Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstracts
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab (SEC; AIN457), a fully human anti–IL-17A monoclonal antibody, has demonstrated efficacy in phase 3 trials for treatment of plaque psoriasis and preliminary results also support efficacy in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Here we report the efficacy and safety of SEC vs placebo [PBO] and etanercept [ETN] in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis and concomitant PsA.
Methods: Subjects aged ≥18 yrs were randomized 1:1:1:1 to SEC sc 150 or 300 mg, PBO, or ETN sc 50 mg. Subjects received treatment at baseline and weeks 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every four weeks from week 4 through week 48. At week 12, PBO-treated subjects not achieving PASI 75 were re-randomized 1:1 to SEC 150 or 300 mg. Subjects in the ETN arm received ETN 50 mg twice per week from baseline to week 12, and 50 mg once a week thereafter through week 51. The co-primary objectives were to show superiority of SEC vs PBO for Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75 and 5-point investigator’s global assessment (IGA) 0 or 1 response at week 12. A pre-specified subanalysis of PASI responses and changes from baseline in the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index (HAQ-DI) up to week 52 in subjects with concomitant PsA is reported here.
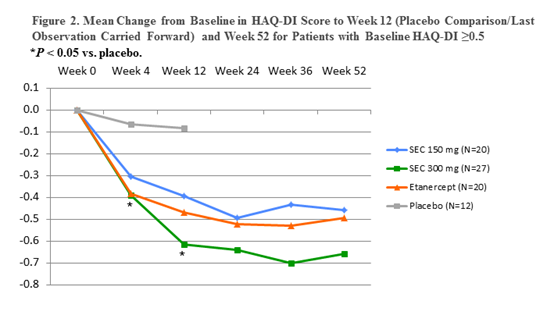
Results: The overall study population consisted of 1306 subjects. In subjects with concomitant PsA (n=192), significant improvements in PASI 75 response rates were observed with SEC 150 mg and 300 mg from week 4. PASI 75 responses at week 12 were: SEC 300 mg, 72%; SEC 150 mg, 59%; ETN, 39%; PBO, 2%; and PASI 90 responses were 44%, 39%, 18%, and 2%, respectively (P < 0.01 for SEC 150 and 300 mg vs PBO; P < 0.01 for SEC 300 mg vs ETN) and responses were sustained through 52 weeks (Fig 1). Improvements in physical functioning as measured by change from baseline in HAQ-DI score (n=158 with evaluable HAQ-DI data) were significantly improved with SEC 300 mg from week 4. HAQ-DI reductions from baseline at week 12 were SEC 300 mg, -0.41 (P < 0.01 for 300 mg vs PBO); SEC 150 mg, -0.19; ETN,-0.29; PBO, 0.02; and reductions were sustained to week 52. HAQ-DI reductions were more pronounced in subjects with greater disability (baseline scores ≥0.5) (Fig 2). Both SEC and ETN were well tolerated with no unexpected safety findings.
Conclusion: In patients with psoriasis and concomitant PsA, SEC improved skin symptoms and physical functioning vs placebo, with benefits evident from week 4 and sustained to week 52. SEC 300 mg demonstrated significantly improved PASI 75/90 responses and greater reductions in HAQ-DI scores compared with ETN. These data strongly support continued evaluation of SEC in patients with PsA.
Disclosure:
A. Gottlieb,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
5,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
2;
R. Langley,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
2,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
5,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
8;
S. Philipp,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
2,
Novartis Pharmaceutical,
5,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
9;
R. Martin,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
3;
C. Papavassilis,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
3,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
1;
S. Mpfofu,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvement-in-psoriasis-symptoms-and-physical-functioning-with-secukinumab-compared-with-placebo-and-etanercept-in-subjects-with-moderate-to-severe-plaque-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-results-o/