Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: SLE – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Deficiency of transaldolase (TAL) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) predisposes to oxidative stress mediated autoimmune hepatitis[1, 2]. Along with TAL, HRES-1/Rab4 (Rab4A), a small GTPase responsible for mitochondrial turnover, is overexpressed in T cells of SLE patients[3] and livers of lupus-prone mice[2]. The expression of Rab4A is dependent on TAL activity[2]. Therefore, we investigated the impact of TAL and Rab4A in pristane-induced and spontaneous models of SLE.
Methods: C57Bl/6J wild-type (WT) mice and strains constitutively lacking TAL (TALKO)[1] or Rab4A in T cells were injected intraperitoneally with pristane (500µL/20g body weight). Mice lacking Rab4A were generated on both C57Bl/6J and lupus-prone SLE1.2.3. backgrounds. The number of inflammatory foci was used as a measurement of lymphocytic inflammation within the mouse livers. Vasculitis measurement[4] was adapted for H&E-stained liver sections. Student’s T test was used to test significance; p values < 0.05 were considered significant for hypothesis testing.
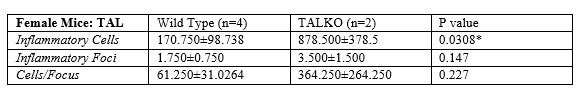
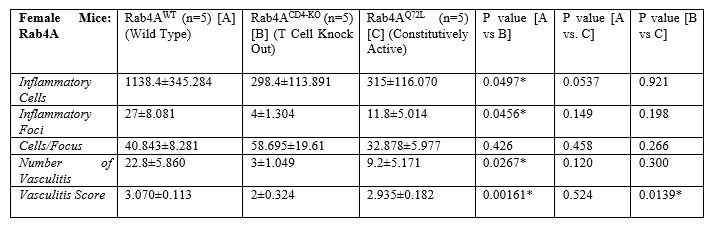
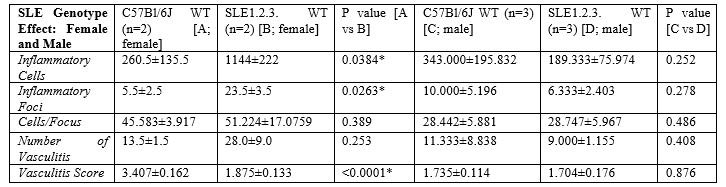
Results: Among pristane-injected female mice, TALKO mice had more inflammatory cells relative to WT controls (p=0.0309). C57Bl/6J Rab4ACD4-KO mice had fewer inflammatory foci (p=0.0456), inflammatory cells (p=0.0497), and vasculitis events (p=0.0266) compared to WT controls. The average vasculitis score was also decreased in C57Bl/6J Rab4ACD4-KO animals compared to C57Bl/6J Rab4AWT (p=0.00160) and C57Bl/6J Rab4AQ72L (p=0.0139) animals. The number of inflammatory foci (p=0.0263) and inflammatory cells (p=0.0384) was significantly higher in SLE1.2.3. mice versus C57Bl/6J controls. There was no difference in vasculitis incidents between the two genotypes; the vasculitis score was lower in SLE1.2.3 mice vs. C57Bl/6J (P< 0.0001). Relative to WT C57Bl/6J controls, SLE1.2.3. mice or pristane-injected TALKO male mice failed to show differences in liver inflammation.
Conclusion: Constitutive deletion of TAL or T-cell-specific deletion of Rab4A predisposes to inflammation and vasculitis in the liver, which is also enhanced in lupus-prone mice. These changes were confined to females, which is consistent with a similar gender bias in humans.
1 R. Hanczko et al., “Prevention of hepatocarcinogenesis and increased susceptibility to acetaminophen-induced liver failure in transaldolase-deficient mice by N-acetylcysteine,” (in eng), J Clin Invest, vol. 119, no. 6, pp. 1546-57, Jun 2009.
2 Z. Oaks et al., “Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Liver and Antiphospholipid Antibody Production Precede Disease Onset and Respond to Rapamycin in Lupus-Prone Mice,” (in eng), Arthritis Rheumatol, vol. 68, no. 11, pp. 2728-2739, Nov 2016.
3 D. R. Fernandez et al., “Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin controls the loss of TCRzeta in lupus T cells through HRES-1/Rab4-regulated lysosomal degradation,” (in eng), Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), vol. 182, no. 4, pp. 2063-2073, 2009.
4 V. R. Chowdhary, J. P. Grande, H. S. Luthra, and C. S. David, “Characterization of haemorrhagic pulmonary capillaritis: another manifestation of Pristane-induced lupus,” (in eng), Rheumatology (Oxford), vol. 46, no. 9, pp. 1405-10, Sep 2007.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Patel A, Huang N, Perl A. Inactivation of Transaldolase and HRES-1/Rab4 Predisposes to Hepatitis in a Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inactivation-of-transaldolase-and-hres-1-rab4-predisposes-to-hepatitis-in-a-mouse-model-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inactivation-of-transaldolase-and-hres-1-rab4-predisposes-to-hepatitis-in-a-mouse-model-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/