Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Despite increased risk of herpes zoster (HZ) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients on immunosuppressive medication, American College of Rheumatology guidelines on HZ vaccination in RA and availability of HZ vaccine that decreases the risk of infection, the rates of vaccination against HZ in RA are very low. The aim of this study was to improve the rate of vaccination and e-record documentation of HZ vaccine in RA patients at high risk for HZ in rheumatology outpatient clinics.
Methods: This study evaluated HZ vaccination and documentation for RA patients using pre- and post-intervention data. All RA patients aged ≥ 60 years were considered eligible for HZ vaccine if they were on or starting DMARDs or starting a biologic agent or steroid >20 mg equivalent of prednisone >3 months. Clinical staff and physicians were educated in vaccine guidelines and planned intervention. Intervention was an electronic medical record (EMR)-based best practice alert (BPA), which is a user friendly system for ancillary staff and physician with integrated vaccine eligibility verification, documentation and vaccine order capability at the time of patient visit. The BPA appeared for eligible patients upon opening the EMR, prompting the medical assistant or nurse to document vaccination status and order HZ vaccine if the patient agreed. The physician subsequently reviewed and confirmed the order. BPA was passed to physician if a patient was unsure. The pre-intervention phase included all eligible RA patients who were seen at the Rheumatology Clinics between 7/1/2012 – 6/30/2013. The intervention phase data was collected for 3 months after implementation of BPA system. Reasons like patient refusal or physician deferral were also documented. The proportion of patients vaccinated and documented among all eligible patients pre- and post-intervention was compared using chi-square tests.
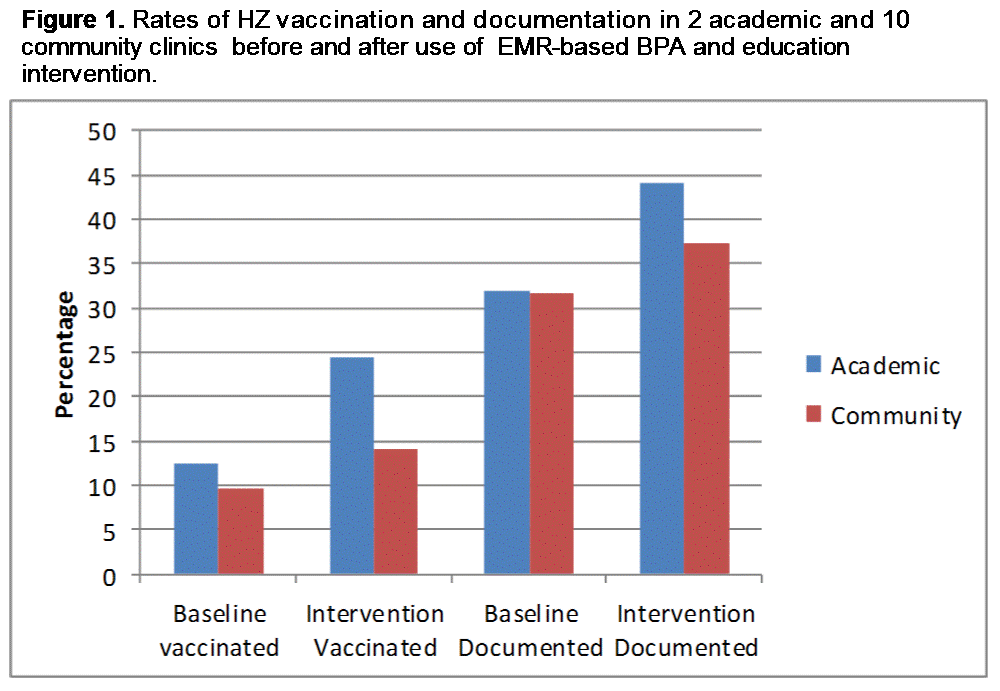
Results: 1846 RA patients were analyzed for pre-intervention (baseline) data (76% female, 90% white, mean age of 72 years) and 1267 patients for the post-intervention data (76% female, 82% white, mean age of 71 years). Overall vaccination rate increased from 9.9 to 15.7% p=0.001, and documentation rate increased from 30.1 to 44.8% p<0.0001. Academic clinic vaccination rate improved from 12.4 to 24.3% p=0.003, documentation rate from 32 to 44% p=0.04. Community clinic vaccination rate improved from 8.6 to 14.5% p=0.0008; and documentation rate increased from average 25.2 to 35.6% p=0.014 (Figure 1). There was 4.4% patient refusal while 15.7% patients had documented physician deferral. The process was automated using EMR and user-friendly interface for ordering and documentation of vaccination without much increase in physician burden.
Conclusion: EMR-based BPA at the time of patient encounter and physician education intervention resulted in significant increase in HZ vaccination and documentation rates in RA patients.
Disclosure:
H. Sheth,
None;
S. Moghadam-Kia,
None;
R. June,
None;
H. J. Peterson,
None;
D. Sa Leitao,
None;
L. W. Moreland,
Pfizer Inc,
9;
R. Aggarwal,
Questcor,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
NIEHS-NIH,
2,
Questcor,
5,
aTyr Pharma,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvement-in-herpes-zoster-vaccination-and-documentation-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-using-electronic-medical-record/