included all patients who received infliximab or rituximab at the Rheumatology Division of the Geneva University Hospitals between September 1st 2019 and February 29, 2020 (last 6 months). We called each patient and administrated a questionnaire with predefined questions on incident COVID-19 symptoms and COVID-19 diagnosis between March 1st, 2020 and end of May 2020, which represents the first wave of the COVID 19 pandemic in Switzerland.
We compared patient characteristics using Wilcoxon test for continuous variables and Fisher test for categorical variables. We calculated prevalence, incidence and their crude and adjusted prevalence and incidence ratio with generalised estimating equations using a Poisson distribution. We adjusted the prevalence and incidence ratio by quartiles of a propensity score based on age, gender, disease (rheumatoid arthritis (RA) vs other), smoking and presence of a comorbidity.
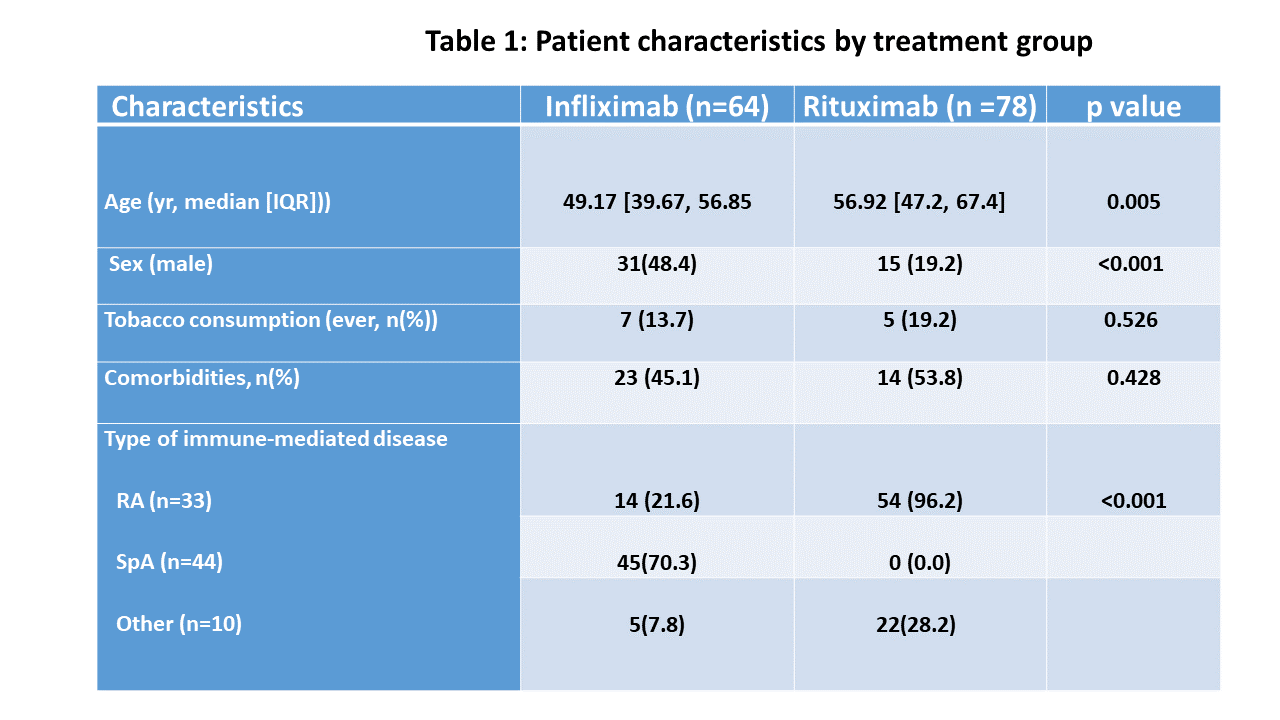
Results: During the study period, 151 patients received either rituximab (RTX, n=86) or infliximab (IFX, n=65). We were able to retrieve complete COVID-19 information from 142 (94.0%) patients. RTX patients were older than IFX patients with an average of 56.6 (47.2, 67.4), and significant different in the underlying diagnoses (more RA on RTX and more spondyloarthritis (SpA) on IFX) (Table 1).
Overall, 15 (10.5%) patients have reported symptoms of plausible COVID-19; 9 (13.8%) on IFX and 6 (7.0%) on RTX (p= 0.18). All 15 patients (RTX=7, IFX=8) were tested for Sars-Cov2 using nasopharyngeal swab PCR. Three patient developed severe pulmonary manifestations requiring hospitalisation (two hospitalized in intensive care units, one died). These patient’s were 74, 62, 45 years of age respectively, without any of the established at risk comorbidities, but tobacco smoking.
During this first wave of COVID-19 epidemic, the prevalence of plausible COVID-19 in these immunosuppressed patients was 13.8% (95%CI: 7.5-25.4) on IFX, compared to 7.0% (95%CI: 3.2-15.1) on RTX (crude p=0.17, adjusted p=0.03). The incidence rate of COVID-19 was 2.10 (95% CI: 0.94-3.92) cases/1000 patients-days on IFX, compared to 0.97 (0.35-2.10) cases/1000 patients-days on RTX, a significantly increased rate with IFX compared to RTX (crude p< 0.001, adjusted p=0.03).
The incidence rate of severe COVID-19 was null on IFX (95%CI: 0.0-0.76) compared to 0.47 (0.10-1.38) cases/1000 patients-days on RTX. On RTX, tree out of six patients had a severe evolution compared to zero out of 9 patients on IFX (p=0.04).
Conclusion: The incidence of severe COVID-19 tended to be higher in patients on RTX compared to IFX. The study is ongoing, with an analysis of a broader patient sample.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Melong Pianta C, Lauper K, Courvoisier D, Cunningham T, Allali D, Finckh A. Incidence of COVID-19 in Patients Treated with Infliximab Compared to Patients Treated with Rituximab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-covid-19-in-patients-treated-with-infliximab-compared-to-patients-treated-with-rituximab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-covid-19-in-patients-treated-with-infliximab-compared-to-patients-treated-with-rituximab/