Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstracts
Background/Purpose: PF-04236921 is a fully human mAb that binds to circulating IL-6 and neutralizes its activity. This may be beneficial in reducing the disease manifestations of active SLE. The purpose was to assess the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of PF-04236921 in subjects with active generalized SLE.
Methods: 183 subjects with active SLE (SLEDAI ≥6 and ≥1 BILAG 2004 A or ≥2 Bs) were randomized to receive 3 doses of of PF-04236921 (10, 50, or 200 mg) or placebo administered subcutaneously every 8 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of SLE Responder Index 4 (SRI-4) responders at Week 24 using a general linear mixed model. The BILAG-based Combined Lupus Assessment (BICLA), frequency of severe flares, and SF-36 were also evaluated.
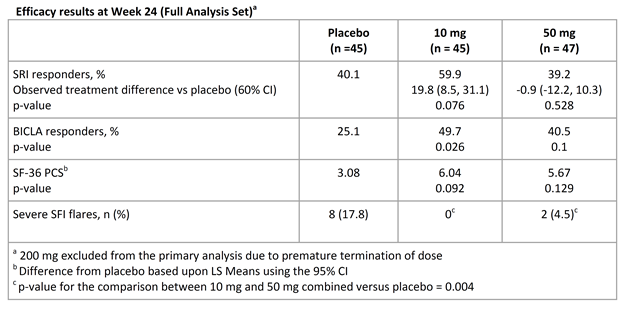
Results: The majority of subjects were female (91.8%), mean age 40.4, with musculoskeletal and mucocutaneous organ system involvement. Baseline demographics were similar across groups. At Week 24, there were more responders in the 10 mg group compared with the placebo group for the SRI (p = 0.076) and BICLA (p = 0.026). Improvement in the SF-36 PCS domain was also noted for the 10 mg group compared with the placebo group (p = 0.092). For the 50 mg group there were no significant differences versus the placebo group for the SRI (p = 0.528) or BICLA (p = 0.1). In contrast, there was a significant reduction in the frequency of severe SELENA-SLEDAI Flare Index (SFI) flares for the combined 10 and 50 mg groups compared with the placebo group (p = 0.004). In subjects with higher disease activity at baseline, a greater effect size was observed for the SRI and BICLA in a post-hoc analysis. Adverse events (AEs), infectious AEs, and discontinuations due to AEs were comparable across groups. The rate of SAEs was highest in the placebo and 200 mg groups and the rate of serious infections was highest in the 200 mg group. There were 4 deaths; 3 in the 200 mg group [cardiorespiratory arrest, urosepsis with pulmonary embolism (PE), and disseminated tuberculosis] and 1 in 10 mg group (suspected PE); further dosing of the 200 mg group was subsequently terminated.
Conclusion: An efficacy signal was apparent following the administration of an IL-6 mAb notably with regard to severe flare reduction. The safety profile with 10 and 50 mg doses appeared acceptable; dosing with 200 mg was terminated due to safety concerns.
Disclosure:
D. J. Wallace,
None;
S. Popa,
None;
A. J. Spindler,
None;
A. Eimon,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
T. González-Rivera,
None;
T. O. Utset,
Eli Lilly and Company,
5,
GlaxoSmithKline,
5;
M. Petri,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
2;
P. E. Lipsky,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
J. T. Merrill,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
V. Strand,
Abbvie,
5,
Alder,
5,
Amgen,
5,
Antares,
5,
AstraZeneca,
5,
Biogen Idec,
5,
Biotest,
5,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
5,
Celltrion,
5,
Corrona,
5,
Crescendo,
5,
Genetech,
5,
GlaxoSmithKline,
5,
Hospira,
5,
Incyte,
5,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
5,
Merck Serono,
5,
Mesoblast,
5,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Protalex,
5,
Regeneron,
5,
Sanofi-Aventis Pharmaceutical,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Genzyme Corporation,
5,
Takeda,
5,
UCB,
5,
Vertex,
5;
J. Wajdula,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
J. Christensen,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
C. Li,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
A. Diehl,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
M. Vincent,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
J. Beebe,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
S. Sridharan,
Pfizer Inc,
3.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvement-of-disease-activity-and-reduction-of-severe-flares-following-subcutaneous-administration-of-an-il-6-monoclonal-antibody-mab-in-subjects-with-active-generalized-systemic-lupus-erythematos/