Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: ARHP Fibromyalgia, Soft Tissue Disorders, Regional and Specific Clinical Pain Syndromes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Fibromyalgia patients complain of poor sleep. We assessed whether patients with fibromyalgia who were able to significantly improve their sleep, including sleeping uninterrupted through the night, had less pain. It is possible that solid rest at night can lead to muscle relaxation and central nervous system rest and result in improvement in fibromyalgia symptoms.
Methods: 37 patients were given the opportunity to participate in this rheumatology office trial. Patients with diagnosed fibromyalgia according to the 2010 ACR criteria who had poor sleep were given amitriptyline, doxepin, or trazodone in gradually increasing dosages, enough for them to sleep through the night. Those who completed at least two weeks of medication therapy in doses enough to make them sleep well were further evaluated for a response in terms of pain level and fatigue.
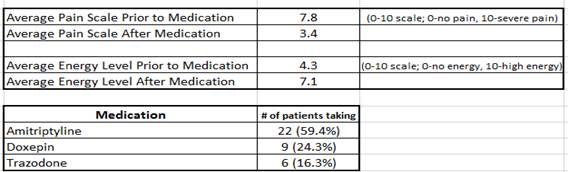
Results: See graph below
Conclusion : In this open label, uncontrolled study, we found that many patients who are able to sleep through the night by using amitriptyline, doxepin, or trazodone had an improvement in pain and global scores for Fibromyalgia. Starting with low dosage given early in the evening, generally 7 PM, and titrating upward until uninterrupted sleep was achieved. Good sustained sleep maybe therapeutic in this illness, but to achieve that may require a significant step-wise increase in these medications until uninterrupted sleep is achieved.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Katz RS. Improving Sleep in Fibromyalgia Patients Ameliorates Their Pain [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-sleep-in-fibromyalgia-patients-ameliorates-their-pain-2/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-sleep-in-fibromyalgia-patients-ameliorates-their-pain-2/