Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Vasculitis Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Incidence
and Intensity of 18FDG Uptake on Whole Body PET/CT in Patients with
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
C.E. Owen1,2,
A.M.T. Poon2,3, S.T. Lee2,3,4, K. Pathmakaj3,
C. McMenamin1, A.M. Scott2,3,4, R.R.C. Buchanan1,2
1Department of Rheumatology, Austin
Health, Heidelberg VIC 2Department of Medicine, University of
Melbourne, Parkville VIC 3Department of Molecular Imaging and
Therapy, Austin Health, Heidelberg VIC 4Olivia Newton-John Cancer
Research Institute, Heidelberg VIC
Background/Purpose:
To characterise the incidence
and intensity of 18Fluorodeoxyglucose (18FDG) uptake on
whole body PET/CT in untreated patients with newly diagnosed Polymyalgia
Rheumatica (PMR).
Methods: Patients with newly diagnosed PMR according
to the 2012 EULAR/ACR Classification Criteria[1]
were prospectively recruited. A whole body scan from skull vertex to toes
(including dedicated hand views) was performed at baseline using a Phillips TF
PET/CT machine in all untreated patients. A range of demographic, clinical and
laboratory data were collected. Images were reviewed with Medview software by
an experienced Nuclear Medicine Physician. Both qualitative and
semi-quantitative (standardised uptake value maximum [SUVmax])
analysis of joint and vascular 18FDG uptake were performed. Statistical
analyses were undertaken using Stata 13.0 (Statcorp, College Station, TX, USA).
Results: Thirteen patients with PMR were
recruited. Mean age was 68.47 years, there was a slight male predominance (53.85%)
and all were Caucasian. All patients reported bilateral shoulder pain at presentation,
but hip symptoms were less common (69.23%). Disease activity was high (mean
PMR-AS 80.29) and the median HAQ-DI score was 2.125. In addition to involvement
of the shoulder capsule (11/13, 84.62%), hip capsule (11/13, 84.62%),
trochanteric bursae (12/13, 92.31%) and interspinous bursae (10/13, 76.92%), a
high incidence of 18FDG uptake at the ischial tuberosities (12/13, 92.31%)
and knee capsule (9/13, 69.23%) was seen. Involvement of the palmar aspect of
the hands/wrists and feet was also observed in 5/13 (38.46%) and 2/13 (15.38%)
cases respectively. With respect to SUVmax at sites of 18FDG
uptake, the highest mean result occurred at the ischial tuberosities (4.38)
followed by the shoulder capsule (3.94), interspinous bursae (3.62) and knee
capsule (3.48).
Conclusion:
Patients with newly
diagnosed, untreated PMR exhibit most intense 18FDG uptake at the
ischial tuberosities on whole body PET/CT. Frequent involvement of peripheral
joints, especially the knee capsule, is also observed.
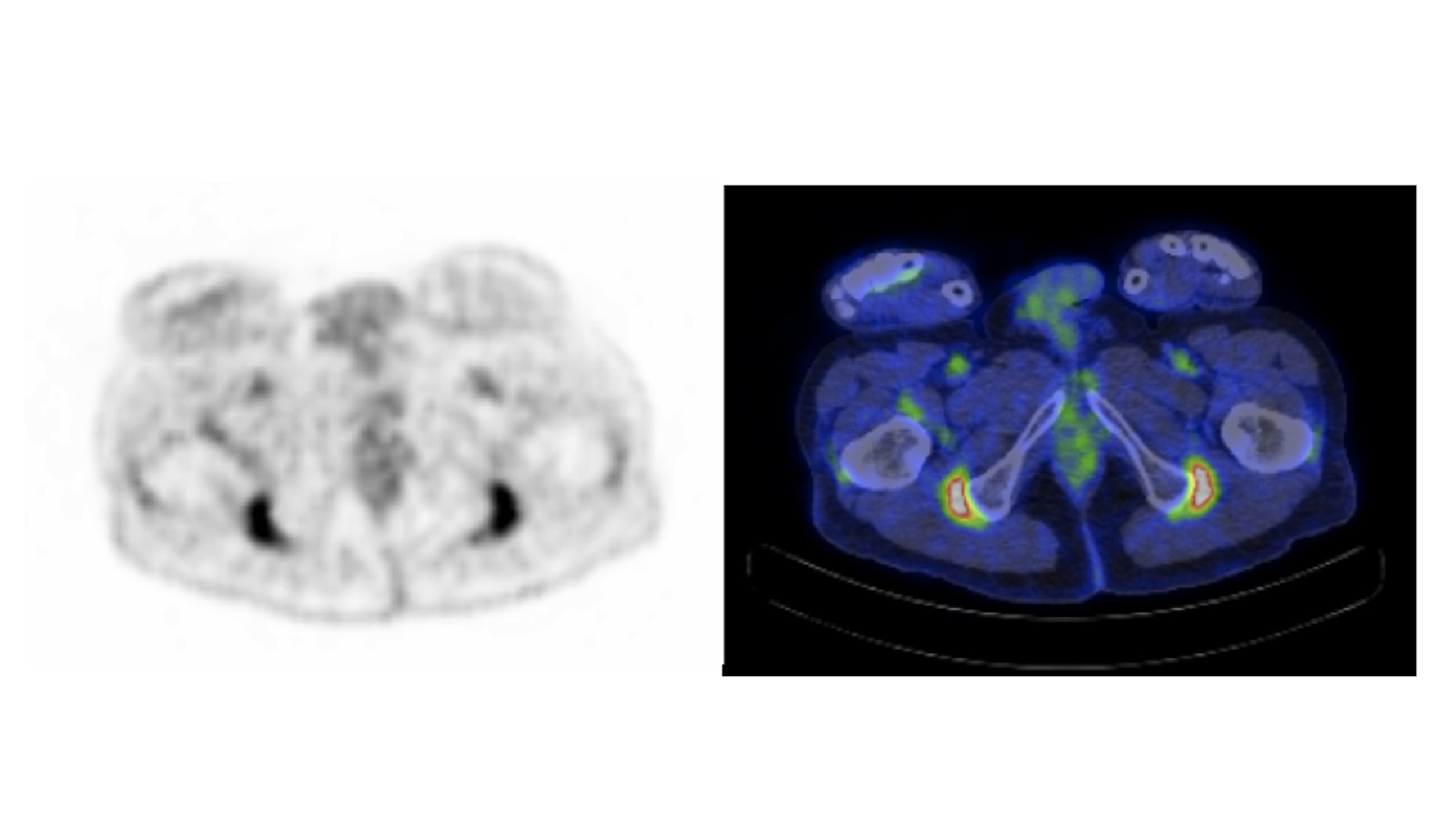
Figure 1: Intense 18FDG uptake at
the ischial tuberosities in a patient with newly diagnosed, untreated PMR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Owen C, Poon A, Lee ST, McMenamin C, Pathmaraj K, Scott A, Buchanan R. Incidence and Intensity of 18fdg Uptake on Whole Body PET/CT in Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-and-intensity-of-18fdg-uptake-on-whole-body-petct-in-patients-with-polymyalgia-rheumatica/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-and-intensity-of-18fdg-uptake-on-whole-body-petct-in-patients-with-polymyalgia-rheumatica/