Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Response to therapy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is heterogeneous. Early identification of patients (pts) who are unlikely to achieve a meaningful clinical response may inform decisions to stop treatment in individual pts (Wijbrandts and Tak; Mayo Clin Proc; in press). This would improve benefit:risk ratio in pts who continue treatment, and allows earlier cycling to alternate treatments for those who do not respond. Sirukumab (SIR) is a human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the cytokine IL-6 with high affinity, and has demonstrated efficacy in Phase 3 RA studies. This post hoc analysis explored whether lack of change in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) after a single dose of SIR could be used to identify pts with a low likelihood of clinical response after continued treatment.
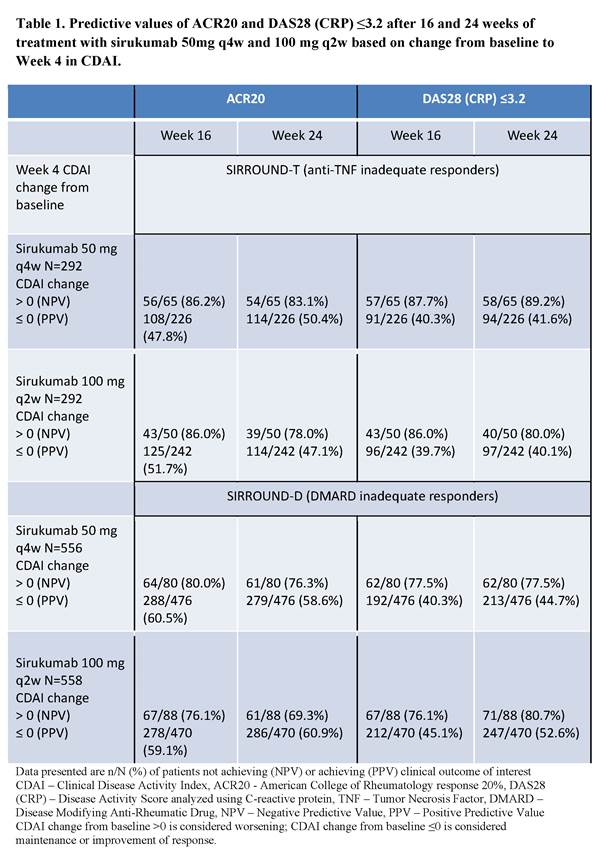
Methods: We evaluated clinical response to SIR in two Phase 3 clinical trials in anti-TNF inadequate responders (IRs; SIRROUND-T; Aletaha D, et al. Lancet. 2017;389(10075):1206-1217) and DMARD IRs (SIRROUND-D) using CDAI – a simple composite measure of disease activity which does not include measurement of inflammatory markers. In both studies pts were randomized 1:1:1 to placebo, SIR 50 mg every 4 weeks (q4w), or SIR 100 mg every 2 weeks (q2w). We evaluated whether a change from baseline in CDAI >0 (representing worsening) at Week 4 could predict clinical outcomes including ACR20 (primary endpoint) and DAS28 (CRP)≤3.2 at Week 16 in pts receiving SIR 50mg q4w in SIRROUND-T. Analyses were repeated for Week 24 outcomes, SIR 100 mg q2w and in SIRROUND-D.
Results: A significantly greater proportion of pts achieved the primary endpoint of Week 16 ACR20 response on both doses of SIR compared to placebo in SIRROUND-T and -D (p<0·001). Worsening in CDAI at Week 4 after a single dose of SIR 50mg q4w was predictive of non-response at Week 16 in SIRROUND-T: 22% (65/291) of pts had CDAI worsening at Week 4; of these pts more than 85% did not achieve ACR20 or DAS28 (CRP)≤3.2 at Week 16 (NPV in Table 1). The 22% of pts with CDAI worsening at Week 4 could consider stopping SIR at Week 4 based on predicted non-response. In the remaining subgroup of pts, there was an approximate 20% relative increase in ACR response rates compared to the overall population rates. Results were comparable for the SIR 100 mg q2w dose, Week 24 outcomes, and for both doses in SIRROUND-D (Table 1).
Conclusion: SIR has demonstrated robust efficacy in RA. Lack of clinical efficacy at 16 weeks can be predicted using worsening from baseline in CDAI after a single dose of SIR 50mg. This approach can be further refined using different cut-offs and methods of prediction. It can also be extended to determine probabilities of achieving other outcomes, e.g. remission, which may be specific to the individual pt. These results have the potential to enable early treatment discontinuation decisions for individuals who are unlikely to respond to continued therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Daga S, Aletaha D, Hsu B, Gilbride J, Christie J, Loza M, Dasgupta B, Campbell K, Brown K, Rao R, Tak PP. Inadequate Clinical Response to Sirukumab, an Anti-IL-6 Monoclonal Antibody, Can be Predicted after a Single Dose of Treatment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inadequate-clinical-response-to-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-monoclonal-antibody-can-be-predicted-after-a-single-dose-of-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inadequate-clinical-response-to-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-monoclonal-antibody-can-be-predicted-after-a-single-dose-of-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/