Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: This quality improvement project was conducted to increase pneumococcal vaccination rates in eligible Pediatric Rheumatology Clinic patients. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a leading cause of bacteremia, meningitis, pneumonia, sinusitis, and acute otitis media. Many patients in the Pediatric Rheumatology Clinic are at increased risk of pneumococcal disease secondary to a deficient immune system and/or immunosuppressive medications. Infections remain one of the leading causes of hospitalization and death in patients with certain rheumatic diseases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends both the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) for this high-risk population.
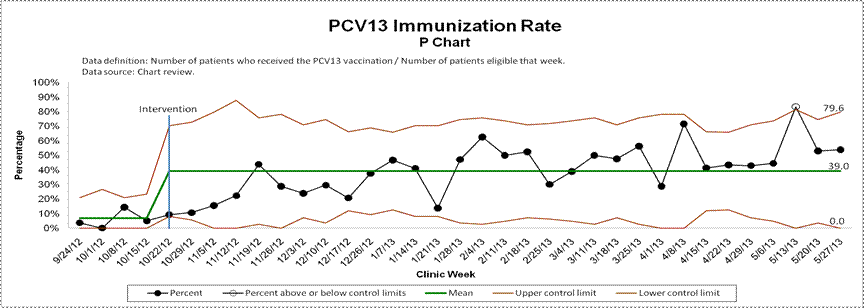
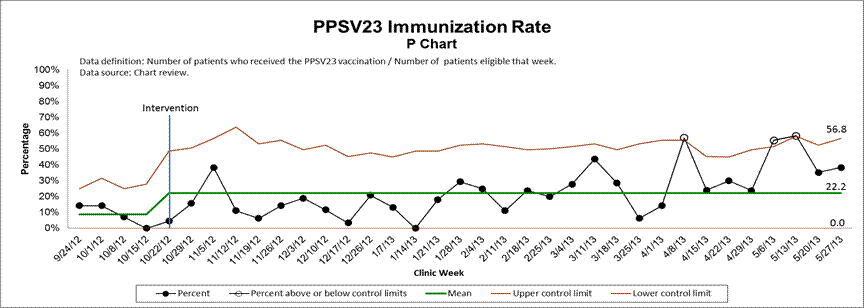
Methods: Baseline immunization rates were assessed for eligible clinic patients over a four week period. Eligible patients include children at least two years old and adults with systemic lupus erythematosus and patients currently on or starting an immunosuppressive medication. Interventions included a presentation to rheumatology providers and nurses, creation of clinic document with immunization algorithm, previsit planning, placing reminders on patient clinic forms, and sending letters to out-of-state patients. Chart reviews of eligible patients occurred throughout the study period. Control charts were established to portray change in immunization rate.
Results: The pre-intervention immunization rate for 90 eligible Pediatric Rheumatology Clinic patients was 6.7% for PCV13, 8.9% for PPSV23, and 0% for both vaccines. Data from 31 weeks were analyzed following the interventions for a total of 679 eligible patient visits and 265 separate patients. The average post-intervention immunization rate was 39.0% for PCV13, 22.2% for PPSV23, and 16.3% for both vaccines. These rates are statistically higher than the pre-intervention rates (p<0.001, p=0.003, and p<0.001, respectively). The final eight weeks of assessment showed a shift above the mean in pneumococcal rates for both PCV13 and PPSV23.
Conclusion: Pneumococcal vaccination is an important part of the care for systemic lupus erythematosus patients and pediatric rheumatology patients on immunosuppressive medications. Simple interventions through this quality improvement project led to a marked increase in pneumococcal vaccination rates in this vulnerable population.
Disclosure:
J. G. Harris,
None;
K. I. Maletta,
None;
B. Ren,
None;
J. C. Olson,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-pneumococcal-vaccination-rate-in-the-pediatric-rheumatology-clinic/