Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We have recently validated the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis Scale (QOL-RA). Redundancy between questions Nº 3 and Nº 6 was observed, and it was influenced by age and disease duration. For this reason, with the author’s permission, we have changed these questions and developed a new version of Spanish QOL-RA. The aim of our study was to validate this Spanish version in patients with RA.
Methods: A cross-sectional multicenter study was carried out. Patients ≥18 years old, with a diagnosis of RA according to ACR-EULAR 2010 criteria were included. Patients with difficulties in answering the questionnaire (illiterate, blind) and with decompensated comorbidities were excluded. Sociodemographic data, comorbidities, RA characteristics, disease activity current treatment were registered. Questionnaires were administered to assess quality of life by EQ-5D-3L and QOL-RA, functional capacity by HAQ-A and depression by PHQ-9. The time to complete and calculate both quality of life questionnaires was measured, and the difficulties that the patients presented to complete any item were recorded. The QOL-RA was re-administered in 20 patients to evaluate reproducibility. Statistical analysis: Student´s T, ANOVA and Chi2 tests. Spearman correlation. Reliability by Cronbach´s alpha. Reproducibility using ICC. QOL-RA linear tendency based on RA activity by multinomial logistic regression with completed factorial model. Multiple linear regression.
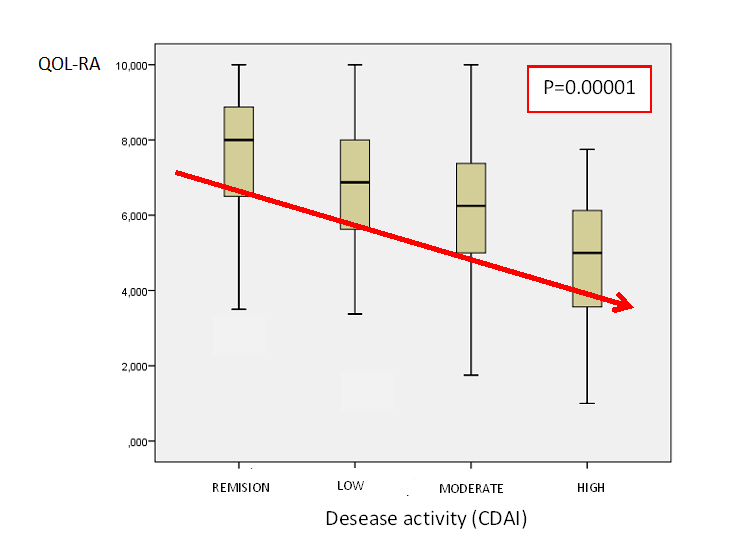
Results: 430 patients were included. 87.7% were females, with a median (m) age of 53.1 years (IQR 45-62) and m disease duration of 8.9 years (IQR 4-16). Disease activity by DAS28-ESR was m 2.9 (IQR 1.9-3.9). The median of QOL-RA was 6.6 (IQR 5.3-8) and it had a good correlation with EQ-5D-3L (Rho: 0.6), PHQ-9 (Rho: -0.56), HAQ-A (Rho: -0.55), CDAI (Rho: -0.47) and DAS28-ESR (Rho: -0.4). Worse QOL-RA was observed in current smokers (mean 6.1±1.7 vs 6.6±1.9, p= 0.016), unemployed (mean 6.1±1.8 vs 6.9±1.8, p=0.0001), patients not doing physical activity (mean 6.3±1.9 vs 7±1.9, p=0.0001) and those with morning stiffness (mean 5.8±1.9 vs 7.1 ±1.7, p=0.0001). It showed very good reliability (0.97) and reproducibility (ICC= 0.96 IC 95% 0.90-0.99). Ceiling and floor effects were 2.8% and 0.7%, respectively. Only 0.9% of the questionnaires presented at least one missing answer. There was no redundancy between questions. Patients with higher disease activity had a significant poorer quality of life. (Figure 1) In the multivariate analysis, using QOL-RA as dependent variable, adjusting by age, sex and disease duration, disability, disease activity, and the presence of depression were independently associated to worse quality of life.
Conclusion: This new version of QOL-RA demonstrated better construct validity, reproducibility and reliability compared to the original version and it was easy to complete and calculate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Isnardi CA, Capelusnik D, Schneeberger EE, Correa MDLA, Lim R, Hu M, Tapia MJ, Kerzberg EM, Blanco ES, Benavidez FL, Gonzalez Lucero L, Barbaglia AL, Bazzarelli M, Maldonado Ficco H, Pérez SK, Hartvig C, Salcedo M, Citera G. Improving the Performance of the Spanish Version of QOL-RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-the-performance-of-the-spanish-version-of-qol-ra/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-the-performance-of-the-spanish-version-of-qol-ra/